Your people need to get excited about how the latest tech can help them succeed. Our Deploy play gets employees using the technology as soon as possible—a critical first step towards realizing value from GenAI.
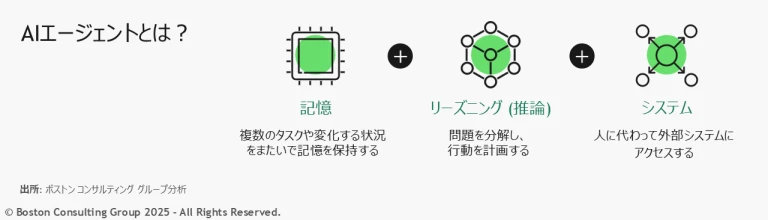
AIエージェントとは
一言でいえば、AIエージェントとは「ツールを活用して目的を達成するAI」を指します。AIエージェントは、複数のタスクや変化する状況をまたいで記憶を保持でき、必要に応じて複数のAIモデルを使い分けながらタスクを遂行します。また、ユーザーに代わって社内外のツールやサービスにアクセスするタイミングを自ら判断することも可能です。AIエージェントはこうした特性により、人間の介入を最小限に抑えた形で、自律的に意思決定し行動することが可能になっています。
例えば、ある消費財メーカーでは、AIエージェントを活用して業務プロセスを変革し、グローバル規模のマーケティングキャンペーンの最適化に取り組みました。従来は週に6人のアナリストを必要としていたプロジェクトが、現在ではAIエージェントと協働する担当者1人のみで、1時間もかからずに成果を出せるようになっています。その仕組みをご紹介します。
- AIエージェントがデータを収集する: 毎週、接続済みのパイプラインを通じて、マーケティングデータを自律的に収集・統合する。
- AIエージェントがパフォーマンスを分析する: 収集したデータに基づいて、文脈を踏まえた分析を行う。必要に応じて担当者からビジネス上の前提や背景情報を受け取りながら、キャンペーンの成果指標を把握し、期待値と比較する。
- AIエージェントが改善案を提示する: 最適化の提案を含む定型レポートを作成する。その内容を担当者が適宜検証・調整し、提案の精度を高めていく。
- AIエージェントがプラットフォームを更新する: 担当者の承認を得たうえで、提案内容を各種の広告プラットフォームに反映する。
AIエージェントの仕組み
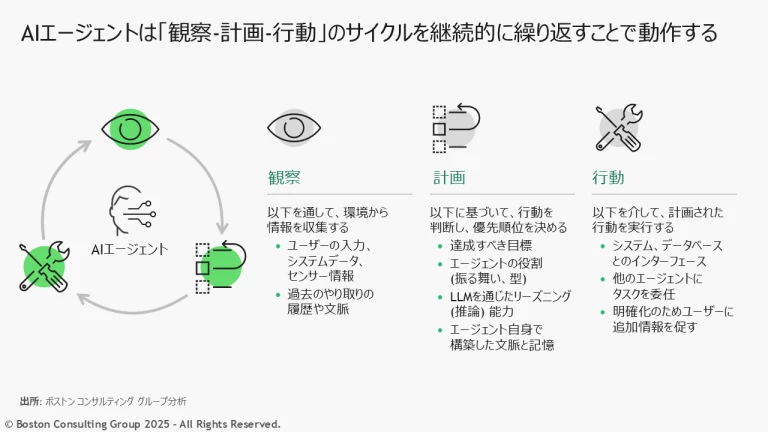
AIエージェントは、周囲の状況を観察し、大規模言語モデルを活用して計画を立て、接続されたシステムにアクセスすることで動作を実行し、目的を達成します。
- 観察: AIエージェントは、ユーザーとのやりとり、主要な成果指標、センサー情報などの環境から常に情報を収集し、継続的に処理する。また、会話をまたいで記憶を保持できるため、複数のステップにわたる計画や業務に一貫性を持たせることができる。
- 計画: AIエージェントは言語モデルを活用し、対処すべき課題、達成すべき目標、文脈や履歴について理解したうえで、どの行動を取るべきかを自律的に評価し、優先順位をつける。
- 行動: AIエージェントは、エンタープライズシステムや各種ツール、データソースとのインターフェースを活用してタスクを実行する。各タスクは、大規模言語モデル(LLM)、または小規模言語モデル(SLM)で生成された計画に基づいて管理される。AIエージェントはタスクを実行する際、人事システム、受注管理システム、CRM(顧客管理システム)といった企業内サービスにアクセスしたり、他のAIエージェントに処理を委任したり、場合によってはユーザーに追加情報を求めたりすることもある。こうした高度なAIエージェントは、エラーを検知して修正をかけ、複数ステップにわたる計画や自己検証を経ながら学習していく能力を備えている。
この「観察-計画-行動」のサイクルは、AIエージェント自身を強化する働きをします。エージェントツールは、過去のやり取りをもとに環境の変化を継続的に分析し、時間の経過とともに、より効率的かつ効果的に行動する方法を学習するためです。
AIエージェントを構成する要素
実装の形式によって異なるものの、AIエージェントは一般的に次の5つの要素で構成されています。
- AIエージェントを設計の中心に据えたインターフェースには、AIエージェントがユーザーやデータベース、センサー、その他のシステムと接続する際に使用されるプロトコルやAPIなどが含まれる。高度なAIエージェントは、これらのインターフェースによって、自らの環境を観察できる。
- メモリーモジュールには、直近の出来事やその時々の状況を扱う短期記憶と、事実情報、概念、過去の会話の内容、これまでにタスクがどのように実行されたかに関する知識を蓄える長期記憶の両方が含まれる。
- プロファイルモジュールは、AIエージェントの役割、目標、行動パターンといった属性を定義する。
- プランニングモジュールは通常、LLMやSLMを活用し、メモリーやプロファイルも含めて環境から取得した観察情報をもとに、AIエージェントが実行すべき適切な計画を組み立てる。
- アクションモジュールは、AIエージェントが実行可能な行動の範囲を規定するAPIやシステム連携によって構成されている。
AIエージェントの役割
AIエージェントは従来のソフトウェアの能力をはるかに超えて、 AIの新時代を切り拓く存在です。受動的なツールではなく、自律的に意思決定を行う高度なソフトウェアとして機能します。データを分析し、タスクを計画し、行動し、そして多くの場合リアルタイムで、絶えず状況に適応していきます。
- AIエージェントは、与えられた入力にただ応答するだけではなく、自ら判断して行動を起こす主体性を持っている。周囲の環境と関わりながら、その過程で学習し、適応していく。また、さまざまな情報源から常にデータを収集し、メモリーや専用のツールを活用して、自らの置かれた環境の中で何が起きているのかを理解し、重要な情報を把握し続ける。
- AIエージェントは、目標、役割、制約を考慮しながら、最適な行動方針を判断する。状況の変化に応じてリアルタイムで計画を更新できるため、ロボティック・プロセス・オートメーション(RPA: PC上で行う定型業務を自動化できるソフトウェアロボット技術)のような手法と比べて、業務プロセスの変化や例外的なケースにも柔軟に対応できる。
- AIエージェントは接続されたシステムを活用し、他の高度なエージェントと連携して、タスクを遂行する。
- AIエージェントは、ワークフローにおける能動的な参加者として設計されている。単なるツールではなく、チームを支える“有能で高いパフォーマンスを発揮する仲間”として、目に見える価値をもたらす。
AIエージェントの種類
AIエージェントは、その設計によってこなせるタスクの複雑性に幅があり、シンプルなコード作成支援ツールから、人間がチームで行う業務を自動化できる高度なネットワーク型までさまざまな種類があります。コード作成を例にとると、一口に「高度化」と言っても、エージェントの種類によって実現できるレベルに差があることが分かります。
- 最もシンプルなレベルでは、コーディング・コパイロット(コード作成支援ツール)は開発者からのプロンプト(指示)に応じてコードを生成する。
- より高度なAIエージェントであれば、既存のコードベースを自動的に読み込み、それに応じて出力を適切に調整できる。特に指示がなくとも、開発者が単体テスト(関数単位でプログラムが正しく動作するか検証するテスト)を書けば即時に、そのテストに合格するコードを自動的に生成することすら可能だ。
- さらにAIエージェントを進化させれば、コードを生成するだけでなく、テスト環境でアプリケーションを実行できる形式に変換し、実際に動かすことまで可能になる。
- 将来的にはもう1歩進んで、AIエージェントが人間の承認を得たうえで、自動化されたパイプラインを通じてテスト済みのアプリケーションを本番環境に反映できるようになるかもしれない。
AIエージェントの使い方
AIエージェントは人間の思考プロセスを忠実に模倣することによって、高いパフォーマンスを発揮します。これは、エージェントの中核となる計画機能を担うLLMが、人間の認知能力を再現できるよう訓練されているためです。LLMは人間の膨大なアウトプットをもとに学習しており、人間と同じように課題を解く力を備えています。
AIを活用したバーチャルエージェントもLLMと同様、問題を構成要素に分解する場面で高いパフォーマンスを発揮します。ただ、タスクを与える際には小さく分割し、仕事を明確に定義する必要があります。さらに、エラーを繰り返し修正できる密なフィードバックプロセスが整っていれば、より高い性能を発揮します。
AIエージェントがビジネスにもたらす価値は、大きく次の3つの領域に分けられます。
- 標準化された業務プロセスの自動化: AIエージェントは反復的な作業を正確かつ迅速に処理できるため、人的ミスを減らし、従業員がより付加価値の高い業務に集中できるようになる。
- 人間との協働: AIを活用したバーチャルエージェントは、知的な協働者としてチームの力を高める。実行可能なインサイトを提供し、意思決定をサポートし、人間の専門性を補完することで、チームに貢献する。
- データに基づくインサイトの導出: AIエージェントは、データが豊富な環境において、人間のチームでは到底対応しきれない規模の情報を分析・統合し、パターンを特定して、戦略的な意思決定につながるインサイトを提供する。
企業はいま、AIエージェントをどう使っているのか
AIエージェントは、さまざまな業界で急速に普及しつつあります。先進企業は、マーケティング、営業、カスタマーサービス、研究開発(R&D)、データ・テクノロジーといった多様な領域において、すでにこうした高度なAIエージェントから価値を引き出し始めています。しかし、これはまだほんの一部にすぎません。企業が現在、実際に取り組んでいるAIエージェントの活用例を紹介します。
- マーケティング: ある大手消費財メーカーは、AIエージェントを活用してブログ記事の作成を自動化し、コストを95%削減、作業スピードを50倍まで向上させた(従来4週間かかっていた新規記事の公開が1日でできるようになった)。
- カスタマーサービス: グローバルに事業を展開するある大手銀行は、AIエージェントを顧客対応に活用し、コストを10分の1に削減した。
- 研究開発(R&D): あるバイオ医薬品企業は、リード(見込み客)創出にAIエージェントを活用して取り組み、1件あたりの処理時間を25%短縮した。また、治験報告書の作成でも作業効率を35%向上させた。
- データとテクノロジー: ある企業のIT部門では、旧型のシステム環境の刷新にAIエージェントを活用し、生産性を最大40%向上させた。
AIエージェントは今後、主流となるか
AIエージェントはビジネスのさまざまな領域で急速に注目を集めており、市場規模は今後5年間で年平均成長率(CAGR)45%で成長すると見込まれています。
AIエージェントが一般的な存在としてビジネスに浸透していくにつれ、人間はチームメイトとしてAIエージェントと密接に協働することになります。AIエージェントは、人間の従業員と同じように組織に加わり、役割や責任を学んで、重要な企業データや業務情報にアクセスし、ワークフローに統合されながら、人間の仕事を支援する存在となっていきます。
ソフトウェア開発、カスタマーサービス、データ分析といった、これまで大規模な人員を必要としていた複雑な業務領域は、今後、多様なAIエージェントと協働する少人数の人間のチームへと置き換わっていくと考えられます。AIエージェントは迅速に複製可能なため、組織の規模はより速いスピードで拡大し、企業は人材採用の必要性を抑えながら成長できるようになります。
AIエージェントを構築することで、企業は新たなビジネスモデルを開拓し、生産性の向上を加速させることができます。AIエージェントはタスクの自動化と管理を担い、従業員がより創造的な業務に集中できる環境をつくります。同様に、労働集約的かつ時間のかかるプロセスを高速化し、従業員の生産性をさらに高めることが可能です。
AIエージェントを適切に監督する能力は、チーム運営における中核的なスキルとなります。エージェントが目的を達成し、プライバシー、公平性、倫理的使用といった基準を遵守できるようにするためです。AIエージェントが普及すればするほど、それを管理する従業員の役割が重要となり、組織のあらゆる階層で「責任あるAI」に関する教育がさらに求められるようになります。
導入し、再設計し、創造する
Your people need to get excited about how the latest tech can help them succeed. Our Deploy play gets employees using the technology as soon as possible—a critical first step towards realizing value from GenAI.
End-to-end AI transformation is within reach—but if you think too small, you’ll come up short. Our Reshape play reimagines entire functions to deliver the cost savings and greater ROI that AI makes possible.
With AI, innovation can move at a pace you’ve never seen before, bringing new products and businesses to your organization. Our Invent play is a chance to find growth opportunities that you may never have found otherwise.
The Future of Science Is AI-Powered
AIエージェント 最近の論考など






AIエージェント エキスパート