AI is reshaping the marketing landscape, offering breakthrough capabilities like unlimited permutations of personalized marketing for modern consumer journeys, predictive insights, and real-time decision making. But for most marketers, the whole idea of AI feels overwhelming. They are constantly bombarded with pitches from tech providers and platforms, each claiming that their AI solution will revolutionize the way their brand engages with customers. They wonder: Where do I start? Which areas should I prioritize?
To address these questions, we conducted one of the largest studies of its kind, surveying more than 2,000 marketers globally and speaking with over 50 marketing leaders. (See “About the Study.”) Through our research, we developed a clear framework to help marketers cut through the noise, pinpoint where AI can drive the most impact, and build a roadmap for growth. In this article, we share insights from the study. We then outline the essential steps for making AI an integral element of the marketing function to create an AI flywheel that seamlessly integrates capabilities across media planning, creative, activation, and measurement to boost efficiency, deliver results, and keep brands ahead of the curve.
About the Study
The survey consisted of more than 50 questions about companies’ maturity level, AI capabilities and practices, and the extent to which their AI-based marketing was integrated across the enterprise. We asked about such issues as:
- Their use of AI for developing consumer insights (for example, automating traditional audience research and creating synthetic insight tools such as conversational personas that represent different target audience segments and their preferences)
- Their audience segmentation and media-bidding strategies (e.g., setting inputs for AI models to conduct automated bidding and using predictive AI to build audiences)
- Their use of GenAI across creative and content tasks (such as developing creative concepts, auto-populating briefs, and designing assets)
- Their people and process strategy (including talent development, governance, decision making, and their enterprise strategy for AI)
To gain deeper qualitative insights, we also conducted more than 50 interviews with marketing decision makers, inquiring about the impact of their AI program on ROI and overall performance over the previous 12 months. Correlating practices with performance, we then distilled the capabilities list down to the essential six and identified the most important actions marketers can take at each stage to forge a path to AI excellence.
What AI Excellence Looks Like
Most brands are still in the early innings with AI: more than 80% of our survey respondents are exploring off-the-shelf solutions, adopting use cases, or experimenting. Two-thirds claim they are stymied by either a lack of knowledge or the sheer number of options. But a select few have started to figure it out. About 20% of respondents have integrated AI tools deeply into their marketing workflows. They are testing AI-assisted decisions and personalization approaches in such areas as content creation, predictive analytics, and synthetic research methodologies. In the past 12 months, these leaders have achieved powerful results: they report 60% greater revenue growth than their peers and are adapting to consumer trends twice as fast as their peers.
So what are the 20% doing right? We’ve identified six key actions. (See Exhibit 1.)
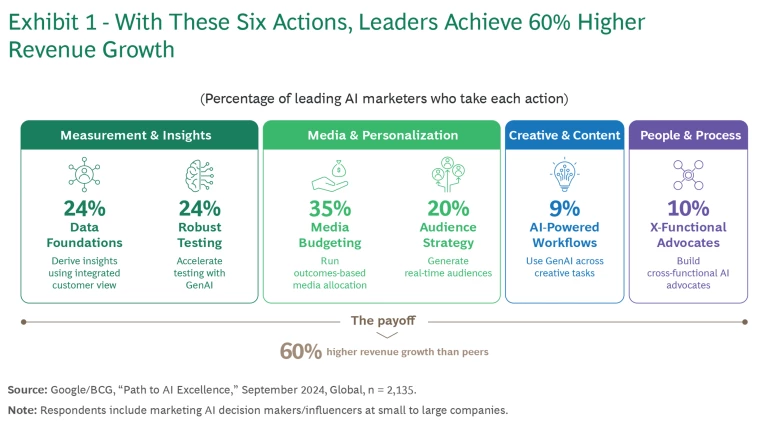
They have an integrated view of the customer. The modern consumer journey is less linear and more varied than ever. Leaders understand that AI can help them address that complexity, starting with a comprehensive view of the customer—a view built on first-party data that feeds AI models and connects to media activation.
Take, for example, the bank that wanted to present personalized offers but lacked a unified customer view. It integrated first-party data from branch interactions, call logs, and emails and then connected systems with segmentation, rules, and content assignments. Predictive AI models powered cross-selling campaigns based on the individual customer’s history. The bank was able to cut offer launch times by more than 60%.
They accelerate test design, execution, and analysis. Fewer than 25% of respondents have tapped into AI’s potential to support always-on testing by accelerating insights. Leaders, however, are using AI to create new campaign ideas with greater speed and volume than traditional approaches. Consumer and B2B marketers alike are creating breakthrough models and accelerating their testing. Because it can quickly produce content variants, AI helps companies scale high-impact strategies—in other words, invest in what works.
Because it can quickly produce content variants, AI helps companies scale high-impact strategies—in other words, invest in what works.
An insurance company’s experience illustrates AI’s dramatic impact on speed. The company used GenAI to analyze various data sources, propose testable hypotheses, and design structured experiments to reduce bias. Tests are now out into the market in half the time, and the company reduced its analysis time from more than eight hours to 30 minutes.
They shift budget allocations dynamically to maximize outcomes. Capitalizing on opportunity requires fast action and spending efficiency—the ability to redirect limited resources to where they will have the greatest effect. AI’s ability to automate budget shifts unlocks new potential for both efficiency and effectiveness. Some 35% of companies we surveyed are able to shift budgets across platforms and channels, dynamically adjusting their marketing allocations to take advantage of new opportunities.
One e-commerce company used a predictive AI model to forecast outcomes based on channel allocations (e.g., paid search, social media) and outreach timing. The company applied these forecasts to inform its decisions about coupons, promotions, and loyalty points and tracked results quarterly. It cut media budget-planning time by 66% and increased brand awareness by 11%.
Subscribe to our Marketing and Sales E-Alert.
They’re able to reach real-time audience segments with personalized messages. AI helps marketers define the most valuable audiences based on real-time signals and target them with the right messages. While more than half of the companies surveyed define their strategic audiences based on precise signals (such as proximity to purchase), only 20% have integrated real-time, AI-powered segmentation into their activation strategies.
Consider the B2B software company that wanted to develop new audiences without raising costs. It used its customer data platform to group high-value customers and prospects, creating a seed audience. This audience was fed into a predictive AI model, which generated new look-alike audiences—expanding the company’s outreach and cutting lead costs by 25%.
They use AI to develop creative throughout the whole creative lifecycle. Although 48% of companies surveyed frequently use GenAI for tasks like copywriting or developing taglines, only 9% have adopted AI for their end-to-end creative workflow. More than half lack content management systems, so they are unable to organize creative in a way that AI can access. Leaders, however, take advantage of AI’s ability to dramatically accelerate the creative process, improving both its speed and quality.
Leaders take advantage of AI’s ability to dramatically accelerate the creative process, improving both its speed and quality.
An online retailer, for example, used AI to analyze performance data on hundreds of creative assets, probing the effectiveness of such elements as color and calls to action. The insights they gained improved add-to-cart rates and conversions, and were then included in new briefs so the creative team could use them to develop and test campaigns and predict performance pre-launch. Development time fell by 75%.
They’re building an AI culture by enlisting advocates across core functional areas. Currently, only 26% of companies enlist four or more key functional areas in their AI initiatives. But AI marketing leaders understand that scaling AI successfully calls for building strong partnerships with virtually every core function. These partnerships are essential for promoting new workflows, securing funding, and implementing talent strategies. IT, for example, overhauls legacy systems, streamlines processes, and redesigns tech infrastructure to support future needs. Finance validates AI business cases, ensuring sustained resource allocation. HR secures the talent with the necessary AI marketing skills. Data engineering advises on buy-or-build tech decisions, while legal assesses data privacy, IP, and compliance risks—crucial tasks in a rapidly evolving environment.
To foster cross-functional partnerships, one global consumer packaged goods company adopted a “squad” model that spanned marketing, finance, demand planning, and trade, with support from legal, R&D, and sales. This approach reshaped demand and improved brand positioning, helping to unlock personalization across the consumer journey.
Charting the Path from Vision to Value
From our survey analysis and qualitative findings, we developed a data-derived view of the path to AI marketing success. For each of four maturity stages—essentials, scaling, leading, and transforming—we identify the most high-impact actions to take. (See Exhibit 2.)
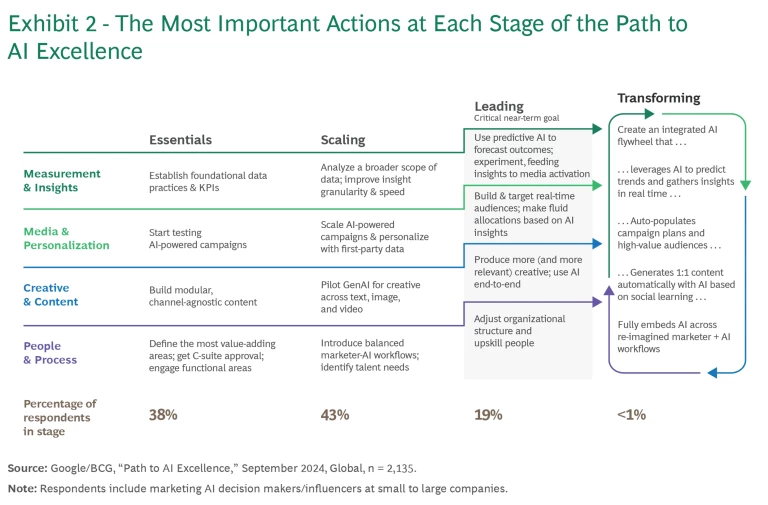
Stage 1: Essentials—Building the AI Foundation. At this stage, companies address gaps in foundational capabilities, implementing AI-ready data management tools and testing AI-powered campaigns with first-party data. They redesign creative processes to translate hero assets into modular, channel-agnostic content to be read by AI. They use built-in AI tools within ad platforms to make fast progress. Further, they establish a view from the top about where in the organization AI can add the most value and engage stakeholders across functions for early support.
Stage 2: Scaling—Implementing Top-Priority Use Cases. In the scaling stage, organizations focus on expanding AI-powered use cases across media and creative, ensuring content compliance and performance tracking. They expand the scope of the data fed to AI, improving the granularity and speed of insights for decision making. In addition, they introduce balanced marketer-AI workflows backed by responsible AI governance.
Stage 3: Leading—Developing Leading Capabilities to Integrate AI Workflows. This stage involves building real-time audiences and targeting them by shifting funds fluidly across channels as needed. Leaders increase the volume and relevance of creative by using AI throughout the creative lifecycle, from ideation to measurement. They use predictive AI to forecast outcomes and inform media activation efforts. Finally, marketing teams collaborate with stakeholders to implement a next-generation talent strategy that supports the new AI-driven processes.
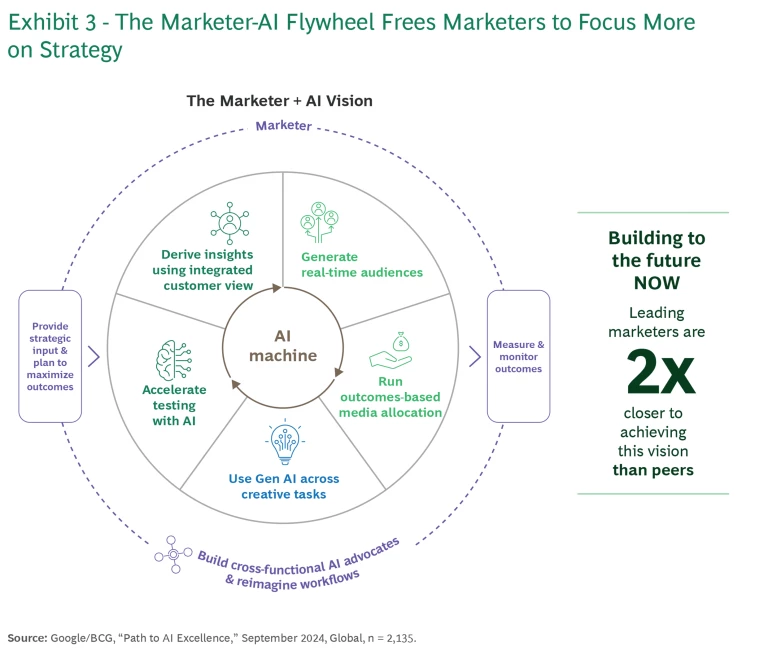
Stage 4: Transforming—Creating a Transformative Marketer + AI Flywheel. No company has truly reached this stage, as technical limitations still exist. But in the next five years, marketers and machines will increasingly play complementary roles to create a flywheel whereby AI and marketers together power campaign planning and execution. (See Exhibit 3.)
In the next five years, marketers and machines will increasingly play complementary roles to create a flywheel that powers campaign planning and execution.
Marketers will drive transformation by embedding AI into reimagined workflows, defining strategy, priority audiences, and business goals. AI will play a much greater role in analysis and execution and in supporting strategy development. It will predict trends, gather insights in real time, auto-populate campaign plans, select high-value audiences for 1:1 messaging, generate personalized content, and suggest real-time adjustments. Leading companies believe they are twice as close to achieving this future vision than their peers.
To get started, CMOs can follow a few simple steps:
- Conduct an AI excellence assessment to understand your starting point relative to peers.
- Identify key steps in your end-to-end workflow where AI could play a role (for example, in measurement and insights, media, or creative).
- Set two to three AI goals for the quarter (such as establishing your data foundations or piloting three use cases with key partners using off-the-shelf tools).
- Launch a cross-functional AI task force that includes marketing, engineering, IT, finance, HR, legal, and agency partners.
Reaching higher levels of AI integration requires more than just deploying the latest technologies and tools. Marketers must rethink their role, shifting their emphasis from the tactical and executional to the strategic. They must become orchestrators, guiding AI to deliver better outcomes while trusting the machine to handle the complexity of execution.
What’s on the Horizon?
Although the AI revolution in marketing is still in its early stages, the sophistication and quality of AI output is improving literally by the week. As technology advances, the gap between leaders and laggards will only widen; and at the speed of change we’re witnessing, that gap may—sooner rather than later—become unbridgeable.
Over the next 12 months, leaders are planning to expand AI use cases: 46% will use GenAI for video creative, 36% will launch AI chatbots (internal, customer-facing, or both), and 35% will customize creative by platform. As the number of advanced use cases grows, the system becomes more sophisticated and faster.
By harnessing the power of AI effectively, CMOs can not only improve the efficiency of their operations; they can also unlock new avenues for growth. The path to AI excellence—and to realizing the power of the marketer-AI flywheel—is clear. Marketers who take bold steps today will be shaping the future of their organizations.
Reach out to the team for information on how to take an AI self-assessment.
This content is the result of a joint research effort between Google and BCG.