Generative AI has been in the public’s consciousness for less than a year, but it’s already changing the world of consumer products, retail, online shopping, and marketing.
For consumers, GenAI will bring seamless, personalized shopping and customer service experiences, personalized advertising, and even personalized products. These features won’t just be novelties or “nice to haves”—consumers will soon come to expect them.
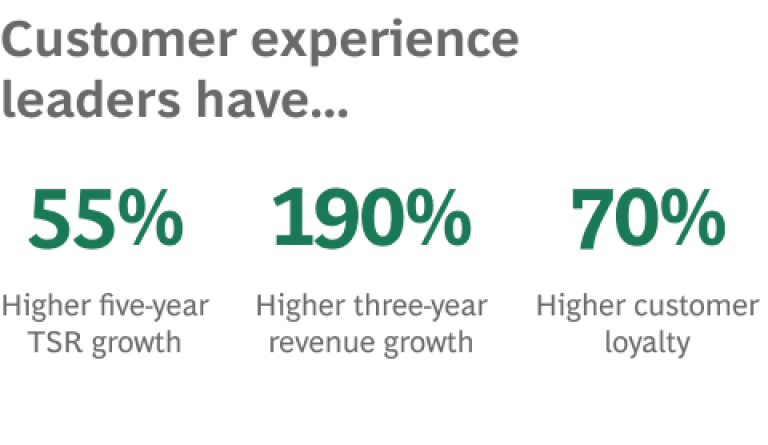
For businesses, this means a radically altered competitive landscape—one that was already being transformed by a multiplicity of consumer touchpoints and on-demand services, not to mention previous waves of AI-enabled automation. And it means getting the customer experience right is more crucial than ever.
Leading companies know this. In our recent Build for the Future survey, respondents ranked customer experience as the highest-priority investment. And it’s no wonder: today’s winners are crushing the competition.
Still, companies must keep in mind that, in a generative AI world, customers can be lost as quickly as they are won. And customer trust, once eroded, can be difficult—if not impossible—to regain. That’s why AI systems must be deployed responsibly.
Reimagining the Customer Experience
Generative AI is already remaking the online shopping experience. Consumers can order groceries and make dinner reservations via third-party sites such as Instacart and OpenTable using OpenAI’s ChatGPT plug-in; Expedia, meanwhile, has incorporated OpenAI’s model into its own application, allowing users to plan trips via ChatGPT while remaining on the Expedia website.
In the near future, AI-powered virtual assistants and chatbots could become a universal gateway to the internet, allowing consumers to search for services in a more conversational way while receiving personalized results. Someone planning a vacation, for example, could tell the virtual assistant their preferences—the destination, dates of travel, budget, and so on—and the assistant would then create an itinerary, manage any requested adjustments, and make the reservations, doing all the work from search to final transaction.
But GenAI, while important, is just one part of the equation. A new era of consumer touchpoints is dawning, ushered in by connected devices, the metaverse , and other interfaces. Harnessing data, as well as AI and other technologies, will be essential to maximizing customer satisfaction in these spaces. The future includes:

Remaking Customer Service and Support
With its ability to respond to prompts with human-like text and voice and to answer complex questions with seeming ease and sophistication, generative AI is a natural fit for customer service operations. Once implemented at scale, the technology could increase productivity by 50% or more and reduce costs by up to 80%, our estimates indicate. According to a 2022 BCG survey of global customer service leaders, 95% expect their customers to be served by an AI bot at some point within the next three years.
How Are Customer Care Centers Using Generative AI?
Meanwhile, JetBlue has implemented a generative AI–enabled solution to augment its online chat function, saving the company’s customer contact center an average of 280 seconds per chat—a total of 73,000 hours saved in a single quarter, giving human agents more time to serve customers with complex problems.
Elsewhere, a North American tech company is deploying a generative AI “sidekick” to help customers and support engineers complete technical support requests, gain access to product information, and automate routine tasks. Initially, the tool will provide support for relatively simple requests, such as how-to guides and basic product configuration information; as the technology matures, the company hopes to use the tool for troubleshooting and solving problems.
Even so, challenges remain. Generative AI models have been known to output inaccurate information—a particular danger in the context of customer care. Moreover, GenAI-based applications can incorporate biases inherent in the data on which the foundational model was trained, which could lead to unfair treatment of certain customers. The technology also runs the risk of revealing proprietary information, intellectual property, or inappropriate customer data.
To minimize these risks, companies are keeping human agents in the loop for more complex interactions, checking the content produced by AI before it reaches the customer; in the near term, high-value, premium services will likely require direct human oversight.
As generative AI matures, companies will gain confidence in its performance, reducing the need for human oversight and allowing customers to interact with AI chatbots directly. Still, companies will need to ensure that the technology maintains the human touch—effective customer care requires a capacity for empathy.
But generative AI systems can do more than just solve customers’ problems. As GenAI models learn more about a company’s products, operations, and customers, they will likely be able to predict customer behavior—and thus reach out to customers proactively. And as generative AI advances, it may also be able to use data gained through customer interactions to help guide production and resource planning; it could even work directly with suppliers.
Revolutionizing the Marketing Function
If you’re a marketer considering whether to deploy generative AI in your organization, you’re late to the game. Some 70% of the chief marketing officers we surveyed in 2023 said that their organizations already use generative AI, while another 19% are testing it.
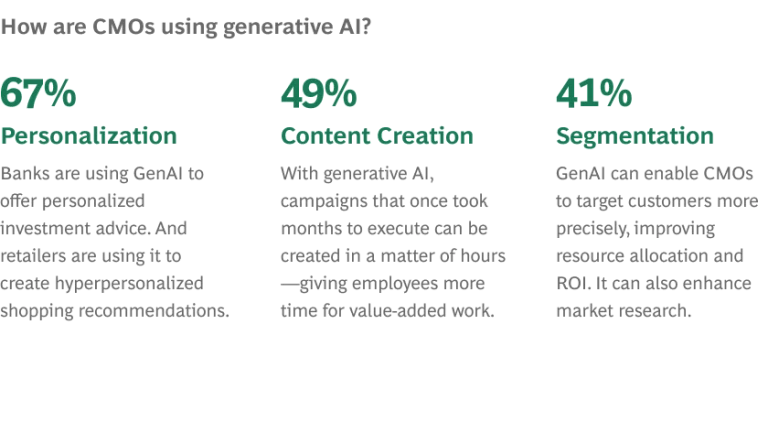
So how can companies successfully implement generative AI? We recommend that CMOs take these key actions.
- Start experimenting. Identify valuable GenAI applications, experiment with operating models, and start building transformative use cases. One approach: create agile marketing pods charged with launching a marketing campaign using GenAI as much as possible.
- Seek game-changing outcomes. To create a competitive edge, prioritize “golden” use cases—those that apply core data and IP assets that are unique to your brand, that can help reach consumers in new ways, and that enable step-change gains in productivity.
- Implement responsible AI guidelines. Encourage the use of GenAI—your employees are probably using it anyway, and your competitors surely are—but create centralized guardrails to prevent misuse.
This last point is crucial. Among the many risks of unmanaged AI are proprietary data leaks, copyright infringement, biased output, and more sophisticated forms of fraud. There is also the risk of a shadow AI, in which people within an organization use AI tools without proper guidance and supervision. Given the high volume of GenAI content that will be consumer facing, any slipups could be greatly damaging to a brand—which makes responsible AI a particular concern for CMOs.
Companies should layer branding plug-ins on top of their algorithms to ensure that the organizational styles that their marketers and agencies work with—such as tone of voice, color coding, authorized themes, and content—adhere to the brand’s approved framework.
Just as important, companies will need to provide a top-of-the-line user experience. AI tools must integrate seamlessly with new and existing applications, and users should be provided with guidance on how to interact with them. Sample prompts and chatbot-initiated dialogues can show users how to achieve the best results; a conversational AI interface can tell a customer why a certain product makes sense for them and can even build additional products or product extensions in real time—all while establishing an emotional connection with the user.
Generative AI is set to disrupt retail and marketing in the same way that search engines and other online platforms upended business models and unleashed creativity three decades ago. It won’t just revolutionize how companies perform certain marketing tasks—it will redefine the role of marketing itself.
This creates pressure for companies to race ahead with GenAI and other AI-based technologies; indeed, consumers expect it. But as marketers experiment with artificial intelligence, they must do so in a thoughtful and responsible way, working with their customers to build trust in AI systems. That’s one thing that won’t change in the future—trust and connection are what keeps customers coming back.






