Key Messages
The analysis by BCG’s Center for Energy Impact of global energy sector investment needed through 2030 to reach emissions reduction goals yielded the following key findings:
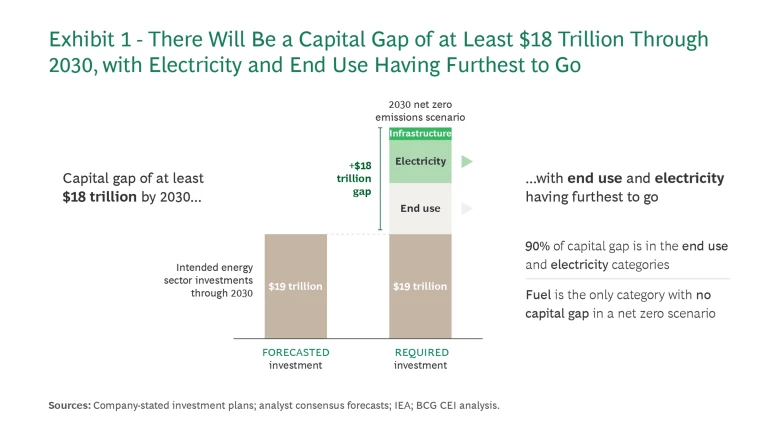
- Capital Challenge. An $18 trillion capital gap exists between current commitments and the investments needed for alignment with net zero goals in 2030. Electricity and end-use sectors account for 90% of that shortfall.
- Transition Barriers. Higher inflation and supply chain disruptions over the past 24 months have significantly hindered energy transition progress, stifling momentum and increasing costs.
- Investor Behavior. Rising risks drive investors to seek higher returns, favoring businesses that prioritize capital discipline and cost efficiency even in high-growth renewables markets.
- Sector Restructuring. Energy sector deals surpassed $320 billion in 2023, as companies optimize capital structures for energy transition investment. Oil and gas companies are leading with acquisitions, while utilities offload more assets to access capital and focus portfolios.
- Strategic Adaptation. Companies should emphasize refining capital strategies, boosting efficiency, seeking innovative transactions and collaborations, bolstering financial foundations, and fortifying supply chains. These measures are essential to amplify investments, satisfy shareholders, and move toward net zero outcomes.
- Government Role. Policy reforms, subsidies for low-carbon solutions, and expedited project approvals are essential for accelerating investment.
Navigating the path to a 2030 net-zero-aligned scenario reveals a staggering $18 trillion capital gap between current energy transition commitments and the required investment levels. Electricity and end-use sectors account for 90% of that shortfall. (See Exhibit 1.) With companies in the industry poised to drive 80% of planned energy transition investments through 2030, their strategies and execution plans are paramount.
However, their journey is riddled with hurdles. In the present climate, higher inflation, persistent supply chain pressures, and rising capital costs cause significant bottlenecks, slowing the pace of the energy transition. The setting is also reshaping investor behavior; companies face more demanding calls for higher returns, more disciplined capital management, and more efficient resource allocation, even within the high-growth renewables space.
The energy sector’s response has been proactive. A flurry of transaction activities signals a strategic push to fine-tune capital frameworks for the energy transition; so far in 2023, total energy sector deals exceed $320 billion. Oil and gas companies have emerged as dominant buyers, while utilities are using carve-outs to raise funds and recalibrate. As capital markets evolve, only projects that strike the right balance between risk and returns will receive sufficient funding. Regions where stakeholders effectively align policy directives and market mechanisms will be the prime recipients of future investments.
To flourish in the face of growing capital demands, energy companies must reassess portfolios, create innovative capital strategies and new partnerships, optimize their financial structures, and emphasize stringent cost and supply chain efficiencies. This report highlights the sector’s crucial capital allocation dynamics and the implications for competitive success in the energy transition.
Follow the Capital: Tracking the Investment Landscape of the Energy Transition
BCG’s Center for Energy Impact recently analyzed the investment plans of the world’s leading energy companies, governments, and private equity players, to compare real-world energy transition investments with net-zero scenario benchmarks.
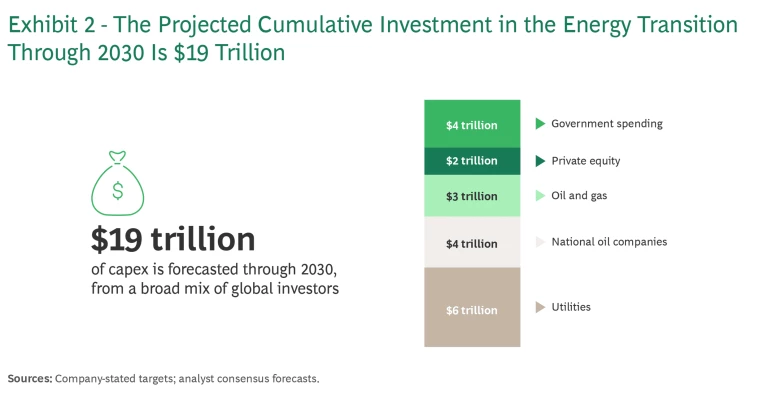
The study reveals two major trends. One is that energy companies and governments aim to inject an impressive $19 trillion into the energy transition over the next seven years. This includes nearly $2 trillion in new government spending, spurred by US and European legislative initiatives. Company targets suggest a 15% increase in energy expenditures between 2023 and 2027, with an increasing share allocated to low-carbon investments. (See Exhibit 2.)
Yet the shadows of the war in Ukraine loom large. The repercussions of the conflict, marked by skyrocketing commodity prices in 2022 and 2023, have tightened capital availability, particularly for European utilities—the linchpins of European decarbonization efforts. These financial headwinds, coupled with higher inflation and capital costs, have curbed enthusiasm for new investments.
The Pivotal Role of Policymakers in Accelerating Transition Investment
There is an urgent need for global policymakers to address existing challenges and ensure a fair and efficient shift to low-carbon energy . Energy transition investments are most effective in regions where market structures and policy guidelines align to produce favorable risk-to-reward profiles for capital.
BCG’s Blueprint for the Energy Transition outlines six essential steps for public sector leaders to bridge the investment gap and support the flow of capital into transition projects. These steps include electricity market modifications to produce adequate pricing signals for new investments; faster approval processes for projects, particularly grid expansions; enlarged green investment subsidies through incentives and research grants; and revised liability guidelines to enhance investor confidence.
Strategic Imperatives: Shaping the Energy Transition Through Corporate Action
The energy sector stands out for its intense capital demands, marked by a capital intensity rate that is more than double that of other industries. Accounting for approximately one-third of the world’s yearly capex, it encompasses diverse peer groups, segments, and stakeholder interests. Yet organizations throughout the sector share a mission to amplify investments, satisfy shareholders, and navigate toward net zero outcomes.
To accelerate the energy transition, every company in this sector should treat six actions as mandatory:
- Refine capital allocation. Evaluate and enhance current allocation processes to weigh trade-offs between traditional investments and low-carbon alternatives, ensuring a comprehensive approach to decision making. Look for processes that need revamping. In particular, low-carbon investments are much more sensitive to cost-of-capital increases than traditional energy sector investments. Improved cost-of-capital assessments across global portfolios would paint a more detailed picture of favorable assets.
- Focus on efficiency. Emphasize cost and capital efficiency in energy transition investments. Such an approach may entail completely transforming the way a company runs major capital projects and operations. For example, companies are evaluating the factory model that has successfully reduced costs in the US shale sector for use in large-scale renewables and other low-carbon settings.
- Explore strategic M&A and divestitures. Mergers and acquisitions may work for some companies, while others may benefit from divestments that enable them to concentrate their resources more effectively.
- Forge new partnerships. Explore alternative deal structures such as minority shareholdings, joint ventures, strategic partnerships, and corporate venturing. These structures can be complex, but they offer strategic flexibility that is essential for navigating capital constraints in certain areas of the energy sector. They also promote specific collaborations to advance decarbonization efforts.
- Strengthen the balance sheet. A volatile market forces companies to adopt robust financial strategies. The disparity in valuations between US oil and gas majors and their European counterparts highlights the importance of financial resilience, as does the surge in total shareholder returns by more debt-averse utilities in 2023.
- Stress-test the supply chain. It is crucial to rigorously evaluate supply chains for cost efficiency, carbon intensity, and resilience. Reevaluating supplier relationships and identifying dependencies can cut costs and minimize risks.
The energy transition’s immense capital demands underscore the need for companies and policymakers to adopt robust and innovative approaches. As the world advances toward its net zero goal, harmonizing investment strategies with collaborative solutions is paramount. Although the energy sector is already making strides, consistent policy support and forward-thinking financial maneuvers are crucial to bridging the existing gaps and ensuring an ordered, equitable, and sustainable shift to a greener future.