The Art of Performance Management, which looks at the critical components of a best-in-class performance management system and operating model, is part of a publication series by BCG on CFO excellence. The Art of Planning examines the ten principles driving best practices in corporate planning. The Art of Risk Management discusses the ten principles that should govern an approach to risk management.
Recent years have witnessed a radical expansion in the responsibilities of the CFO. Increasingly, CFOs are being called upon not only to get the numbers right but also to be the chief custodian of shareholder value and a genuine strategic advisor to the business. In this respect, the chief financial officer is becoming the corporation’s “chief performance officer.”
Unfortunately, most CFOs are poorly served in this role by the current state of their company’s performance management system. The proliferation of information technology has allowed organizations to generate more data and reports than ever before. The paradoxical result, however, is that senior managers and boards of directors are drowning in a sea of data without the tools needed to translate that data into genuine intelligence and insight about the business.
At most large companies, the performance management system is a hodgepodge of legacy systems. KPIs are not aligned across the organization. Different information systems categorize data differently—what some parts of the organization define as fixed costs, others define as variable; human resources, finance, and payroll often have different definitions of what constitutes an FTE. Decision rights as to who decides what data to collect are so distributed that there is no consistent approach to reporting across the entire company.
As a result, the finance organization spends an inordinate amount of time simply putting the data together and trying to resolve the inconsistencies so that executives can make apples-to-apples comparisons. We estimate that this task consumes roughly 30 percent of the resources in a typical corporate finance function . But the far more serious cost is the negative impact of poor data quality on senior management time and decision making. As one senior executive told us, “Our leadership team spends so much time trying to make sense of the data and debating whether it is right that we never get around to exploring what it really means for the business!”
CFOs are keenly aware of the problem. “We generate some 20,000 reports every year—one for every three employees! That can’t be right,” said one. “We’ve stitched together our performance management system on blood, sweat, and Excel,” said another. “It’s a controller’s nightmare.”
Too often, however, companies try to address the issue as if it were mainly a software problem. They focus on selecting the right vendor to build a state-of-the-art information system for performance management and “business intelligence.” And they make massive investments in new technology without first thinking through what kind of metrics really matter for the business or what kind of organizational interactions and governance are necessary to translate data into effective decision making.
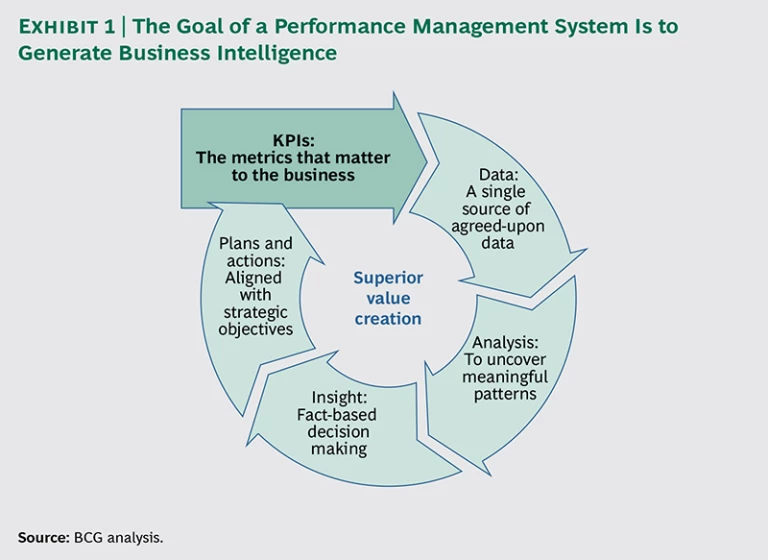
There is a better way. Companies can significantly improve performance management without investing substantial resources in new IT systems. To do so, however, they need to step back and take a more strategic and holistic approach. The senior management team, led by the CFO, needs to start by identifying the metrics that really matter in guiding the business and building an organizational system for translating that data into actionable business insights and more effective decision making. (See Exhibit 1.) Automation and software can be important enablers, but only when their use is informed by this strategic perspective.
A Single Source of Truth
Based on our work designing such systems for a broad cross-section of client organizations, BCG has identified five critical components of a best-in-class performance management system:
- Consistent—and relevant—KPIs
- A universal data taxonomy
- Integrated management reporting
- User-friendly executive dashboards
- Real-time business analytics
Let’s consider each of these components in turn.
Consistent—and Relevant—KPIs. A best-in-class performance management system doesn’t measure everything. Rather, it focuses on metrics and KPIs that are especially critical for achieving a company’s business strategy. Identifying these KPIs—both what to include and what not to include—is the starting point in the development of an effective performance management system.
Identifying the metrics that really matter for the business ensures that the system is not just generating data for data’s sake. Think of it, rather, as establishing a “common language” that the management team will use to guide the business. Developing a consensus around this common language is an effective way to make sure that managers throughout the organization are focusing on what is really important for the success of the business.
Finally, choosing a consistent and relevant set of KPIs addresses one of the key shortcomings of existing performance management systems: inconsistent KPIs across different parts of the business. At one company, for example, the proliferation of different metrics used by different brands, regions, and key accounts to track performance led to a situation where, although the company had established a centralized data warehouse, only about 20 percent of the data generated across the company and used in company reports actually came from that warehouse. (To learn how the company addressed this problem, see “Developing ‘My Scorecard’ at a Beverage Company.”)
DEVELOPING "MY SCORECARD" AT A BEVERAGE COMPANY
When a new executive team took charge of the U.S. operations of a global beverage company, the executives were frustrated by how difficult it was to get a clear sense of the health of the business. Over the years, various brands and regions and key customer accounts had developed their own systems for reporting business results, leading to the generation of fragmented reports with no consistent presentation. Just to give an idea of the scale of the problem: although the company had an existing data warehouse, only about 20 percent of the data generated across the company came from that warehouse. “There are so many different reports that we have no idea whether we are doing well or not,” said one member of the senior management team. “We get multiple and conflicting answers on whether a part of the business is up or down, and we don’t know where to go to find out which is right.”
To address the problem, the company is designing a standardized set of executive dashboards, known as My Scorecard, that will be used throughout the company and serve as the key input to managers’ monthly performance meetings. The idea is to focus on a core set of metrics that really matter in assessing business performance and to present those metrics in a clear and simple fashion, with the emphasis on “telling a story” rather than just inundating executives in data. The company’s CEO has made it clear that the My Scorecard dashboards aren’t just for the senior team. Rather, the goal is to provide everyone in the company with the information needed to know what is going on and a shared language for analyzing business performance.
The team designing the scorecards has focused on four key questions:
- What is going on in the market and with consumers?
- How are we tracking against our long-term objectives?
- Are we profitably growing the business?
- Are we creating the conditions necessary to ensure our future success?
To identify the metrics necessary to answer these questions, the team began with the high-level goals and objectives identified in the company’s recently developed five-year plan. But team members also extensively interviewed sales and marketing personnel throughout the company to find out what kind of information they considered most useful in driving decision making in their part of the business. What kind of data did they need? What was the minimum number of KPIs that would allow them to say whether they were on track or not?
The end result is a list of some 50 metrics that shed light on one of the four initial questions posed by the team. Some are output metrics—for example, data on volume, sales, and profitability. Others are input metrics—indicators of brand health, return on advertising spend, and the like. The design concept for the dashboards organizes these metrics into six separate screens in an integrated online scorecard. A “market context” screen includes data on macroeconomic and industry trends (for example, the unemployment rate, consumer price index, consumer spending, and retail sales). A “goals” screen shows data on how the company’s various brands and categories are performing against its corporate objectives. Two “results” screens track top-line results (sales) and financials (profitability). And the last two screens track key enablers of the business: brand health and the quality of the company’s distribution network. (See the exhibit below.)
The dashboards will allow managers to drill down across multiple dimensions—for example, to access the specific metrics for a given region, brand, or key account. Local managers will also be able to add interpretive comments on specific data that communicate their best understanding of why the numbers are what they are. And users will have the ability to zero in on exceptions—parts of the business that are doing especially well or especially poorly to understand what’s going on in those particular cases. Finally, because all executives throughout the company will have access to the same system at the level of information appropriate to their role, the scorecards are designed to be a highly effective mechanism for structuring discussion and debate during monthly performance meetings.
This new performance management system is a work in progress. The company is still in the development phase, finalizing the metrics it will use and planning implementation. What’s more, not all the data that executives would like to have are currently available in the company’s information systems. But the design of the new executive dashboards is already helping to create a shared context about what numbers really matter to the business and how to use them to assess performance. “Dashboards add transparency for the executive team,” said one senior executive at the company. “The business units are no longer the sole arbiter of their business.” What’s more, the project is defining the top priorities for developing new sources of data as the company builds and refines its data repository.
A Universal Data Taxonomy. Once the critical metrics and KPIs are identified, they need to be translated into a universal data taxonomy with a consistent information architecture and standardized definitions and metrics used across the entire organization. Think of this taxonomy as creating a “single source of truth” that is comprehensive, timely, accessible, and accurate—no matter where the data comes from or who is providing it.
Once a company has a set of standards for defining and collecting the data, it will be in a position to automate much of its standard report production, thus freeing up finance staff to focus on more analytical tasks. The ultimate goal is to establish a single data repository where all the relevant data is categorized and stored.
Integrated Management Reporting. This standardized information architecture is the foundation for a set of management reports that integrate financial, operational, and human capital reporting. The integrated reporting system includes both data about past performance and forecast data about estimated future performance; incorporates both internally generated data and external data about markets, customers, and economic trends; allows for easy drill-down and roll-up, as well as the generation of a nested hierarchy of reports that are relevant to each level of the organization; and offers a 360-degree view that allows executives to navigate across information from multiple sources such as finance, human resources, operations, and sales.
User-Friendly Executive Dashboards. Sitting on top of these standard management reports is a set of user-friendly executive dashboards that synthesize and summarize key trends for senior executives. In some respects, these dashboards are even more important than the reports generated by the system because they are designed to help users focus on what actually matters and to facilitate the identification of critical insights about the business.
At a business services company, for example, the designers of the new performance management system used an analogy to Apple’s iTunes music library to describe the different functions of reports and dashboards. The reports were like the iTunes library—that is, the in-depth underlying data and information on which the executive dashboards would draw. The dashboards, by contrast, were the iTunes playlist—the high-level information, trends, and key indicators that senior executives would track regularly and that would serve as the basis of monthly performance meetings. (See “Creating the ‘iTunes Playlist’ at a Business Services Company.”)
CREATING THE “iTUNES PLAYLIST” AT A BUSINESS SERVICES COMPANY
Because it had grown largely through acquisition, a major U.S. business services company had a decentralized set of business units, each with its own criteria for tracking performance. That was fine in an era of healthy growth; however, the economic downturn after the financial crisis forced the corporate center to manage the businesses more tightly. But senior management didn’t have the data to do so effectively.
One particularly contentious executive team meeting became the catalyst for the redesign of the company’s performance management system. Executives spent most of the meeting arguing about whether the company’s customer base was growing or shrinking. Different service lines defined customers in different ways; double and even triple counting was rife. Different databases showed the company’s customer base simultaneously growing and declining. Which data source was correct? No one knew with any certainty.
As one senior executive put it, “We are data rich but information poor.” The company had huge binders of reports filled with data from the various businesses but no easy way of comparing the data or figuring out which metrics really mattered and which did not. Something had to change.
The company’s CFO created a team of senior finance staff to develop a more rational and effective system. Early in the process, the team made a key decision: to design the ideal system without regard to whether the data was currently available or not. The team decided to focus on five key categories of metrics:
- Income Summaries—creating a standard structure and uniform definitions across the P&L statements of all business units
- New Business—identifying KPIs to measure the efficiency and effectiveness of the sales process
- Operating Metrics—focusing on processing volumes and productivity
- Human Capital—developing a common set of metrics for understanding costs, productivity, and return on human capital
- Executive Dashboards—designing visual presentations of key data trends to pinpoint key issues and guide the agenda of the executive committee (a tool that, at the time, the company did not have)
An important part of the team’s efforts was defining the most important KPIs for the business, including critical operational metrics such as the cost to serve new customers, which the company had never collected before. These ideal metrics became the map for identifying key gaps in data availability and technology that would have to be filled in order to populate the reports and dashboards designed by the team.
Another key part of the team’s efforts was to develop an integrated data taxonomy that highlighted those metrics that were most relevant at each level of the business and how they related to each other. Take the example of total shareholder return relative to the company’s peer set, a key metric at the corporate-wide level. One important component of TSR, however, is earnings, as defined by the combination of revenue and costs, and that needs to be tracked at the level of the individual business. And for business unit presidents, it’s valuable to further disaggregate those metrics by individual customer, region, and product. The goal: to create a nested hierarchy of data that not only delivers the right data to the right people at the right level of granularity, but also makes it easy for the senior executive team to “double click” on the data to see what is driving the high-level trends.
This data taxonomy became the foundation for the reports of the new performance management system, which the team conceived of as the “iTunes library”—that is, the regular outputs of data and information that would be circulated throughout the organization and serve as backup to the executive dashboards. Meanwhile, the dashboards were the “iTunes playlist”—that is, the high-level information, trends, and key indicators that senior executives would track regularly and that would serve as the basis of monthly performance meetings.
Once the key elements of the new system were defined, staff in the finance organization manually sifted through existing databases in order to populate the new system. Although a time-consuming task, the value added in better decision making from having the data organized in a standard and easy-to-use format more than offset the costs of organizing the data. Over time, as the company has invested in new IT systems, the data collection process is increasingly being automated.
As a result of the redesign, the company’s monthly sales report has gone from 40 pages of data to 3 pages of carefully selected information, which is then summarized in 2 pages of visual executive dashboards. And key data across the main areas of the business are further summarized in a 3-page executive dashboard for the company’s executive committee, a kind of output that was never available before.
Even more important, the new system is generating insights that are changing the company’s fundamental approach to its business. Take the example of cost to serve. Before the creation of the new performance management system, senior executives knew that it was getting more expensive to serve the company’s customers. But they did not have a good understanding of just how expensive it was. The new data generated by the system made clear that the company’s expenses as a percentage of first-year revenue from new customers were, in fact, orders of magnitude greater than executives had initially estimated. This insight on the dynamics of the business has led to new programs to improve operational effectiveness and new pricing strategies to maximize customer revenue.
Well-designed executive dashboards typically visualize data in a compelling fashion. Visualization helps executives access a much broader cross-section of data than more traditional spreadsheets or reports. It also helps make connections visible across different KPIs and trends over time.
Real-Time Business Analytics. Beyond standard management reporting, a good performance management system also includes the capacity to go into the system in order to run analyses in real time in response to questions from managers in different parts of the business. In this respect, the system empowers both finance staff and users in the line business, allowing the former to respond quickly and efficiently to requests and allowing the latter, in some situations, to use the system to do their own analyses. There are many software packages on the market for business analytics that enable an organization to automate much of this ad hoc report generation.
Over time, an organization will find that many of these real-time analytics can be standardized. At one company we worked with, for instance, we found that many of the so-called ad hoc requests actually were recurring requests for the same types of data. By categorizing these “frequently asked questions” and preparing for them in advance, the finance organization was able to develop a routine for responding to such requests that was both faster and less costly than in the past.
Increasingly, companies are using analytical techniques associated with big data to incorporate vast quantities of external customer information into their business analytics. In the retail sector, for example, companies often capture a deluge of data about their customers—most notably, transaction histories that can reveal detailed product affinities and promotional and marketing response rates. More and more retailers are harnessing this data to improve business performance—for example, by boosting the effectiveness of promotions, targeting their pricing more precisely, and quantifying the value of the retail network. (See “ Making Big Data Work: Retailing ,” BCG article, June 2014.)
A Dynamic Operating Model
The organizational dimension of performance management—the rules and practices that ensure that the system is used properly and maintained over time—is as important as getting the metrics, data, and output right. A good performance management system also needs the right operating model to ensure that the data generated by the system leads to new insights about the business and better decision making.
A Value-Adding Finance Function. A critical part of this new operating model is a different vision for the role of the finance function itself. Instead of merely pushing out data, the finance organization needs to deliver business intelligence—that is, it should be able to identify the key needs of the business and provide reports and analysis that help the organization meet those needs. The goal: fewer and better reports and the automation of low-value-added activities, allowing the finance staff to focus on high-value-added business analytics.
Some companies centralize the business intelligence function in a corporate center of excellence within the finance department. Others decentralize the activity among the businesses with some coordination from finance. And still others try some combination of the two. We recommend that companies consolidate and co-locate business intelligence teams in the finance organization. That way, finance has a full line of sight across the totality of reports being created in the company, ensuring consistency, reliability, and good governance.
Business Intelligence Partnership. The second part of a good operating model is for business intelligence teams to function as genuine partners of the line businesses. They should be interacting regularly with their clients in the business in a scheduled routine of structured performance meetings.
A key organizing principle for such meetings is what we call “talk, challenge, act.” In other words, it’s not enough just to ask for or deliver data or analysis. That data and analysis need to be discussed and debated jointly by the business intelligence team and the unit requesting it. What does the data mean? What are the implications for our business? What are the decisions or actions that we will take as a consequence of this data? What can we do to make the trend line move in a more positive direction? Discussing these questions helps develop trust in the data generated by the performance management system across the organization.
The existence of well-designed executive dashboards will help enable constructive discussions around the data. At one company, the introduction of a technique as simple as categorizing performance against business plan targets by means of “traffic lights” (green for on track, yellow for minor shortfalls, red for major deviations from the plan) caused business unit leaders to dig deeper for explanations and think harder about potential solutions—in advance of their performance management meetings. The result: a richer and more productive conversation and better and faster decision making.
Ongoing Maintenance and Governance. Finally, in today’s fast-changing business environment, a company’s circumstances, challenges, and opportunities are often a moving target. And as circumstances change, sometimes a company’s performance management system must change with it. Therefore, attention must be paid to developing principles of governance for the ongoing management and maintenance of the performance management system.
Among the issues that a governance committee must address: What are the decision rights of the system? Who gets to add or subtract reports over time? One problem with current systems for performance management is that such rights are so distributed that finance staff tend to deliver the kind of reports that the head of their own business unit wants, whether or not such reports make sense for the company as a whole. The result is a proliferation of different data definitions and poorly integrated data. We recommend a more centralized approach—like the one used at the beverage company—that starts from the top but also consults broadly throughout the organization to ensure that the chosen KPIs are relevant to all parts of the business.
Traveling Up the Performance Maturity Curve
Putting all these elements in place takes time—in our experience, anywhere from six months, to get some of the basic building blocks in place, to as much as three years to create a fully integrated and automated performance management system. Most organizations will find themselves traveling along what we call the “performance management maturity curve.” (See Exhibit 2.)
The starting point is the definition of comprehensive metrics and KPIs and a common data taxonomy. Once that foundation is in place, the finance function can begin to focus on providing in-depth business analytics and insight. Eventually, the entire system will be built around a standardized set of reports and executive dashboards. And once those are in place, the organization can attend to how these reports and dashboards are configured to maximize ease of use, including the use of visual displays to portray the most important trends in the data.
BCG has distilled its experience working with companies as they travel along the maturity curve into 12 general principles. (See “Twelve Principles of World-Class Performance Management.”) When managers follow these general principles, each step in the process along the maturity curve releases considerable value, in terms of both a more value-adding finance function and better business decisions.
TWELVE PRINCIPLES OF WORLD-CLASS PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT
- Strategic and Insightful: focus on a limited set of KPIs that are relevant to the company’s business strategy and aligned with long-term value creation.
- Backward and Forward: combine historical data on past performance with strategic insights into future opportunities and challenges.
- Internal and External: measure performance against internal benchmarks (plan, forecast, etc.) as well as external benchmarks (market, competition, investor expectations, etc.).
- Single Source of Truth: create consistent data definitions and a common language to achieve accuracy, integrity, and timeliness of data.
- Cascaded Through the Organization: reflect corporate priorities at all levels of reporting through a clear hierarchy of reports with the capacity to drill down and roll up information.
- 360-Degree Views: integrate information from finance, human resources, and operations and sales and evaluate performance in an end-to-end, holistic fashion.
- User Friendly: standardize and visualize to enhance insight identification.
- Agile and Responsive: include responsive real-time business analytics.
- Embedded Throughout the Organization: build a culture of data-based decision making based on a strategic partnership between finance and the business.
- Talk, Challenge, Act: encourage challenging discussions and debate around reports to foster ownership and accountability.
- Sustained and Adaptive: define clear responsibilities for data and reporting governance and adapt reporting as strategic and business needs change.
- Efficient and Automated: automate low-value-added processes and focus the finance organization on value-added activities.