Bancassurance, an important line of business for retail banks, is under threat as interest rates remain high and banks on the hunt for higher profits are prioritizing their core savings and lending products over insurance. Compounding matters, banks are closing branches and focusing on digital channels where insurance cross-selling is typically lower—with some of our clients, it was 50% lower than in branches. As a result, banks are missing out on some key advantages of bancassurance, namely a higher return on capital and a steadier, more resilient source of profitability over the long term.
To grow their bancassurance businesses, banks need to increase the volume of leads dedicated to insurance products and increase conversion rates. That means building a bancassurance sales model that is both hyperpersonalized and embedded in the customer journey. Leveraging customer transactional data and high-precision AI personalization models, banks can target more precisely which clients to communicate with; when to have these communications; and which type of message to transmit and through which channel. At the same time, they can help average sales agents perform better.
Banks that use AI to hyperpersonalize their sales models and embed them in the customer journey can dramatically improve their insurance sales.
Companies that take this approach, in our experience, have the potential to increase conversion rates by three to five times and by as much as eight times for high-propensity customers.
Building a Hyperpersonalized and Scalable Sales Model
Banks are well suited to sell insurance—even more than traditional insurance intermediaries—because of their voluminous customer data and closer relationship with customers thanks to more-frequent personal interactions with them. Yet so far conversion rates in the sales funnel have been suboptimal because banks have not yet developed a sales model that leverages these personalization capabilities to their full potential.
To develop a hyperpersonalized sales model that scales, banks should develop a hybrid model that leverages the advantages of online and physical channels. Instead of introducing complex sophisticated products or a complex sales process—both of which can add unnecessary costs—we recommend banks focus on six key dimensions.
To develop a hyperpersonalized sales model that scales, banks should leverage the advantages of online and physical channels.
Improve propensity models. Propensity models provide a way to identify the customers who are most likely to buy insurance. To improve the quality of the model’s output, banks can use more-advanced modeling techniques, such as random forest. We’ve seen these techniques achieve 10% to 30% higher conversion rates than traditional techniques.
Including more variables can also help. Adding in credit scores, for example, allows banks to prioritize their leads and focus their cross-selling efforts on the customers who are most profitable for the insurer. More-accurate propensity models are a win-win: less risky clients will get lower prices, which in turn will improve conversion rates. Banks should experiment continuously to keep evolving the quality of personalization models with this in mind.

Banks can also complement static propensity models with dynamic models, such as a library (a precompiled list) of events. We’ve seen some events can increase lead conversion by 10% to over 130%, though the amount of the increase depends on the insurance product. (See Exhibit 1.)
Develop better pre-quote offers. If a bank has enough information about a particular customer, it can estimate the price of an insurance policy before offering it to the customer, preferably in a targeted communication. A more personalized pre-quote offer can also increase conversion rates by 2x to 4x. But determining a price for a pre-quote in most cases (and certainly in the case of car insurance) requires the bank to share the client’s data with the insurance provider. That may be difficult to do, given the regulatory constraints around data sharing, such as the EU general data protection regulation (GDPR).
To circumvent this obstacle and still generate value, banks can obtain clients’ consent to data transmission. Alternatively, banks can duplicate pricing engines in the IT infrastructure to prevent data sharing. They can also use anonymized data and proxy variables and clusters.
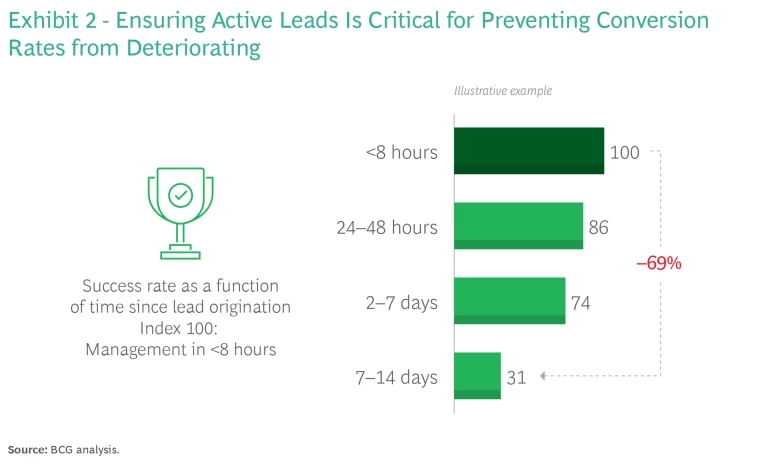
Build a seamless omnichannel journey. The longer it takes to process a lead, the less successful it is likely to be. (See Exhibit 2.) This is especially true for leads linked to customer events, such as getting married or having a child. If the bank relationship manager (RM) is not able to respond to a lead while it is still warm, there needs to be a call center, home-banking webpage, mobile, or another channel that the bank can steer the lead to. That way, the bank can guarantee a seamless omnichannel journey and avoid losing a sales opportunity. If the bank manages the lead 48 hours after receiving it instead of two weeks later, it can prevent the conversion rate from dropping significantly.
Ensure proper operationalization of leads in bank channels. Bank customers are increasingly doing their banking outside of physical branches—more than 60% of customers reported that they had not visited a bank branch during the last 12 months, according to a 2022 Rebex survey. Therefore, banks need to ensure they can collect and send leads from all possible online channels as well. They also need to leverage transactional data to extract more of those leads through understanding the customer’s life cycle. At the same time, banks need to use digital advisory tools to increase customers’ risk awareness and generate new sources of leads. It’s critical, therefore, for banks to structure the sales conversion funnel, ensure real-time visibility and accountability at each step, and monitor the performance of salespeople along the way.
Develop personalization engines. Different client segments purchase insurance for different reasons—family protection, access to premium assistance services, and so on. By leveraging unstructured data, such as past interactions with sales representatives, contact center call transcripts, and notes of the RM, GenAI can help banks develop personalized sales scripts. In our experience, banks that personalize scripts this way can as much as triple their conversion rates in certain customer segments.
GenAI can help banks develop personalized sales scripts.
Support remote interactions with an AI-driven copilot. At contact centers, banks can experiment with innovative operating models whereby GenAI bots provide live support to sales agents, explaining the key points about an insurance product the agents may not be familiar while focusing on the issues that are most relevant to the client. And GenAI can help RMs develop personalized letters for clients, improving productivity and commercial effectiveness.
Taking the First Steps
Building a scalable, personalized sales model is no small undertaking. Banks, however, can make the journey in steps, beginning with some quick wins like a library of customer events. That said, banks and their insurance partners need to keep a few things in mind.
- Set up a close collaboration with the insurance partner. After the bank and its insurance partner align on the vision, they will want to work closely together, sharing resources and expertise to build personalization at scale. They will also need to share information and discuss how to improve performance. If both parties make this business a priority, they can develop the right approach and governance to optimize collaboration along the value chain.
- Invest in digital. To enable the operationalization of leads in channels, banks will need to make some IT investments. They may also need to develop novel operating models. In the beginning, the technology investment is rather contained, since add-on AI solutions are all that will be needed—they will leverage capabilities already available for other products.
- Simplify products and processes to ensure flexibility. Implementing an omnichannel journey will require banks to simplify products and underwriting processes to make products digital-ready. Banks may also need to adjust their pricing strategies.
- Develop a robust talent strategy. The bank and its insurance partner will need to ensure they have the data science expertise (internally or externally) on hand to handle the complexities of AI and GenAI, such as integrating internal and external data sources. A sales force with the needed expertise will also be important.
Bancassurance is a source of profitable growth that few banks today can afford to ignore. Although the required effort is substantial, those that seize the opportunity now will reap the rewards in the mid to long run.




