Today, many companies are struggling with multiple challenges. They are working to provide engaging, more personalized customer experiences that offer compelling reasons for customers to come back often and buy more products and services. At the same time, companies are seeking higher levels of operational efficiency to maintain profit margins in increasingly competitive markets in virtually every industry. Accelerating advances in enabling technologies—among them, communications, cloud, analytics, and mobile—have significantly amplified the role that mapping and geospatial data play in addressing these issues.
Deeper, data-driven insights into customer demographics and preferences, combined with mapping and geospatial data, have enabled companies to optimize their operations to better address their customers’ needs, including pricing, products, and service delivery. What began as a few basic uses of mapping and geospatial data, such as for store listings tailored to user locations, has evolved into much more complex applications.
Broadly speaking, we refer to location intelligence as the use of mapping and geospatial data, in combination with a company’s internal customer data, to improve the customer experience and underlying business processes. Location intelligence is already changing the way businesses operate. But to what degree?
To answer that question and to explore the roles that these programs play today and will play in the future, BCG surveyed more than 500 executives in the US, the UK, Singapore, and India, focusing on companies in five sectors in which location intelligence has significant impact: financial services, retail and e-commerce, logistics and delivery, real estate, and travel and tourism. Google commissioned BCG to conduct this study and to subsequently analyze and assess the location intelligence market. In conjunction with the survey, BCG independently interviewed top managers at these companies who make purchasing and collaboration decisions about geospatial data and about mapping platform programs and providers.
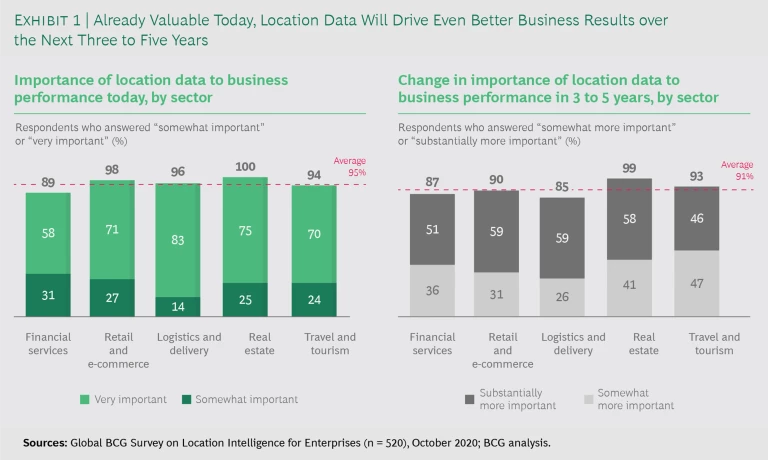
The first thing that stands out in our research is the extent to which these sectors already depend on mapping and geospatial data to enhance business processes. (See Exhibit 1.) Of the executives surveyed, 95% said that mapping and geospatial data are important in achieving desired business results today, and 91% said that it will be even more essential in three to five years.
As further evidence that location intelligence is very important in many businesses, more than 50% of respondents said that their C-level executives participated in the decision-making process pertaining to using mapping service providers. Often, this required cross-functional participation—including IT/digital, strategy, operations, finance, and marketing—emphasizing the interdisciplinary nature of the opportunity. In describing the impact of location intelligence programs, the director of digital product management at a global financial services company said, “If you had asked six to seven years ago, I would have said geospatial data is nice to have, but now it's a must-have for a company like ours to grow revenues and ensure personalized customer experiences.”
What Drives Success?
Not every company can claim high levels of returns from its location intelligence program. In our study, we found that certain attributes of location intelligence programs are more closely correlated with success than others. The factors with the highest correlation to performance included the degree of alignment between mapping and geospatial data and a company’s core business strategy, the extent to which the company employs location intelligence across its business, the maturity of the company’s underlying location intelligence capabilities, and the effectiveness of its efforts to measure value from location intelligence initiatives.
Using the respondents' self-reported maturity on these factors, we categorized them into three location intelligence archetypes—followers, challengers, and leaders—defined as follows:
- Location Intelligence Followers—companies that are in the early stages of using location intelligence, with limited implementation of mostly basic use cases, typically lagging behind peers
- Location Intelligence Challengers—companies that are seeing initial benefits from implementing location intelligence but can further expand the number and sophistication of use cases across their organizations and build stronger location intelligence capabilities
- Location Intelligence Leaders—companies that have defined a holistic location intelligence data strategy, built strong in-house location-based capabilities, and incorporated more advanced location-based use cases across multiple business areas and customer journeys
Only about 15% of the companies we surveyed qualified as location intelligence leaders, while the lion’s share (45%) consisted of location intelligence challengers. Examining these categories by sector, we found that financial services had the highest percentage of leaders (21%), with retail and e-commerce (18%) close behind.
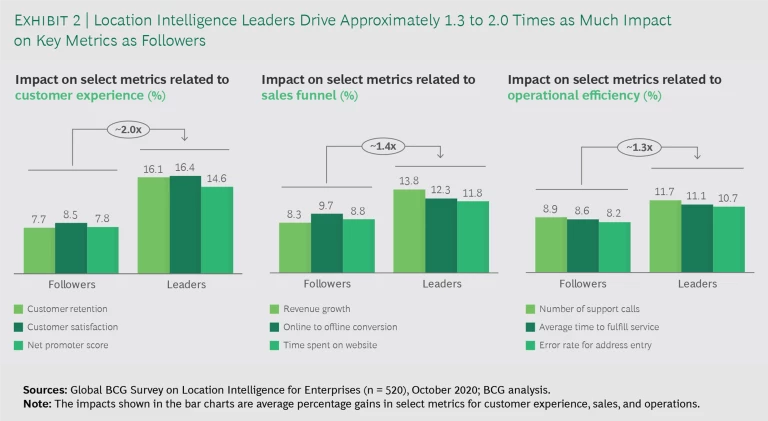
Although all types of companies enjoy some gains from location intelligence applications, leaders far outshine the others. Leaders reported improvements that were 1.3 to 2.0 times as great as those achieved by followers in three key metric categories: customer experience, sales performance, and operational efficiency. (See Exhibit 2.) These higher returns did not vary significantly by industry, company size, or digital adoption relative to peers.
A Broad Spectrum of Location Intelligence Uses
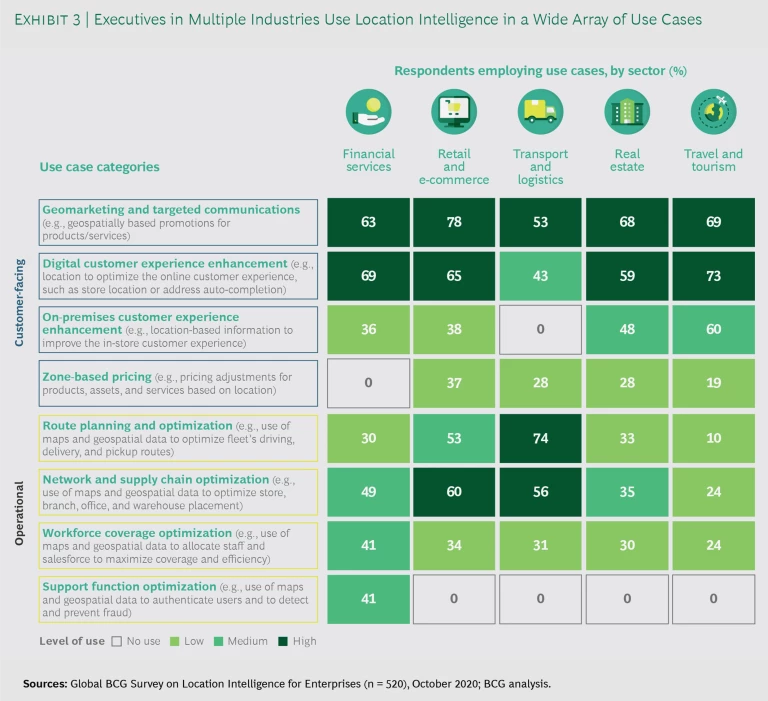
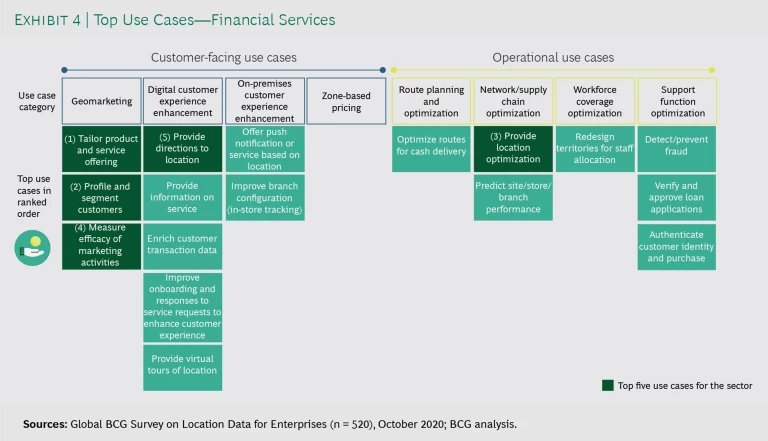
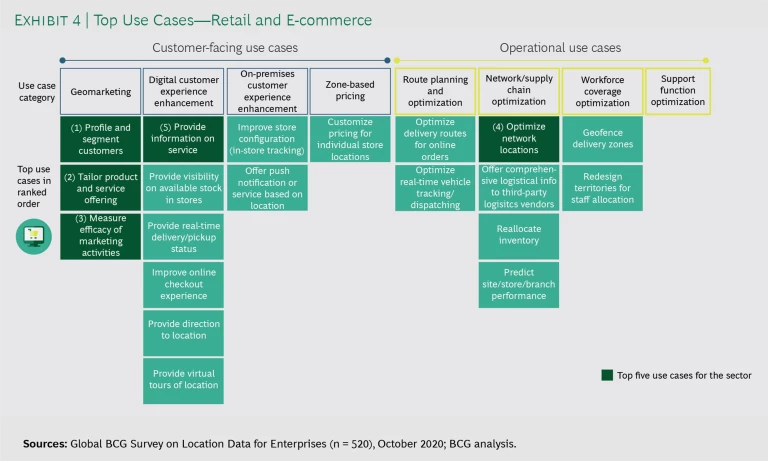
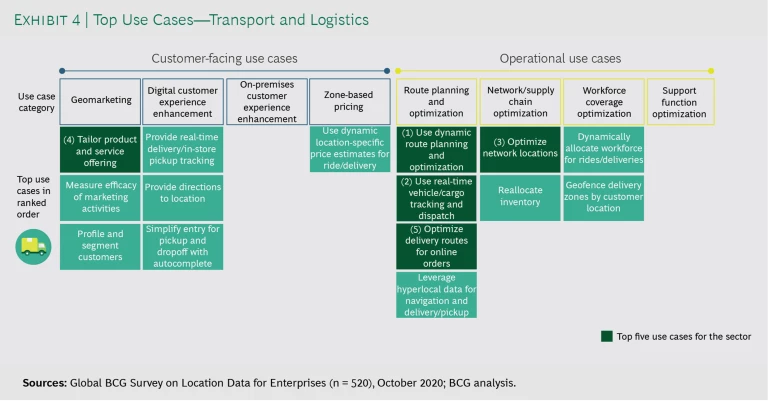
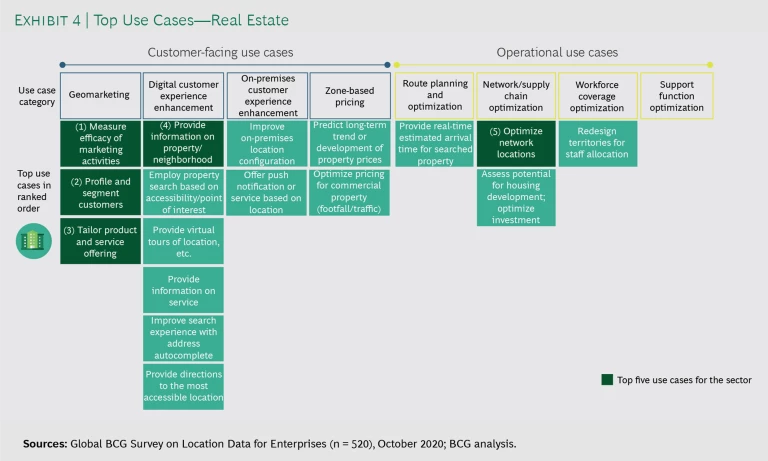
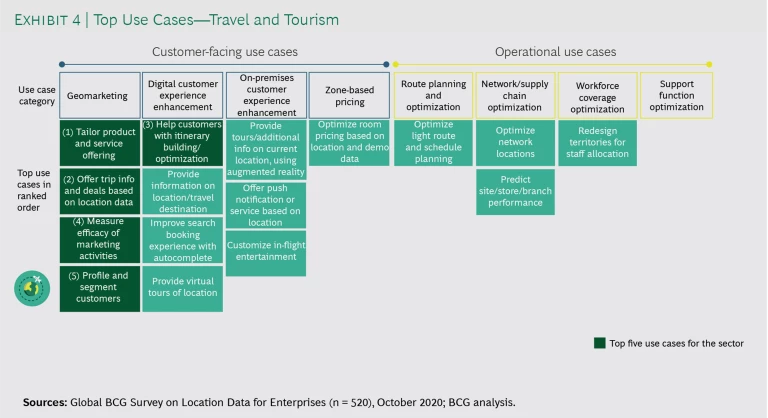
Survey respondents reported that they use mapping and geospatial data across eight categories and more than 100 specific applications. (See Exhibits 3 and 4).
Customer-facing categories include geomarketing, digital customer experience enhancement, on-premises customer experience enhancement, and zone-based pricing. Operations-oriented categories include route planning and optimization, network and supply chain optimization, workforce coverage optimization, and support function optimization. On average, the most active companies leverage geospatial data to implement applications across five to seven categories. (See “How Companies Evolve from Basic to Advanced Location Intelligence Applications.”)
How Companies Evolve from Basic to Advanced Location Intelligence Applications
Retail and E-Commerce
Retailers typically begin using location intelligence to support fairly basic customer-facing activities, such as helping them find store locations or use an autocomplete utility to simplify online search or address entry. Today, these are table stakes applications.
As retailers’ location intelligence capabilities have advanced, more sophisticated uses involving optimizing the end-to-end customer experience have emerged, including the following:
- Making store-level inventory data visible to customers to confirm that a product is available before they come to a store to buy it
- Scheduling store-specific appointments and consultations
- Developing optimized shopping lists and store-level shopping guidance to locate products efficiently
- Making in-store recommendations based on a customer’s past purchases, known preferences, and location within the store
- Optimizing the store experience by using location intelligence to predict queuing
- Using geomarketing to communicate with customers who are near stores and who have opted in, enticing them to shop by presenting them with relevant offers
A growing number of retailers also use location intelligence when planning store locations, taking into account direct attributes of the particular location (such as urban versus suburban and level of expected foot traffic), but also understanding the surrounding environs at a granular level to support better planning decisions. This includes leveraging geospatial data on available transportation modes, parking facilities, competitors’ store locations and plans, and nearby retailers and points of interest that may have complementary traffic patterns.
As retailers develop their e-commerce businesses, some have used location intelligence to improve their management and tracking of in-store pickup and home delivery of products. These programs aim to ensure that items are available when promised at retail outlets or, if shipped, are picked up by drivers on routes and schedules that are dynamically optimized for maximum efficiency and timely delivery, cutting costs and keeping customers satisfied. One former head of online and digital operations at a chain retailer told us that the company “found a 3% to 4% reduction in delivery costs for online orders by better optimizing the fleet.”
Logistics and Delivery
Initially, logistics companies tend to focus on fleet optimization and enhanced package delivery tracking as their core location intelligence applications. Over time, though, some logistics companies expand their use of location intelligence to include helping their largest customers plan their shipping locations for maximum efficiency. For instance, helping shippers locate their facilities for maximum coordination with the logistics vendor’s pickup routes and schedules can improve the timeliness of package pickup, save delivery time, and reduce shipping costs.
Some logistics companies have also leveraged location intelligence to enhance the end customer’s package delivery experience—for example, by offering target time windows for delivery, enabling real-time rescheduling of package delivery if no one will be at home to receive it, and using location intelligence to select the retail store or distribution center to hold the product for pickup.
Logistics company executives who responded to our survey indicated that by using dynamic route planning and optimization they were able to increase the number of deliveries per driver by 4% to 7%. In addition, using location intelligence to provide real-time tracking of vehicles and cargo enabled them to improve their customer satisfaction scores by 6% to 11%.
Geomarketing, which consists chiefly of location-based promotions and advertising for products and services, is widely used across all five industry sectors for customers who have opted in. At least half and up to 78% of respondents say that they have implemented these programs. Retail and e-commerce outfits deploy geomarketing to the greatest extent, while logistics and delivery firms are less likely to adopt this technique. Geomarketing programs typically include customized marketing messages based on a customer’s location; maps to locate nearby stores highlighting discounts and deals; personalized messaging and offers linked to where customers shop and what brands they prefer, if they opted in; and measurement of the incremental impact of these offers and promotions on customer spending.
Companies use geospatial data to enhance the digital customer experience across industry sectors, but especially in travel and tourism, retail and e-commerce, and financial services. (See “An Online Bank Uses Geospatial Data to Address an Underserved Market.”) Such applications include autocompletion of address information for online checkout and search; virtual tours of sites and locations; map-based search for products and services; and listings of inventory, services, hours, and directions for nearby facilities and outlets.
An Online Bank Uses Geospatial Data to Address an Underserved Market
Current’s most powerful location intelligence application, however, is a point-based rewards platform for customers who use their debit cards at nearby retail sites. By increasing points for targeted retailers during promotional periods, Current has seen an uptick in spending of as much as five times week-over-week at one fast-food chain, as well as an 8% lift in basket size and a 10% increase in shopping frequency as part of a multiple-month campaign with another national restaurant chain. A similar campaign with a leading pharmacy chain delivered a 6% gain in average basket size and a 3% increase in frequency.
“Location-based transaction attribution is central to our rewards platform business model,” Current’s chief technology officer Trevor Marshall said. “We are able to circumvent traditional costly attribution models and provide more granular targeting to our merchant partners. By proving the lift of campaigns with high precision, we are able to garner much higher reward amounts for our users. Location-based attribution enables us to provide real-time rewards for cash-sensitive customers, which they can use immediately. Not only are we providing many customers with their first card-based rewards program, we're able to offer best-in-class reward amounts and a superior user experience, allowing them to leapfrog existing options that have not been properly serving them.”
For example, in the real estate sector , companies often connect the map interface directly to location-based property data to give prospective home buyers a multidimensional picture of the neighborhoods, property attributes, commute times, nearby schools, and valuations in the areas they are considering. According to a project manager at one online real estate firm, map-based search has become so critical to customers that the speed at which the map loads “has a large impact on conversion—a delay of one to two seconds can drive a decline in search-to-listing conversion of 10% to 15%.”
Besides being critical for purely online experiences, location intelligence is increasingly involved in efforts to enhance in-store shopping by integrating mobile devices and location data. For instance, grocers may display a smartphone map that shows shoppers where to find each item included on a shopping list that they create online before visiting the store. More advanced retail applications might make product suggestions and point out store locations on the basis of past purchasing behavior.
To improve operations efficiency and reduce costs, companies use location intelligence for network and supply chain optimization. This is particularly prevalent in retail and e-commerce (60%), logistics and delivery (56%), and financial services (49%). Typically, these businesses use mapping and geospatial data to determine the most promising sites for stores, branches, offices, or warehouses, depending on the locations of customers and suppliers and on location-based cost considerations. For instance, retailers might combine demographic data, proxies for local demand (such as nearby ATMs, gas stations, and shopping malls), the availability of public transportation, and the condition of nearby road networks to assess the best markets to enter and the most promising locations within each potential market.
Another relatively mature operations-oriented option is route planning and optimization—which, not surprisingly, about three-quarters of all logistics and delivery companies employ. (See “Beverage Company Uses Location Intelligence to Fill Drink Orders in Hours.”) These companies use location intelligence to determine the most efficient way to route packages and deploy vehicles from pickup location to destination. “Optimizing fleet delivery routes through real-time guidance resulted in saving about 30 minutes per eight-hour shift, which is about 6% in delivery time and cost,” said the principal for robotics and operations for a large global shipper.
Beverage Company Uses Location Intelligence to Fill Orders in Hours
Flaschenpost’s location intelligence program has improved customer satisfaction and increased the likelihood that customers will order again. It also has enlarged the average number of daily deliveries that each driver can complete, thereby reducing delivery costs. “Every minute is crucial for us in terms of financial sustainability and customer experience,” said Aron Spohr, Flaschenpost’s chief technology officer. “Even small improvements in location data accuracy can have significant impacts. By using better location data we were able to improve estimated delivery time by 2 minutes, which in turn saved our 1,400 drivers 30 minutes per driver per day.”
Use of Location Intelligence by Sector Differs but Benefits Are Similar
Although priority uses for location intelligence vary by industry among the sectors we assessed, location intelligence generally had a significant reported impact on key metrics across a similar range—a high single-digit to low double-digit percentage impact. Here are some examples.
On average, logistics and delivery companies reported a 5% to 11% reduction in delivery costs and a 6% to 11% increase in customer satisfaction. This sector primarily uses location intelligence for dynamic route planning and real-time vehicle and cargo tracking.
Financial services companies included in our survey reported 8% to 17% more user time spent in apps that offered location-based, tailored experiences. In addition, such companies have reduced fraudulent transactions and account applications by up to 30% by using geospatial data to verify customers’ addresses and flag possible dishonest activity.
Retail and e-commerce companies said that they increased their average online cart size by 11% to 15% by using location intelligence to provide more personalized and timely promotions. They also reduced average delivery costs by 3% to 4% when geospatial data supported last-mile logistics programs.
In certain sectors, location intelligence is enabling disruptive business models. For example, a European online challenger bank outpaced brick-and-mortar competitors by using address validation to stem fraud in the application process, primarily by screening for people setting up multiple accounts in remote locations. With this security in place, the bank could offer customers instant accounts and such additional location-based features as logging credit transactions on the basis of merchant location to make identification easier.
A company in the takeout food delivery sector is disrupting traditional business methods by innovatively using location intelligence programs to facilitate customer ordering and to efficiently identify and route drivers. Customers who use this company’s app can track delivery progress in real time. The manager of marketplace growth for this company estimates that “adding maps into the customer experience for pickup orders improves the conversion rate by about 2 percentage points.” The company has also used geospatial data to optimize pricing in response to differences in local pricing elasticity. That program alone is worth “up to 25% of EBITDA,” according to the manager.
Some map-enhanced use cases in various sectors have already been around for several years and have become table stakes as the feature no longer serves as a differentiating element of the experience, but rather has become a core customer expectation. For instance, financial services activities such as profiling and segmenting customers and providing directions to branches and ATMs are now table stakes. And in travel and tourism, maps showing possible itinerary and lodging locations are a requirement. Nonetheless, it is critically important for companies to execute these mature uses well. As the head of data and customer analytics at a major travel site put it, “As our industry becomes much more competitive and the use of maps is now standard practice, we have focused more on doing the fundamentals exceedingly well—for example, keeping the map up-to-date and leading on consistency and quality of data.”
Whether it serves to disrupt or represents table stakes, location intelligence is a common capability across industries. Consequently, companies must use mapping and geospatial data to continuously innovate and to support more routine uses that remain critical to optimal execution.
Measurement—A Key to Unlocking Value
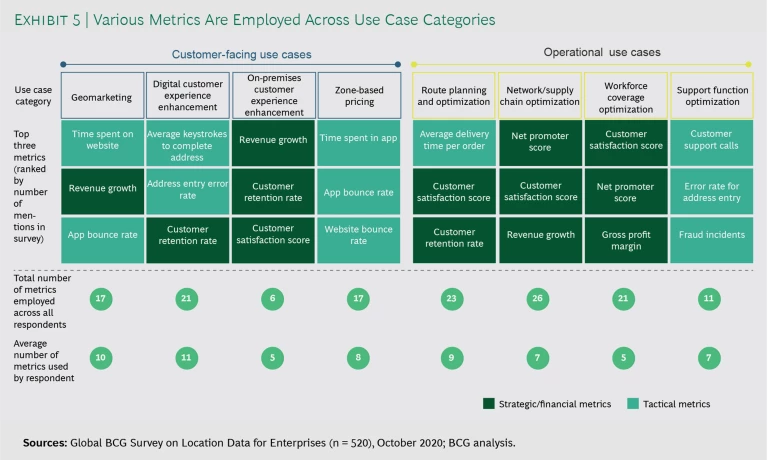
A company’s ability to measure value from location intelligence programs correlates positively with realizing greater value from location intelligence. This finding indicates that developing a nuanced understanding of value is important to successfully adopting location intelligence and using it across an organization. Most survey respondents reported relying on a wide range of metrics to track the success of their location intelligence programs. (See Exhibit 5.) The number of metrics employed across all companies ranged from 6 for on-premises customer experience enhancement to 26 for network and supply chain optimization. On average, individual companies reported using 5 to 11 key metrics to monitor the success of their location programs for each use case category.
Whichever metrics a company decides to use, leaders typically employ four fundamental measurement capabilities to evaluate the performance of their location intelligence programs.
First, they model the return on the initial investment in developing location intelligence capabilities. This simple step is important in justifying the decision to implement a mapping and geospatial data platform. More advanced companies also measure the program’s actual ROI over time as they deploy the capability, make subsequent investments, and realize benefits.
Second, leaders conduct A/B testing. An essential technique for isolating the incremental impact on business results of incorporating mapping and geospatial data in use cases, A/B testing involves, among other things, showing different customer segments variants of a customer experience that uses location intelligence and gauging which variant most effectively drives customer engagement and revenue gains. More advanced companies continuously conduct A/B testing at scale.
Third, they more effectively use customer research, such as surveys and focus groups, to identify critical pain points and assess how to apply location intelligence to mitigate them. With greater understanding of these pain points and the role of location intelligence, companies can track the impact of their efforts through focused measurements.
Fourth, advanced companies use multitouch attribution models to tie revenue to location intelligence programs and tactics. These models help analysts assess the relative contribution and ROI of various customer interactions by attributing credit for a sale to specific customer engagements.
Seven Lessons from Location Intelligence Leaders
Our numerous eye-opening conversations with location intelligence leaders yielded profiles of companies at the forefront of using new types and sources of geospatial data and intelligence to enhance their businesses and improve their revenues, profit streams, and customer relationships. (See the sidebar “Tales from Location Intelligence Leaders.”) Here are the most important lessons we gleaned from our discussions with location intelligence leaders.
Tales from Location Intelligence Leaders
Travel and Tourism: A Leading Global Hotel Chain
A UK-based global hotelier was an early innovator in using location intelligence and mapping—including smartphone maps—to support hotel search and booking and to improve guest experiences. Over time, though, similar map-based interfaces for looking up hotel locations and amenities have become standard throughout the industry.
To raise the level of its location intelligence program, this company added value-enhancing data to the map to help guests make better booking decisions and plan stays. Among the available types of information are travel options, time estimates for travel between locations, parking facilities, local points of interest, dining options, and directions to onsite amenities or services. The company found that many potential customers—especially discovery-oriented leisure travelers who don’t mind rummaging around for the right hotel in the right location at the right price—want to see displays of tangible options and local benefits before reserving rooms. By combining maps with filterable information about surrounding areas and highlights, the company engaged these customers more effectively than it had before. An A/B test on the value of data-enhanced maps showed a 108% increase in property views and a 12% rise in search conversions to bookings.
“Location is important as a confidence builder for our guests and it can be very powerful—the hospitality industry has a huge opportunity to use location intelligence better,” said a former head of digital products.
Retail and E-Commerce: Spencer’s
Spencer’s is a large retail chain in India that sells everything from apparel to leisure items, groceries, and electronics. The company’s location intelligence programs start with basic location capabilities that most retailers use—for instance, online maps and directions for customers to locate stores. But Spencer’s applications go beyond that to include uses of location intelligence that drive substantial value for the business, particularly as the company has moved into the omnichannel e-commerce grocery segment, a rapidly growing component of its overall business. For this part of Spencer’s operations, the company uses location intelligence applications for online ordering, including real-time visibility of store inventory and delivery services, which must take into account customer distance from the store to prioritize product-picking sequence and drivers’ schedules.
One significant business impact that Spencer’s credits to its location intelligence platforms is the elimination of customer orders that could not be fulfilled because the addresses lay outside the company’s service areas. By using location intelligence and mapping to tell customers up front whether nearby stores would deliver to them, Spencer’s reduced nonserviceable orders by 98% and enhanced customer relations in the process. Spencer’s has also used location intelligence applications to improve its on-time delivery performance which it had previously tried to track with a less reliable manual system. Now Spencer’s delivers to customers within a target four-hour window 96% of the time, significantly improving customer satisfaction and reducing customer calls.
Spencer’s has risen above the pack of traditional retailers by pushing forward on some of the more advanced uses of location-based information, despite struggling to implement location-based applications with legacy IT systems—a problem for many large retailers.
“Location intelligence plays an important role in Spencer’s online grocery business, but this is only 3% of the overall business. There’s a huge opportunity to leverage location to improve the conventional grocery business as well,” observed Jawed Ahmed, Spencer’s general manager and head of information technology for the grocery business.
Real Estate: A Leading Online Real Estate Company
A North America–based online real estate company pioneered map-based search for properties, a feature that initially served as a key differentiator but over time became table stakes as other digital players followed suit. In response, the company significantly expanded the breadth of its location intelligence applications by using the most granular prospective customer data available to focus on attracting customers with a high propensity to purchase or rent in the near term; by using property information, location, and topography to model home valuations more accurately; and by using these valuations to offer a new service in which the company purchases properties from sellers who need cash quickly.
In addition, the company has continued to advance its digital property search services by introducing new tranches of information to the map (beyond property location and multiple listing service data) that are highly relevant to home buyers. For instance, the company has added traffic-pattern-based commute time data, local school options, a scoring system that rates the ease of walking to local shops and venues, and nearby similar home comparisons.
The company has found that the use of maps—even those that are similar to competitors’ offerings—is critical to the value of customer experiences and must be executed well. But beyond that, adding specific types of geospatial data to the map experience has had a meaningful impact on business results. A company product manager said, “We used A/B testing to assess the impact of new school data on engagement and found that adding this to the experience drove an up to 10-percentage-point improvement in the conversion of map traffic to listing views.”
Think broadly and strategically about how to leverage location intelligence to enhance customer experience and improve operational efficiencies. Look for ways to use mapping and geospatial data holistically and innovatively, moving beyond a focus on individual uses to optimize company-wide synergies across applications—for instance, by using geomarketing or customer experience personalization, on the one hand, while increasing supply chain efficiencies, on the other.
Anticipate new digital business models and shifting customer expectations in which mapping and geospatial data play a central role in enabling new value propositions. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated digitization and the opportunity for technology to play a larger role as an interface with customers in all settings. In this environment, companies should explore innovative uses of location intelligence that leverage digital interactions to build deeper and more personalized relationships with customers.
Systematically prove the value that geospatial data contributes. Use all available tools to measure the impact of location intelligence, including quantifying the initial business case for adoption, tracking ROI, establishing clear targets for metrics based on benchmarks, employing systematic testing and modeling techniques to assess impact, and collecting targeted customer research.
Invest in strong data management and analytics capabilities. These capabilities should include ingesting geospatial data, integrating with other information sources, building analytical methods to drive insights, and enabling more advanced use cases. For instance, many customer-facing use cases need to be able to link geospatial data with a customer’s profile and purchase history, to support locationally aware offers that take into account a customer's preferences.
Consider location intelligence partnerships carefully and deliberately, focusing on long-term capabilities and reliability. Develop these partnerships with companies that have strong reputations and have demonstrated deep knowledge and expertise in deploying location intelligence platforms. Respondents to our survey reported that the most important factors in selecting a location intelligence partner were geospatial data accuracy, cost, expected value and ROI, freshness and breadth of data, and the location intelligence platform’s compatibility with existing technology infrastructure.
Proactively ensure that customers’ geospatial data is protected. Customers are increasingly wary of marketing use of their private data—in particular, their movements and travel patterns. Companies must address customer privacy concerns by rigorously protecting all data, including contact data in their profiles, with the precautions necessary to build trust.
Excel at the fundamentals of applications based on mapping and geospatial data, including uses that have matured and become table stakes. In those instances, companies may still be able to differentiate themselves by flawlessly executing the basics, such as map images, geocoding, and geospatial data accuracy—as these remain core customer expectations and, therefore, are critically important to get right.
Implications for Companies Moving Forward
Our study uncovered a wide array of approaches to using location intelligence across the five sectors we explored. For nearly all companies in these sectors, as in others, location intelligence will be an increasingly critical part of their future—an essential aspect of personalizing customer engagement online and offline and of optimizing complex operations.
Facing this reality, companies across industries must take firm steps to improve their location intelligence capabilities. They must maintain high levels of quality in current location-based uses while also devising new ways to use location intelligence to transform customer experiences and business operations.
Companies that focus on strategically and holistically leveraging location intelligence across their businesses—while building solid underlying location-based infrastructure, capabilities, and partnerships—will be in an advantageous position. As we’ve seen in our study, location intelligence leaders that develop advanced capabilities drive much higher levels of business performance than location intelligence followers. Companies that become location intelligence leaders will be able to use geospatial data as an increasingly important element of personalizing customer experiences to drive satisfaction and revenue growth and of optimizing complex operations.