Within two months of its launch, ChatGPT had already registered 100 million users—setting a record for the fastest-growing base of users. Such strong adoption underscores the potential that people in many industries see in generative AI. For medtech companies, the technology can make processes more efficient, help companies personalize customer interactions, unlock innovation through unconventional creativity, and better access enterprise data and knowledge to create value in new ways.
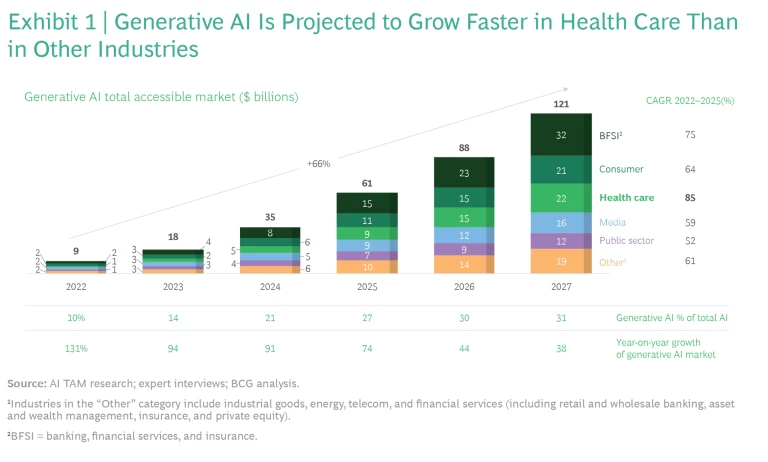
Generative AI is projected to grow faster in health care than any other industry, with a compound annual growth rate of 85% through 2027.
The main challenge is knowing how and where to start. Because generative AI has such a broad set of potential applications, and because medtech is a highly regulated industry where people’s lives are at stake, some companies may adopt a wait-and-see approach. We believe such inaction would risk putting companies at a long-term disadvantage. Generative AI is projected to grow faster in health care than any other industry, with a compound annual growth rate of 85% through 2027, to reach a total market size of $22 billion. (See Exhibit 1.)
For that reason, medtech companies should begin implementing the technology in various parts of their business. We identified more than 60 use cases for generative AI across the entire medtech value chain, and ranked them based on their impact and speed of implementation to identify the biggest near-term opportunities. The common theme? All have strong potential to help medtech companies work smarter and faster—and ultimately create value for the companies ambitious enough to apply them.
How Generative AI Creates Value
Traditional AI sifts through historical data to identify patterns and insights. Generative AI goes beyond that. It still entails models built on vast quantities of data, but it uses that information to generate new content such as text, media (video, images, speech), computer-aided design, and software code. For medtech companies, the main advantages of generative AI are as follows:
- Increased efficiency through reduced manual work or higher-speed processes
- Unprecedented personalization of customer interactions
- Improved creativity to develop novel designs and products
- More comprehensive use of enterprise data and knowledge
In the short term, companies can adopt commercially available generative AI offerings (such as GitHub Copilot X or Jasper), or fine-tune existing generative AI models. Over the long term, companies can unlock greater value by developing more advanced use cases that entail more comprehensive changes to internal processes along the value chain—and ultimately develop novel products and services that are built on generative AI technologies.
Use Cases Along the Entire Value Chain
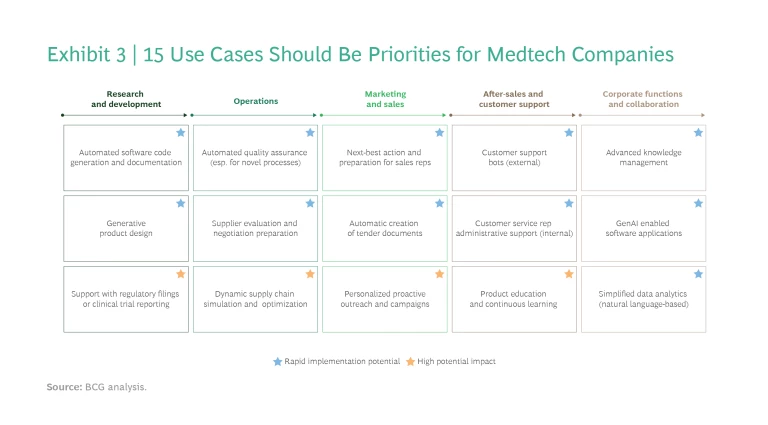
We have developed a repository of more than 60 use cases across the entire value chain as a starting point for exploration. (See Exhibit 2.) Critically, we also ranked these in terms of their impact for medtech firms and speed of implementation, enabling companies to focus on those that could deliver quick wins and thus build up organizational capabilities and confidence. Exhibit 3 shows the 15 use cases with particularly high value based on this prioritization.
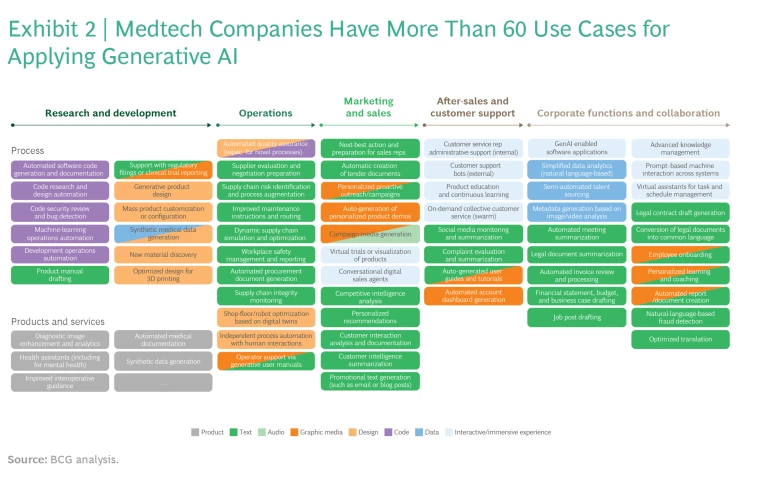
R&D and Software Development
Generative AI models can support software development, an area where medtech companies often struggle with high costs (in some product segments, more than 50% of total product development costs) and insufficient talent. Generative AI solutions can address both challenges. For example, GitHub Copilot X is a generative model trained on billions of lines of code that can transform natural language input into code suggestions, saving programmers substantial time. Initial pilots suggest that tasks can be completed up to 55% faster. In addition, generative AI solutions can create test cases, document code, and automate code reviews (offered by companies such as Mintlify and Amazon CodeWhisperer).
Beyond software, generative AI can apply unconventional creativity to help companies discover new product designs (using generative design tools offered by companies like PTC, nTop, or Autodesk). Further value can come through streamlining the time-consuming process of converting internal documents into regulatory submissions—often hundreds of pages long—or clinical trial reports. Several startups are working on regulatory solutions, though none are commercially available yet.
GitHub Copilot X is a generative model trained on billions of lines of code that can transform natural language input into code suggestions, saving programmers substantial time.
Operations
One of the more noteworthy aspects of generative AI is that it can enable AI applications even with insufficient training data. For example, in a novel process that doesn’t have significant data, the tool can extrapolate from limited information by creating synthetic data that can then be used to train machine learning models. In medtech operations, this approach can improve quality in production processes by identifying flawed products much faster, rather than waiting for the errors to occur in real-world situations. Quality systems trained with synthetic data can detect product flaws from day one, using computer vision or other sensors and automatically removing faulty products from the production line (for example, via robotic bin-picking).
Generative AI can further enhance procurement processes by simplifying access to the broad base of supplier data ranging from existing contracts or proposals to public information on the supplier or industry (for example, financial data, news, and trends). Through advanced natural language comprehension, algorithms can summarize information as well as identify potential risks, thus enabling procurement teams to make informed decisions.
Marketing and Sales
In the past few years, medtech sales teams have faced increasingly tighter restrictions on in-person visits to their customers. As a result, many have invested in digital sales capabilities. Generative AI can turbocharge those efforts, enabling mass personalization and tailoring marketing messages to resonate more effectively with different customer segments—and thus increase conversion rates.
Specifically, generative AI can consolidate information from a wide array of sources, both internal (client visit reports using customer relationship management programs) and external (media coverage, company website) to generate account-specific insights. It can guide sales reps to the next-best action for a given customer and prepare bespoke content to support that action. During and after a sales interaction, Generative AI solutions can automatically document the visit, capturing and analyzing customer information to generate insights that support the next interaction. Key CRM vendors are starting to offer initial versions of this kind of functionality, including Salesforce’s Einstein GPT, HubSpot’s Chatspot.ai, and Microsoft’s Viva Sales Copilot.
Postsales Customer Support
Across medtech companies, customer support is a highly manual and time-consuming task. Generative AI can substantially reduce the manual effort required in areas like order management and other administrative requests. Because it can interact with customers and has all the necessary information at hand, it can offer better customer service without staff involvement, providing real-time details on product availability, delivery timing, and other information.
Generative AI can substantially reduce the manual effort required in areas like order management and other administrative requests.
Looking at specific support for individual products or services, fine-tuned voice or chatbots can incorporate information such as past service tickets and product manuals to provide trouble-shooting suggestions to customers, determine the right supporting documentation or assets from a library, and escalate more complex requests to human agents—all with greater sophistication and service levels compared with current offerings. Potential vendors in this area include Forethought and Zendesk.
Going beyond that, future solutions can use generative AI to analyze customer and product usage data to assess whether customers are capitalizing on the full range of features—or consistently hitting problem spots in a given process. Generative AI can also use advanced language comprehension to engage with customers in a conversation to improve customer success. These solutions can also integrate with sales functions to identify cross-selling and upselling opportunities.
Corporate Functions and Collaboration
Independent of specific steps in the medtech value chain, generative AI can make productivity and collaboration tools more efficient. This applies both to out-of-the-box office applications (such as Microsoft 365 Copilot or Google Workspace) and to customized applications—such as using a generative AI model to respond to company-specific internal questions. For example, Morgan Stanley is testing an OpenAI-powered chatbot trained on a vast amount of internal and external broker reports to support its financial advisors.
Generative AI is also expected to streamline the creation of custom reports and analyses, by converting natural language into machine requests. This would make data more easily accessible and generate actionable insights for business leaders in near real-time.
In HR, generative AI can help companies identify suitable candidates for jobs and draft individualized messages to improve engagement (using tools such as hireEZ). Initial clarifying questions or even prescreenings can be handled autonomously, with the system screening candidates and presenting a subset of finalists for a hiring manager to interview.
Generative AI as Part of a Medtech Product or Service
In addition to the benefits along the value chain as cited in the use cases, generative AI can fundamentally shape how medical services are provided. For example, it can:
- Enhance image quality—such as pathology slides—and improve the accuracy of diagnostics (through offerings from Paige and Pictor Labs).
- Automate patient-clinician interactions to free up time for physicians to treat patients generally or via a link to specific devices (Corti and Microsoft + Nuance).
- Provide guidance along medical workflows, such as supporting the movements of physicians during surgeries (Activ Surgical and Kaliber Labs).
- Identify brain health anomalies and develop personalized treatment plans and interventions (DiagnaMed).
In addition to the benefits along the value chain as cited in the use cases, generative AI can fundamentally shape how medical services are provided.
Incorporating generative AI into products and services more comprehensively will require resolving questions around regulatory processes—particularly in Europe, which is behind the US in terms of providing regulatory clarity about the use of AI in medtech devices. Nevertheless, companies can look ahead and think about how their products can change and use generative AI to interact with patients in new ways. This is especially true for medical software businesses.
Three Steps to Get Started with Generative AI
Given the potential impact from generative AI, medtech companies need to act. In contrast to other emerging technologies, gains in efficiency and effectiveness can come quickly. Therefore, we recommend three steps.
1. Identify, pilot, and scale priority use cases along the value chain.
First, companies need to identify the specific use cases of generative AI that hold the most potential for their offerings of products and services. This entails quantifying their impact and speed of implementation, factoring in elements such as the availability of models and data, error tolerance, data security, affordability, and market demand.
Companies need to identify the specific use cases of generative AI that hold the most potential for their offerings of products and services.
Based on our discussions with several medtech companies and functional experts, we believe the following use cases have significant short-term potential along the value chain:
- Customer Service. Supporting customers who want to place orders or who have other administrative needs, using advanced language comprehension to augment or automate conversations to solve their problems (largely through self-service models).
- Sales. Analyzing past customer interactions and external data to identify personalized next-best actions for individual customers. Automatically preparing corresponding materials such as email messages or sales briefs.
- Software Development. Accelerating software development from code creation to testing in order to address the bottleneck of software development capacities in medtech and help get differentiated offerings to market faster.
- Knowledge Management. Providing access to enterprise knowledge more effectively and efficiently, enhancing employees’ everyday work experience by integrating generative AI capabilities into daily applications (including Microsoft Office applications).
- Operations. Increasing automation opportunities in manufacturing and quality through utilizing synthetic data in model training with the potential to accelerate deployment and increase accuracy.
2. Incorporate generative AI into the overall enterprise strategy to develop a lasting competitive advantage.
Generative AI use cases to accelerate software development and improve customer support bots are novel today. But they will become table stakes as more companies adopt them. Companies need a clear perspective for where they can derive the largest competitive advantage by integrating generative AI into medtech products and services or value chain activities. As an initial step, organizations could review the impact of generative AI on their existing product and service portfolio (where it could be improved) and review their client/patient flows (where new offerings could be added). Note that value chain activities and operating models might change substantially, and companies should be clear about where the largest value potential lies for them.
3. Put the right policies and people in place.
Once use cases have proven their impact, it’s essential to scale them up across the organization to capture their full value in terms of policies and talent.
Once use cases have proven their impact, it’s essential to scale them up across the organization to capture their full value in terms of policies and talent.
- Policies: establish responsible AI mechanisms to manage risks. Despite its tremendous potential, generative AI also has potential risks, such as perpetuating biases in data, violating intellectual property protection, generating incorrect outputs, or creating new cyber vulnerabilities. Regulators will likely adopt a clear stance on the use of generative AI, but companies can take internal steps as well. For example, companies require strong governance to navigate ethical, legal, and technological considerations—commonly referred to as responsible AI—along with a framework to support organizational decision making and a set of tools to monitor and manage generative AI risk.
- People: empower the organization and individuals to jointly benefit from generative AI. To support new ways of working, many organizations will likely need to adapt their organizational structure and operating model, clarify responsibilities and decision rights, and redesign job profiles. Companies will also need to update their talent and skills strategy to ensure employees are familiar with how to operate generative AI enabled applications (such as prompt writing) and to generate capabilities to deploy advanced use cases (such as increased machine-learning expertise).
Generative AI provides clear opportunities for medtech companies to optimize internal processes and later disrupt the market through new products and services. For that reason, medtech leaders must seize the initiative by identifying and piloting high-value use cases; considering strategic implications of the technology; and preparing people and policies to enable the change.
The authors would like to thank Dominik Parak and Michael Nuebler who contributed to this article.












