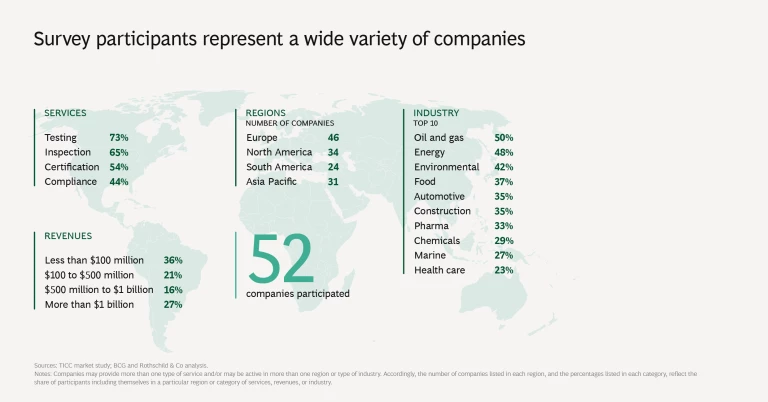
Testing, inspection, certification, and compliance (TICC) companies expect digitization to transform a significant portion of their services over the next five years. Despite these high expectations, the TICC industry’s digital maturity is substantially lower than that of other industries. These findings, from a recent study by BCG and Rothschild & Co, point to the need for TICC companies to accelerate their transformation to comprehensive digital operations. (See “About the Study.”)
About the Study
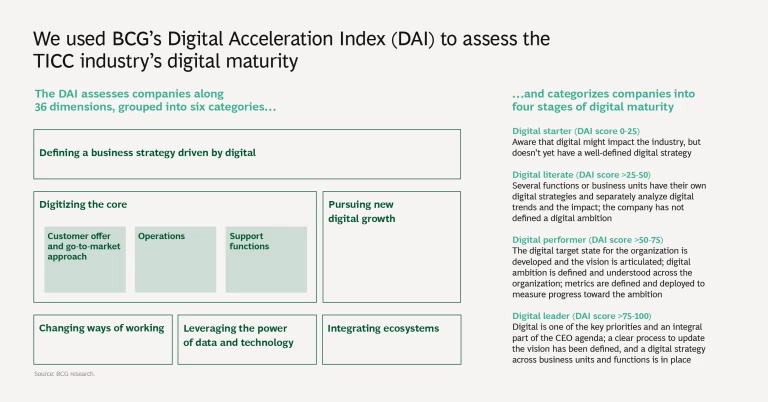
We assessed the TICC industry’s digital maturity using the Digital Acceleration Index (DAI), BCG’s proprietary methodology. Participants estimated their digital maturity on a scale of 1 to 4 in 36 equally weighted dimensions. We then aggregated those raw scores and calculated the resulting response values on a scale from 0 to 100—giving relative weight to all questions—to determine each company’s overall performance.
The slideshow that follows presents details of the study findings.
Five Key Findings
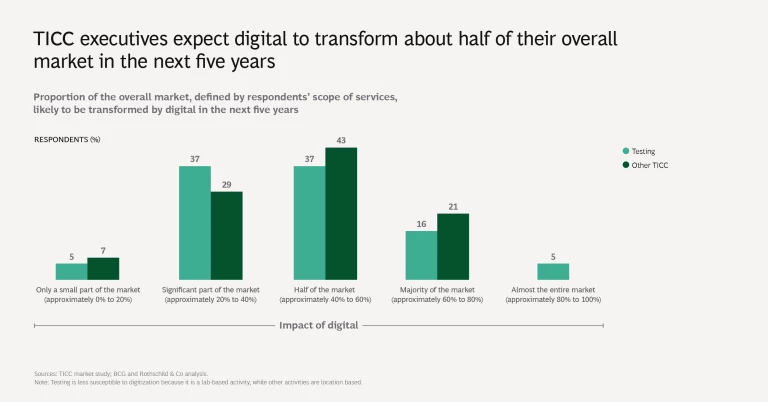
1. TICC companies recognize digital’s potential. Survey participants, on average, said that they expect half of their overall market (as defined by the scope of their services) to be transformed by digital in the next five years. As discussed in a previous BCG article , digital technology is affecting how, where, and when TICC services are provided as well as who provides them. Companies are digitizing their manual activities and performing new activities with the help of digital products and services.
Survey participants, on average, said that they expect half of their overall market to be transformed by digital in the next five years.
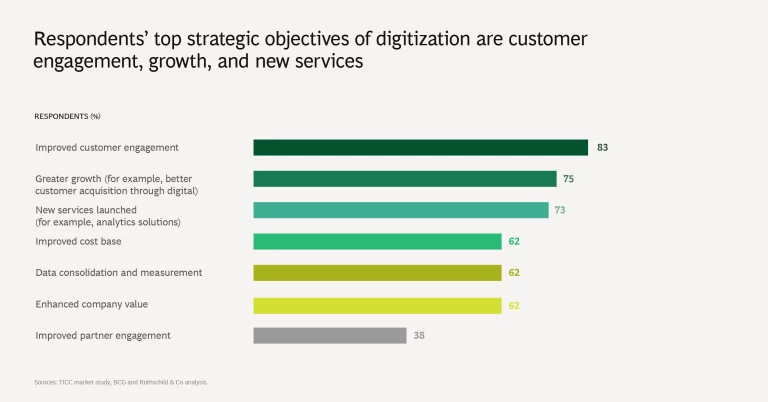
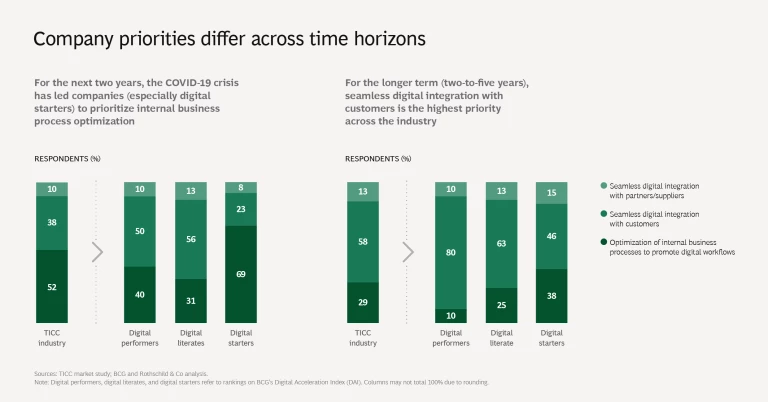
Survey participants expect their digitization efforts to improve customer engagement, bring greater growth, and enable them to launch new services. In light of the COVID-19 crisis, participants’ most important short-term priority is the adoption of digital workflows. Seamless digital integration with customers is their main longer-term focus.
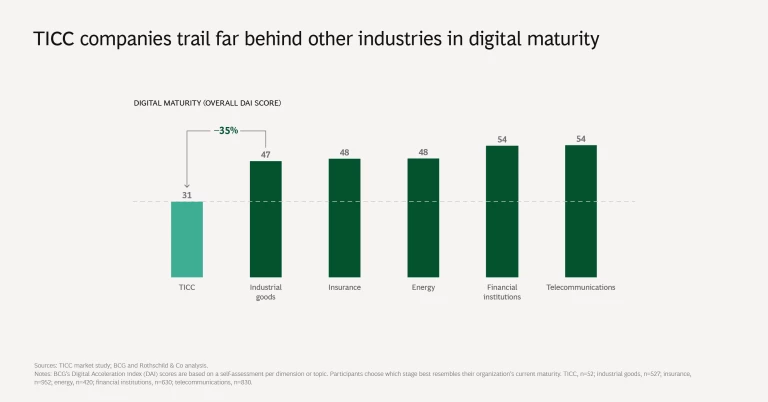
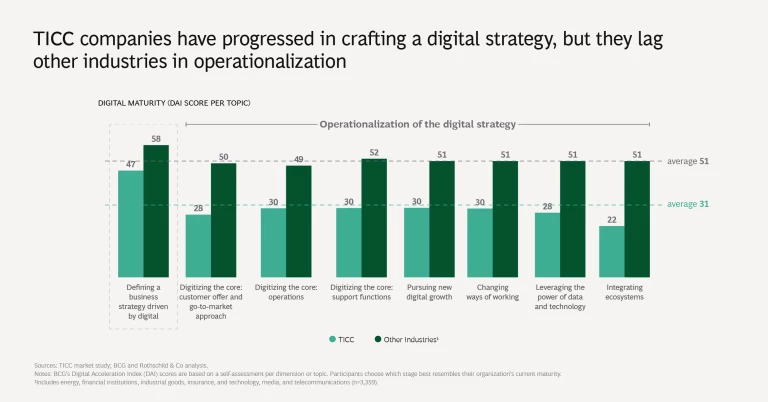
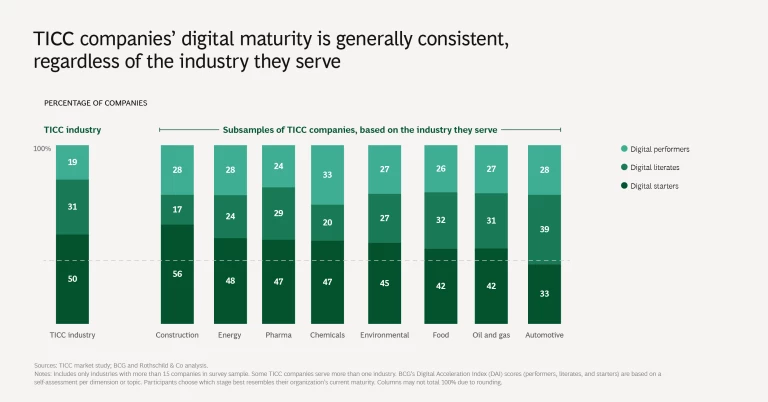
2. Digital maturity lags other industries. TICC companies’ digital maturity, as measured by BCG’s Digital Acceleration Index (DAI), is materially lower than that of other industries, such as energy, financial institutions, industrial goods, insurance, and telecommunications. Although TICC companies have made progress in crafting a digital strategy, they generally lag behind other industries in operationalizing it.
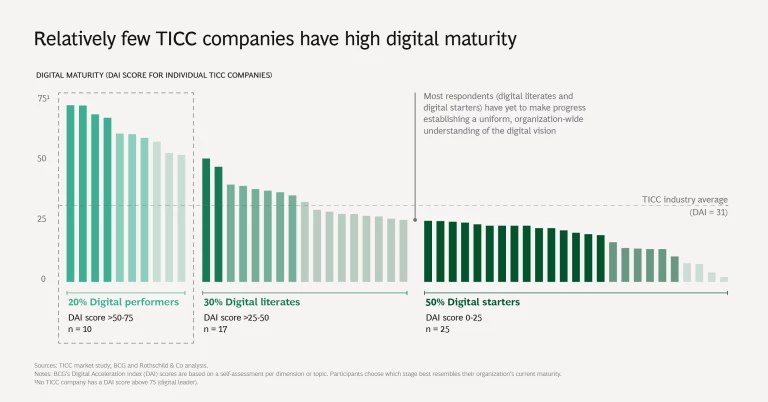
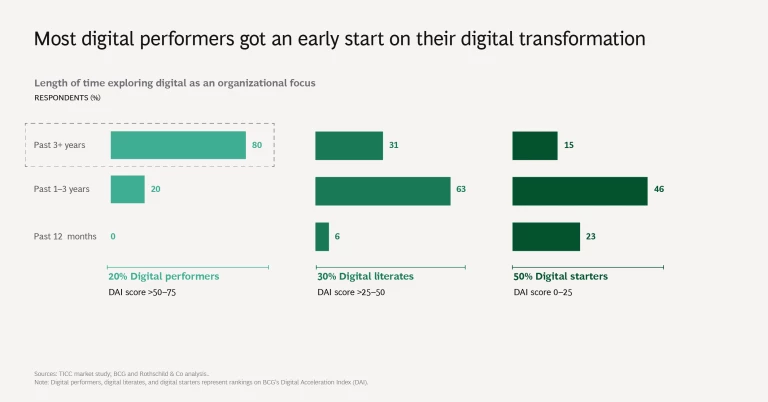
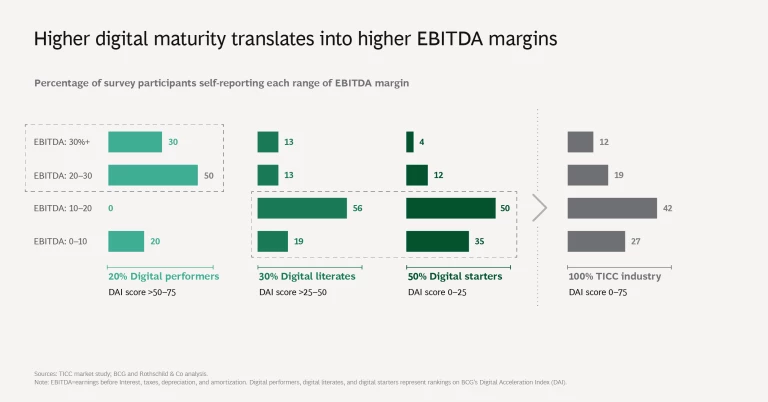
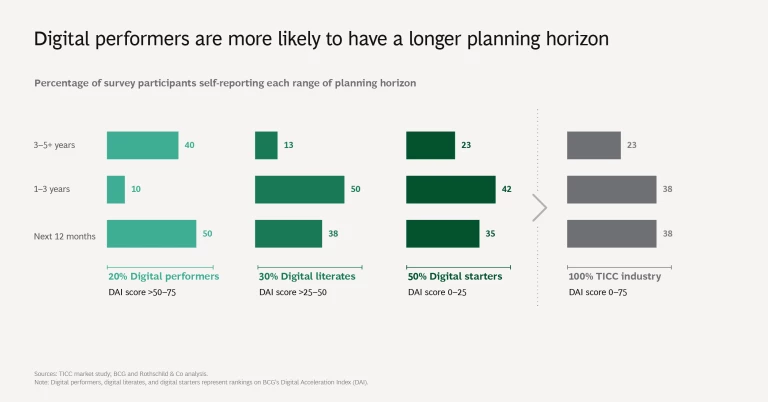
On the DAI’s maturity continuum, none of the surveyed TICC companies rank as digital leaders, the highest level. Approximately 20% rank as digital performers, the second most mature category. The digital performers among TICC companies generally achieve a greater margin of EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization), compared with those operating at lower levels of digital maturity.
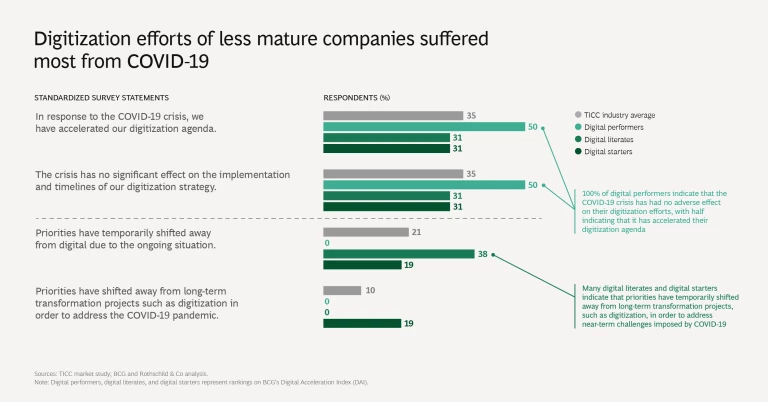
3. COVID-19 has distracted laggards from digitization. For the majority of TICC companies (70%), the COVID-19 crisis has had an all-or-nothing effect on their digital agenda: 35% said that the crisis accelerated digitization, while 35% said it did not affect their digital agenda.
Digital maturity appears to make a difference in this regard. All digital performers indicate that the COVID-19 crisis has had no adverse effect on their digitization efforts, with half indicating that it has accelerated the digitization agenda. TICC companies operating at a lower digital maturity level, however, say that the pandemic has caused them to temporarily divert their attention away from digitization.
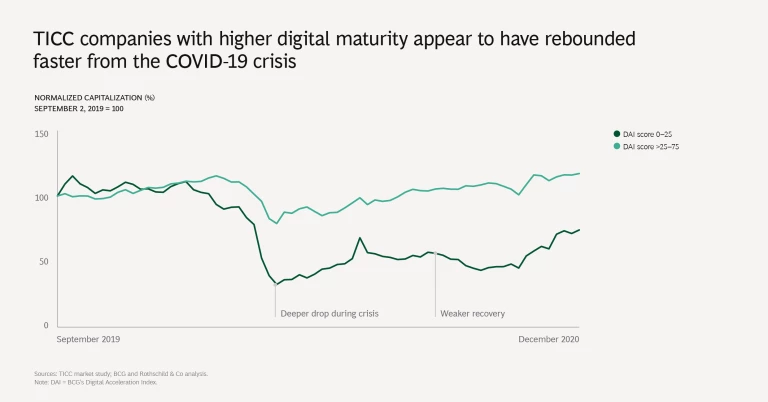
Our analysis shows that digitization may improve resilience: in terms of market capitalization, companies with higher maturity appear to have rebounded faster from the COVID-19 crisis.
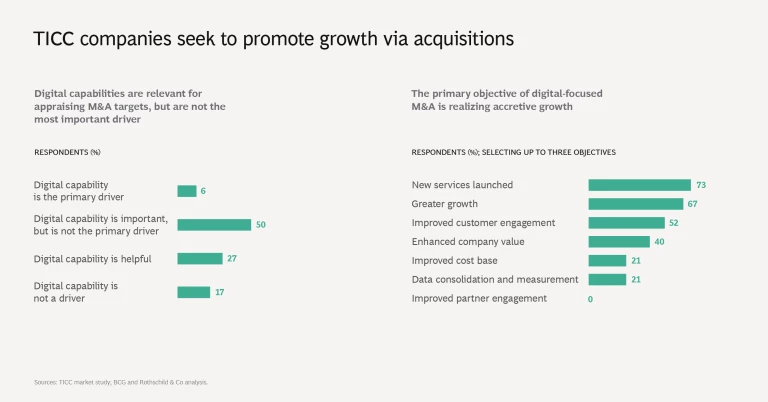
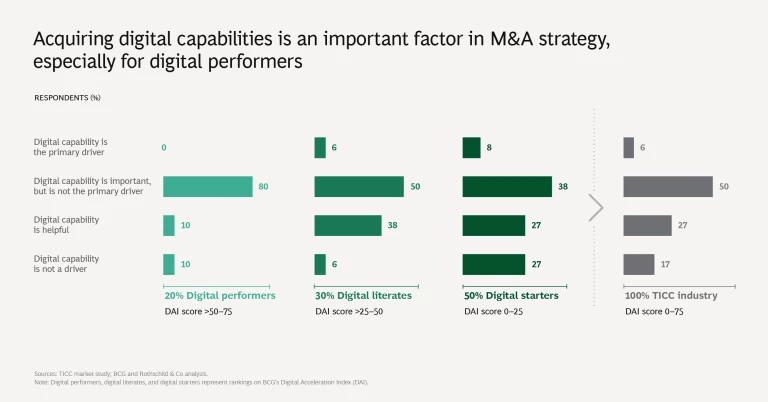
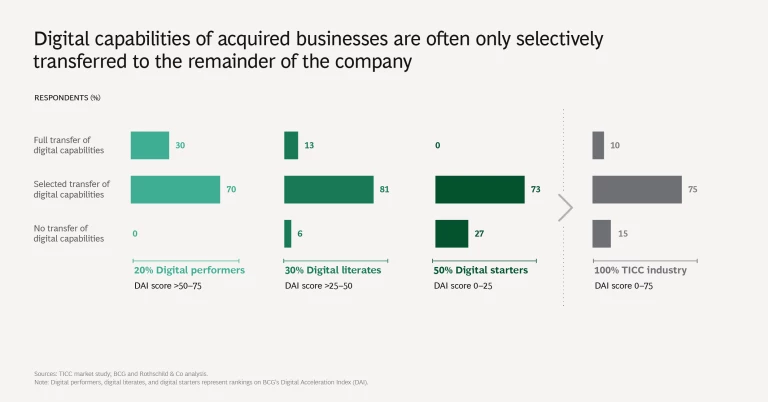
4. Growth is a leading objective of digital M&A. Among all survey participants, 50% say that digital capabilities are an important factor in appraising M&A targets, but only 6% indicate that these capabilities are the primary driver of M&A strategy. Among digital performers, 80% regard a target company’s digital capabilities as an important factor. Participants most commonly pointed to launching new services and achieving greater growth as the main strategic objectives of making digital acquisitions.
Survey participants most commonly pointed to launching new services and achieving greater growth as the main strategic objectives of making digital acquisitions.
In general, TICC companies selectively disseminate acquired digital capabilities within their organization. Only about one in ten of all companies surveyed fully transfer targets’ digital capabilities to their organization, while this figure rises to nearly one in three for digital performers.
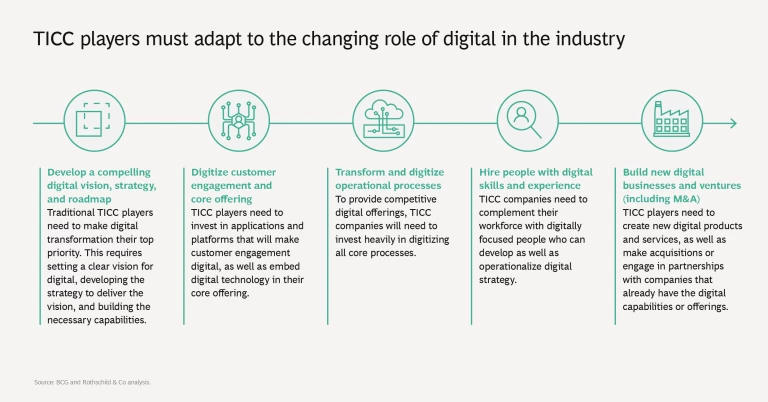
5. TICC players must adapt to succeed. To deliver impact from a digital transformation and succeed in the market, TICC companies need to follow a multistage process. This starts with making digital their top priority by developing a digital vision and culminates in building new digital businesses and ventures. Specifically, to move successfully into the future, TICC companies need to:
- Develop a compelling digital vision, strategy, and roadmap.
- Digitize their customer engagement and core offering by investing in applications and platforms.
- Transform and digitize their core operational processes.
- Hire people with digital skills and experience who can operationalize digital strategy.
- Build new digital business and ventures, including M&As and partnerships with companies that already offer digital capabilities.
Many TICC companies have embarked on a variety of digitization initiatives across many dimensions, but few have achieved a high level of digital maturity. Even as the journey continues for most companies, the growing recognition of the power and impact of digital bodes well for the industry in the years ahead.