Generative AI lets companies capture previously untapped benefits of AI in supply chains. By simplifying user interfaces, automating operations and decision making, and generating actionable insights from large data sets, GenAI overcomes the complexities of earlier AI implementations and promotes higher adoption. As supply chain technology grows more complex and the shortage of skilled professionals intensifies, companies must adopt GenAI to compete successfully.
GenAI can embed advanced supply chain intelligence and complex tools into accessible workflows. Forecasting, supply planning, and other types of advanced analytics that traditionally require specialized algorithms and expert knowledge can be put at users’ fingertips, democratizing usage. GenAI can transform human-machine collaboration and enable faster and more accurate decision making. It can connect disparate systems and, in the more mature cases, enable autonomous orchestration—coordinating activities and processes without manual intervention. We see these benefits emerging as GenAI deployments advance through a stepwise evolution.
To fundamentally transform supply chains using GenAI, organizations must move beyond the limitations of past AI adoption approaches that focused on individual use cases. Effective implementation involves aligning GenAI deployment with business objectives and identifying workflows where the technology can add the most value. Prioritizing the right areas, rethinking end-to-end workflows, and building a partner ecosystem will ensure that GenAI promotes sustainable improvements to ways of working, automation, and analytics.
The Unfulfilled Potential of AI in Supply Chains
Companies have been slow to realize the vision of AI-driven supply chains. This is primarily due to an overemphasis on AI’s analytical powers without adequate focus on applications that include sufficient adaptive learning—the capability to improve with use and over time. AI solutions, laden with complexity, often overwhelm supply chain personnel, leading to low adoption and diminished returns on investment (ROI).
The challenges in unlocking the value of AI in supply chains arise from several factors:
- Processes. Many companies attempt to force-fit AI applications into outdated processes originally designed around legacy systems. In the absence of user-friendly workflows, supply chain professionals struggle with the complexity of layered systems and excessive information. Moreover, the interaction between machines and humans in decision making remains inadequate, largely because AI-generated proposals often fail to align with decision makers’ goals. This challenge is further compounded by variations within organizations (different functions may have conflicting incentives) and across organizations (unique operating models and governance structures often make off-the-shelf solutions less effective).
- Technology and Data. Companies often struggle with disconnected data foundations, poor data quality, and multiple systems of record, such as enterprise resource planning systems. Without continuous data-cleaning processes and effective data-governance mechanisms, AI implementations are hindered by incomplete or outdated information.
- People. Many employees often do not fully grasp how to use AI applications—complex tools that are often not user-friendly—and how AI applications reach their conclusions. Moreover, employees find that using the applications means reconciling data across multiple systems, which requires spending valuable time on low-value tasks. And many companies underestimate the support and training that’s required to help employees transition to AI-assisted workflows. Without an understanding of these tools, employees often resist adopting them or relying on them for critical business decisions.
The impact of these challenges is magnified by a looming talent shortage in supply chain management . Without the wide adoption of digital solutions— including those that are GenAI-based—companies will struggle to run this fundamental business process. Addressing the challenges of AI adoption is essential to develop a way forward for supply chain management.
Subscribe to our Operations E-Alert.
GenAI Resets the Evolution
We evaluated both the emerging possibilities and the ongoing challenges of deploying GenAI to manage complex global supply chains. Our analyses and surveys of supply chain practitioners provide a detailed perspective on what is currently feasible with GenAI—beyond mere chatbots and isolated use cases—and its future potential.
GenAI’s suite of capabilities makes it an ideal solution for optimizing and streamlining supply chain operations , reviving hopes for an AI-powered transformation.
GenAI has four primary benefits for supply chains:
- Enhancing the Data Backbone. GenAI can strengthen data foundations, enabling broader and more accurate data usage across various applications. For example, GenAI can continuously clean and augment master data sets, such as bills of materials, and enhance the search and utilization of supplier knowledge bases.
- Augmenting Supply Chain Analytics. By extracting meaningful attributes from unstructured data—for example, customer behavior and product characteristics—GenAI can enhance capabilities such as product demand forecasting. By designing, running, and analyzing a wide variety of scenarios, GenAI can predict disruptions more accurately. Companies gain the ability to make better decisions proactively, leading to a more responsive supply chain.
- Overhauling the User Experience. GenAI can simplify the use of sophisticated tools. For example, it can enable natural language interfaces for advanced planning systems. Moreover, many users are becoming familiar with GenAI through tools such as ChatGPT. This accessibility and familiarity are making supply chain professionals more open to adopting and using GenAI in everyday operations, such as to create scenarios with various configurations and to interpret AI model outputs.
- Deeply Automating Processes. By coordinating multiple tools and capabilities and driving workflows toward desired outcomes, GenAI can automate processes that previously required significant manual intervention. When processes are automated, companies can identify problems at an early stage and mitigate them much faster.
We found that these four benefits can deliver substantial improvements. For instance, GenAI can accelerate the development of complex applications, interfaces, and supply chain solutions by 30%, significantly enhancing overall agility. User adoption can see a marked increase, with satisfaction and system usage rising by more than 60%. Additionally, administrative and data reconciliation tasks can be reduced by more than 50%, freeing up personnel to focus on more value-added activities. Finally, greater use of advanced analytics can boost decision-making speed by more than 30%, enabling faster and more informed choices.
Our study also included testing ChatGPT’s capabilities to analyze a company’s large data set. (See “Testing ChatGPT’s Analytical Capabilities.”)
Testing ChatGPT’s Analytical Capabilities
Our first objective was to generate a segmented view of products’ characteristics, identifying those that had stable sales, seasonal patterns, or trends. With just a few targeted prompts, ChatGPT quickly delivered the desired segmentation. From there, we explored its potential in both demand and supply planning.
Demand Planning. We tasked ChatGPT with performing basic time-series forecasting. It efficiently selected appropriate forecasting methods on the basis of the sales patterns it found and wrote lines of code to generate the forecasts. For instance, when ChatGPT detected a seasonal pattern, it recommended using triple exponential smoothing, an ideal forecasting method for such scenarios. However, the data set lacked the necessary 24-month history to configure the model’s parameters. Impressively, ChatGPT flagged this limitation and requested additional data to proceed.
The insight here is significant: Basic time-series forecasting capabilities, traditionally found only in proprietary software, are now accessible through publicly available tools. However, more advanced AI-driven forecasting techniques will still require specialized modules, which can be orchestrated by GenAI.
Supply Planning. When we shifted to supply planning, the outcome was different. We aimed to optimize the production sequence of certain products on a single asset, considering various factors, including production outputs and changeover times. The goal was to meet customer demand while minimizing inventory buildup.
In this case, ChatGPT acknowledged that the task was beyond its current capabilities, explaining that a more complex linear programming solution was needed. It even suggested helpful resources to address the challenge.
The takeaway: While GenAI can handle simpler analytical tasks, more complex combinatorial optimizations currently require specialized tools. In these cases, GenAI can serve as an orchestrator, guiding the process rather than directly executing the solution.
Four Levels of GenAI Adoption in Supply Chains
Building on our insights into GenAI’s current and future potential, we have identified four levels of GenAI capabilities for supply chain operations. These levels represent a progression toward increasingly automated, intelligent processes, with each level building on the previous one to create a more seamless and optimized supply chain. (See the exhibit.)
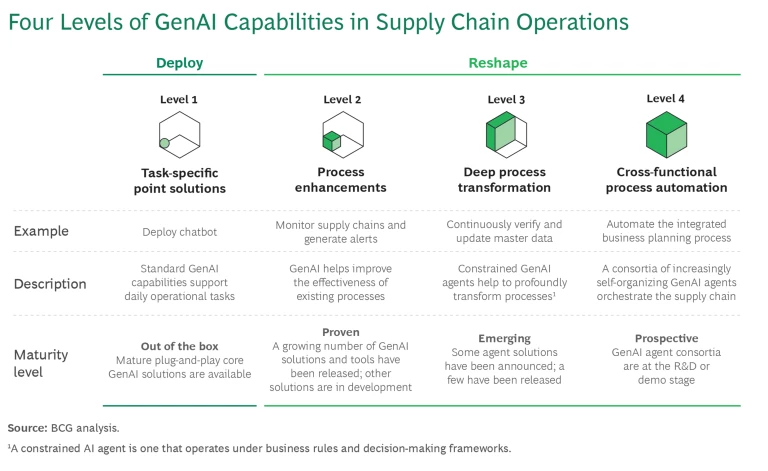
Task-Specific Point Solutions. Initially, GenAI can be deployed through chatbots to support routine, daily operational tasks. These point solutions offer basic automation and efficiency improvements by leveraging standard GenAI capabilities. Such solutions have matured to become plug-and-play tools that companies can easily adopt.
Process Enhancements. At the second level, GenAI acts in combination with current planning and execution systems to improve the effectiveness of existing processes, such as monitoring supply chains for disruptions, generating alerts, and simulating responses. The first GenAI products to provide such enhancements have been released, and more are in development.
Deep Process Transformation. At this stage, GenAI agents continuously verify and update the master data set and drive a rethinking of entire workflows, profoundly transforming core processes. GenAI plays a pivotal role in automating and enhancing the quality of decision making, with humans remaining in the loop. (See “Supercharging Supply Chain Simulation with GenAI.”)
Supercharging Supply Chain Simulation with GenAI
To achieve these objectives, the company partnered with BCG to implement an advanced solution leveraging two BCG X assets: AgentKit, a GenAI agent toolkit (developed in partnership with LangChain and now an open-source solution) and End-to-End Plan by BCG X, an AI-powered planning capability. BCG integrated these tools through a natural language interface, making them accessible to users without technical barriers. BCG also used autonomous GenAI agents to connect the tools and run the technical workflows in the background.
This seamless setup streamlines the company’s sales and operations planning processes, giving planners more autonomy and agility in managing daily operations. Planning professionals can create and run simulation scenarios, analyze the root causes of issues that emerge, summarize KPIs, conduct sensitivity analyses, and share critical insights—all without the need for extensive technical knowledge.
The introduction of this GenAI-driven solution delivered significant business impact. The underlying AI capabilities contributed to a more than 2-percentage-point increase in EBITDA by the second year. Additionally, the GenAI agent facilitated the upskilling of more than 20 planning professionals, enabling them to fully use the tool’s capabilities and achieve a threefold reduction in process cycle times.
Some GenAI agents are already available and are expected to be key drivers of GenAI-enabled value over the next five years. However, to fully unlock their potential, significant process re-engineering will likely be required. In many cases, this re-engineering will necessitate custom-built solutions or at least tailored add-ons to ensure that GenAI is seamlessly integrated.
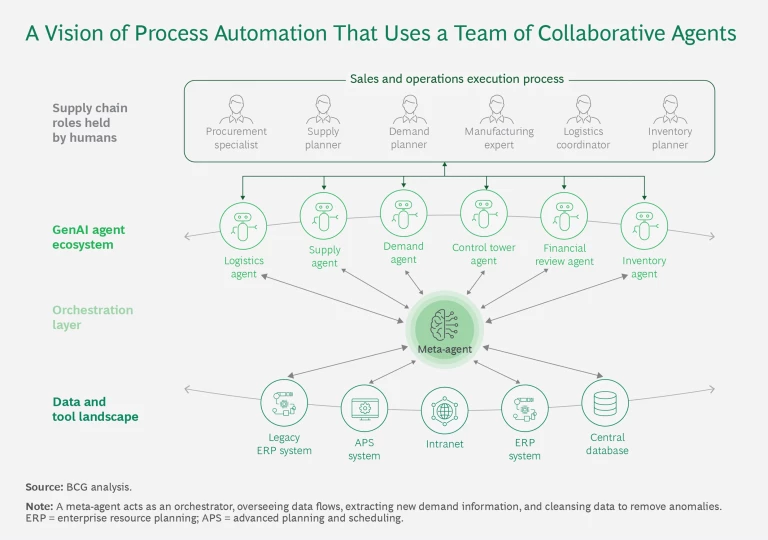
Cross-Functional Process Automation. The most advanced level involves the automation of cross-functional processes, such as the sales and operations execution process. A consortia of self-organizing GenAI agents orchestrate supply chain operations across different functions, creating an automated, intelligent, and collaborative system. (See “A Vision of Deep Automation.”) This visionary use of GenAI is in the research and development stage.
A Vision of Deep Automation
Currently, dedicated teams follow the S&OE process several times a week, aligning demand and supply to meet customer orders and maintain KPIs over a 1-to-12-week planning horizon. Although effective, this process is labor-intensive, limited by data availability, and heavily reliant on manual oversight to ensure smooth execution.
We expect the S&OE process of the future, in contrast, to be powered by an always-on network of autonomously collaborating and learning agents that dynamically balance the supply chain in real time, ensuring optimal performance continually. (See the exhibit.) These agents will be specialized software programs powered by foundational large language models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT, that continuously interact with data inputs and adapt to changing conditions. To minimize potential LLM-generated errors, or hallucinations, the agents will be constrained to operate under business rules and decision-making frameworks. By processing vast data sets, the agents will coordinate tasks without human intervention.
In this envisioned system, the demand agent will continuously monitor demand forecast changes, learning and adjusting actions accordingly. It will leverage specialized machine learning algorithms to generate the forecasts. The meta-agent, acting as the orchestrator, will oversee data flows, extract new demand information, and cleanse data to remove anomalies.
When demand changes occur, the demand agent will collaborate with the inventory agent to assess the impact. The meta-agent will equip the inventory agent with precise, real-time data from various enterprise resource planning systems, allowing it to evaluate supply and inventory adjustments. If KPIs for service, inventory, or cost are at risk, the inventory agent will trigger corrective actions, such as stock transfers or production reorders, to restore balance.
The supply agent will then assess the feasibility of these changes, coordinating with suppliers or adjusting production schedules. If the proposed adjustments incur high costs, such as changeovers, the supply agent will explore alternative scenarios. For example, with support from the meta-agent, the supply agent may collaborate with external optimization tools such as mixed-integer linear programming solvers to determine the best production sequencing.
Through this ongoing collaboration, the agents will continuously learn and refine their ability to rebalance the supply chain autonomously. During the initial stages, human oversight will be necessary, with agents presenting decisions for approval. However, as the system matures, automation will increase—especially in handling transactional tasks—and the agents will eventually make decisions independently within a widely automated network.
Ultimately, the decisions from this autonomous system will feed directly into execution systems, seamlessly orchestrated by the meta-agent. This will help the entire supply chain remain consistently optimized and fully aligned with the company’s strategic goals.
Making It Happen
GenAI enables a comprehensive transformation that improves core aspects of supply chain management, including ways of working and user engagement, process automation, and analytical development.
Successfully implementing GenAI in supply chains requires a structured approach that aligns technical capabilities with business objectives. Here are five essential steps.
Set the ambition. Align the company’s ambition for GenAI adoption with its broader strategic goals. GenAI should not be adopted simply for its novelty. Instead, focus on how it can enhance business outcomes, whether improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, or addressing specific market challenges. Take stock of potential talent shortages and the future of how work will get done, and assess how GenAI can fill gaps by performing tasks or alleviating burdens in operational areas where skilled supply chain professionals are scarce. Defining a clear ambition helps ensure that all efforts are focused on achieving measurable business impact.
Map key decisions across the supply chain. Identify where GenAI can make the biggest impact toward achieving the ambition. This involves mapping out where the most important decisions are made throughout the supply chain and analyzing how GenAI can improve the quality and speed of those decisions. Rather than trying to integrate GenAI into every aspect of the company’s operations, focus on high-value decisions that are critical to success. Such decisions often relate to integrated business planning, inventory management, or production scheduling. Zeroing in on the most valuable areas lets companies target the highest-return investments.
Prioritize where to start. Give priority to the areas in which GenAI can have the greatest initial impact, considering the business value and ease of implementation. Initiatives could involve, for example, automating a particular process or integrating GenAI into a decision-making system. By choosing areas with immediate benefits, companies can build momentum and fund the journey.
Rethink the end-to-end workflow relating to key decisions. Integrate GenAI to streamline processes and improve decision-making quality, pivoting from human-operated to human-designed workflows. For example, automating repetitive tasks, such as inventory replenishment or demand planning, can free up workers to focus on more complex, strategic decisions. Ensuring that GenAI is fully embedded into the workflow—rather than bolted on—can lead to higher adoption and better outcomes.
Start building with the right ecosystem. Successful GenAI implementations rely on a strong ecosystem of partners, including technology developers, user-interface designers, and AI and supply chain experts. Leverage those external partnerships to fill in-house capability and resource gaps, gain access to the latest technologies, and accelerate deployment. By building this ecosystem early, organizations can have the support they need to scale GenAI solutions effectively.
GenAI promotes higher adoption of AI tools through user-friendly interfaces and agent-based automation. It also excels at cross-functional orchestration, connecting different systems and teams to enable faster, more coordinated actions. The results—evident in increased productivity and agility—demonstrate that embracing GenAI bolsters competitive advantage and is an essential strategy for future-proofing supply chains.