Following a period of unprecedented profits fueled by supply shortages and high demand, US auto dealerships have, over the past two years, faced a starkly different reality. High interest rates, affordability challenges for consumers, a rebound in vehicle supply, and shifting consumer preferences are squeezing margins and forcing dealers to rethink their strategies. As new-vehicle prices decline and used inventory becomes harder to source, many dealerships are focusing on operational efficiencies and new revenue streams to stay competitive.
To understand how structural changes in US automotive retailing are unfolding, BCG surveyed more than 160 auto dealers, from small, independent outlets to large franchises. This latest edition of our annual survey, conducted in late 2024 and early 2025, examined dealers’ outlook on the US auto market and how factors such as competition, affordability, shifting demand, and AI adoption are shaping their businesses. The research, combined with insights from our work on more than 500 automotive projects over the past three years, offers a unique perspective on how the industry is evolving.
Our findings highlight key trends in new- and used-vehicle sales and service and parts, as well as some emerging opportunities. The bottom line: dealers are increasingly open to using data, digital solutions, and AI-driven tools to maximize core business profitability while diversifying their service offerings to secure long-term revenue growth. In contrast to past years, when dealers may have had the flexibility to delay such changes, today’s market pressures mean that adapting quickly is no longer optional.
The Evolving Auto Retail Landscape
Since 2023, the auto retail market has been correcting, prompting dealers to shift their focus from long-term concerns identified in previous BCG dealer surveys—such as the transition to electric vehicles and competition from OEMs—to a broader set of immediate challenges, including optimizing profitability across core revenue streams.
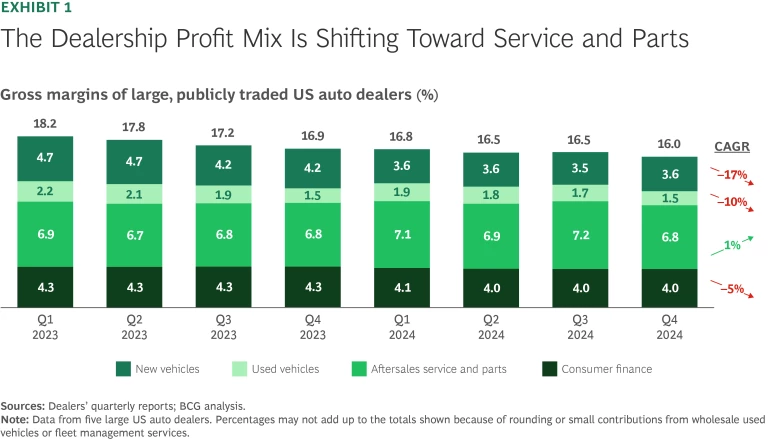
Dealers’ margins are under pressure as the inflow of new vehicles increases while affordability challenges dampen demand. Rising inventories and high floor-planning costs are squeezing profits, with pricing pressures driving transaction prices lower. Meanwhile, service and parts revenues are becoming an increasingly important profit driver as consumers keep vehicles longer. (See Exhibit 1.) However, even with slower than expected adoption, EVs present risks to aftersales—offering fewer routine maintenance opportunities while requiring greater specialization. At the same time, digital retail capabilities are becoming critical, as more of the customer journey, particularly financing, moves online.
Against this backdrop, dealership M&A activity has slowed as market uncertainty complicates deal making. Many dealers seek acquisitions to improve the efficiency of their investments in new capabilities through increased scale. Even so, transaction volume and size have declined as buyers and sellers struggle to align on valuations and market outlooks. Volume fell from approximately 700 deals in 2021 to approximately 500 in 2024. Our survey findings indicate that more dealers are looking to buy than sell, likely intensifying competition for attractive opportunities.
As these dynamics unfold, dealerships are prioritizing margin optimization across all revenue streams to maintain resilience.
New Vehicles: Declining Demand Slows Sales Growth
New-vehicle sales growth has slowed sharply, from approximately 12% in 2023 to approximately 2% in 2024, according to S&P Global Mobility. Although increased supply plays a role, affordability remains a major constraint, as higher interest rates and rising monthly payments are pricing out lower-credit buyers. Among the dealers BCG surveyed, 50% reported that interest rates in 2024 greatly affected local demand.
Reinforcing affordability concerns, dealers noted that the average credit scores of car buyers have risen. This is confirmed by Experian research, which found that the average credit score rose by 11 points for new-vehicle buyers and 18 points for used-vehicle buyers from 2022 to 2024, far outpacing the overall US average credit score increase. The financial strain is also evident in delinquency rates for auto loans, which climbed 63% from March 2021 to June 2024, according to Federal Reserve data. To manage affordability, some buyers are opting for cash purchases or leasing.
In response, OEMs have been more deliberate in managing US volumes. They also more than doubled incentives in 2023 and 2024 compared with 2022; according to Kelley Blue Book data, incentives reached approximately 8% of the average transaction price (ATP) in the fourth quarter of 2024. However, these measures have not been sufficient to offset weakening demand. Days to sell rose from 30 in early 2023 to nearly 60 in 2024, according to both Wards Intelligence data and BCG’s dealer surveys, further straining dealership profitability.
At the same time, 38% of dealers report that higher interest rates have severely or significantly impacted floor-planning costs. As inventory financing becomes more expensive, dealers face mounting pressure in an already challenging market, making it even more critical to reduce days to sell.
Dealers’ desire to clear rising inventories has put pressure on new-vehicle prices, with ATP declining by approximately 4% from the third quarter of 2022 to the third quarter of 2024, according to National Automobile Dealers Association (NADA) data. Notably, about half of this decline was driven by increased discounts, while the other half reflects a changing product mix, such as selling more lower-cost vehicles and reducing premium features—both responses to customer affordability headwinds.
Dealers’ ability to sell above the manufacturer’s suggested retail price (MSRP) dropped by approximately 50% in 2024 compared with 2023, according to dealer survey responses. This marks a sharp reversal from the exceptional pricing power that dealers recently enjoyed. As a result, dealer margins, which reached record highs two to three years ago, are now under significant strain as retailers navigate the challenge of balancing volume and profitability in an increasingly difficult market.
The economic pressure, coupled with lower than expected demand for EVs, has resulted in disappointing growth rates for EV sales. (See “EV Adoption Is Slow as Models Fail to Meet Customer Needs.”) To clear inventory, OEMs have had to boost incentives to 14% of ATP—twice as high as for traditional vehicles.
EV Adoption Is Slow as Models Fail to Meet Customer Needs
The transition to EVs is progressing more slowly than expected, primarily because of a lack of models that meet consumer expectations for price, range, and size. According to a BCG customer survey, 38% of consumers are "next-wave adopters." These individuals share attributes with current EV owners but remain hesitant owing to the market’s inability to meet their criteria, such as models priced under $50,000 with a range exceeding 350 miles.
With prices remaining high, EV buyers at nearly two-thirds of surveyed dealerships generally have higher average incomes than non-EV buyers. To accelerate adoption among lower-income buyers, dealers believe that reduced purchase prices—through fewer premium features or increased discounts—are critical. (See the exhibit below.)
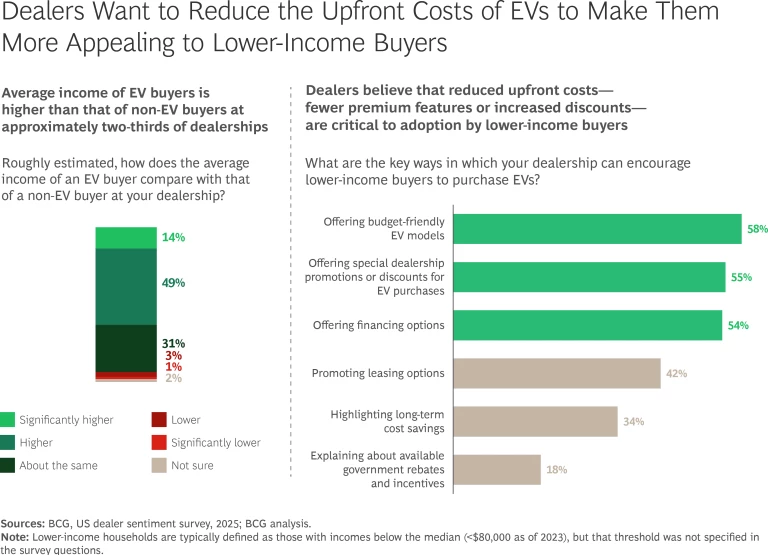
Looking ahead, approximately 25% of dealers view new EV entrants (such as Tesla, Lucid, and Rivian) as significant threats. To compete, they need to collaborate with their OEMs to secure well-equipped, attractively priced EVs—likely requiring adjustments to the traditional sales model.
Despite these pressures, more than 70% of surveyed dealers expect vehicle sales growth to continue in 2025, signaling cautious optimism amid ongoing market adjustments. However, dealer profitability will likely remain under pressure.
To sustain profitability, dealers must take proactive measures. Targeted marketing investments are essential to stimulate demand in priority segments and attract buyers despite affordability constraints. At the same time, leveraging analytics-driven ordering will help align inventory with actual demand, reducing excess stock and mitigating the impact of rising floor-planning costs.
Used Vehicles: Sourcing Challenges and Price Erosion Squeeze Margins
Dealers are facing increasing challenges in sourcing used vehicles while demand has surged. Following a decline in 2023, used-car retail sales rose 10% year-over-year in the fourth quarter of 2024, according to vAuto data. However, 34% of surveyed dealers said the supply of used vehicles was a large or severe challenge at their dealerships, with an additional 42% reporting that it was a moderate challenge.
To fill inventory gaps, dealers are relying more on auctions, which raise acquisition costs. At the same time, the ATP for used vehicles fell by 6% during 2023 and 2024, according to NADA data. The combination of higher acquisition costs and declining retail prices is squeezing dealer profitability. Most surveyed dealers anticipate that 2025 will see an increase in trade-in values and cash offers for used vehicles, increasing sourcing competition.
To remain competitive in the used-vehicle market, dealers must secure high-quality trade-ins to mitigate rising acquisition costs. AI-driven tools are unlocking significant value, helping dealerships optimize local demand and supply, refine pricing strategies (for both vehicle acquisitions and sales), and make smarter purchasing decisions. By leveraging data-driven insights, dealers can better navigate supply constraints and protect margins in a more and more competitive landscape.
Subscribe to our Automotive Industry E-Alert.
Service and Parts: An Increasingly Vital Role in Growth and Profitability
US consumers are keeping their vehicles longer, and this trend is likely to persist. The average age has increased from 12.5 to 12.6 years across all vehicles and from 13.6 to 14 years for passenger cars. As a result, even as new- and used-vehicle sales face headwinds, service remains a critical and growing area for dealerships. Among surveyed dealers, 70% reported growth in service revenues in 2024.
Dealers have a strong competitive position in service and parts, driven by their direct ownership of the customer relationship, rising warranty-related service needs (benefiting franchise dealers), and increasing vehicle complexity. Indeed, service, repairs, and parts sales are the only contributions to dealers’ gross profits that are consistently growing.
However, this revenue stream faces challenges as EV adoption disrupts traditional service models. For example, battery EVs generate about 20% less aftermarket parts spending than comparable fossil fuel cars. Long-term success will require the effective scaling of operations, as revenue per vehicle shifts toward either simple, high-frequency services like tire replacement or complex, infrequent procedures such as calibration and EV battery replacement.
To navigate these shifts, dealers must leverage their existing knowledge of customers. While third-party service providers must build networks and earn customer trust from scratch, dealerships are already positioned to deepen customer loyalty. Capitalizing on this edge requires modernizing their service operations and adapting to evolving vehicle technologies. Establishing EV service capabilities and scaling networks across dealerships—similar to the approach used by collision centers—will be essential. At the same time, enhancing connectivity and personalization through digital scheduling, AI-powered chats, and text message reminders will improve retention and the customer experience while potentially reducing operating expenses. End-to-end automation across service operations will further streamline processes, reduce costs, and drive efficiency.
New Opportunities: Diversifying Revenues and Embracing AI and Digital Retail to Strengthen Core Businesses
To adapt to shifting profit pools and evolving customer preferences, dealers are actively exploring new opportunities outside their core businesses. Emerging revenue streams—such as EV charging and fleet and mobile servicing—are gaining traction as dealerships seek to diversify their offerings. (See Exhibit 2.)
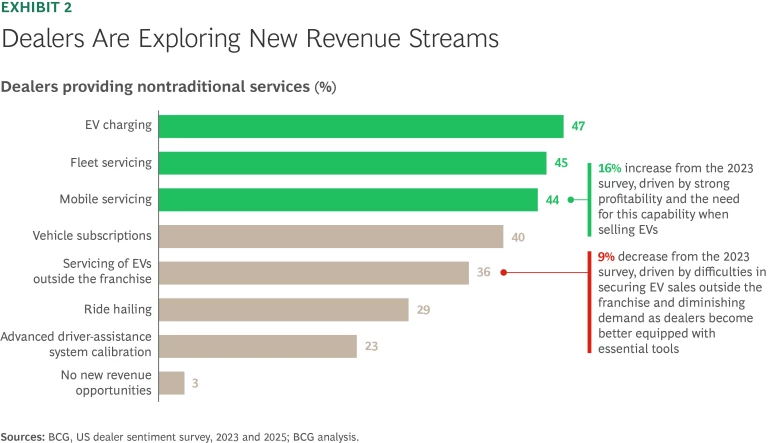
However, no clear industry-wide priority has emerged, reflecting an ongoing experimentation phase as dealers evaluate which avenues best align with their operations and customer needs. The push for innovation is driven by the imperative to capture additional value in a changing market while addressing growing demands for flexibility and sustainability.
At the same time, dealers are embracing AI and digital retail to drive top-line growth and boost the bottom line for their core businesses. Increasingly, they are exploring AI adoption to enhance efficiency and profitability, with more than 80% of surveyed dealers definitely planning to invest in AI in the next two years. (See Exhibit 3.) Although nearly 50% are prepared to invest significantly, another 35% said they prefer a more cautious, moderate investment approach.
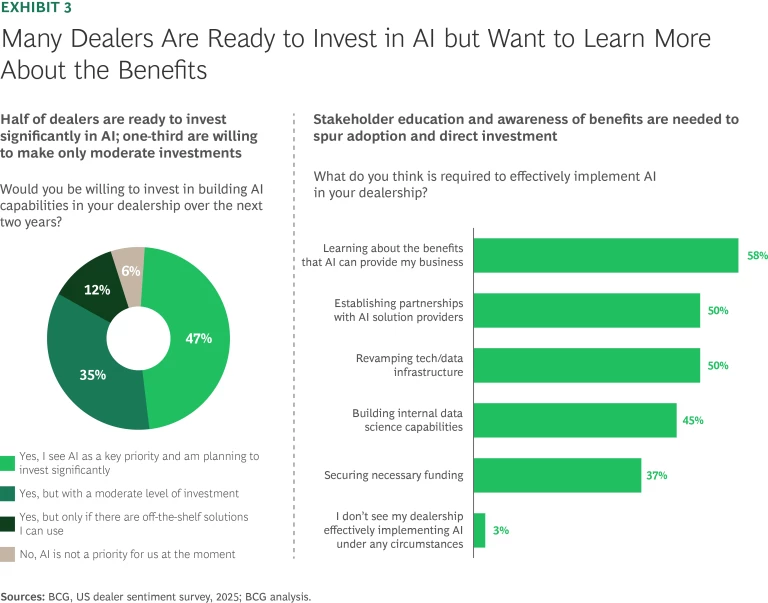
Dealers’ concerns about data security (heightened by industry-related cyber incidents in 2024), along with expertise gaps, uncertain return on investment, and high maintenance costs, could impede adoption of AI. In addition, many dealers remain unsure about which AI use cases will deliver the most value.
Stakeholder education and awareness about the benefits of AI are crucial to unlocking its potential. Many dealers believe that clear insights into AI’s practical applications—such as inventory management, customer personalization, and operational efficiency—are needed to accelerate adoption and drive direct investment.
Dealers will need support to overcome the barriers and scale AI solutions effectively. While many recognize AI’s potential to assist in navigating market headwinds, success will require an action-based test-and-learn approach. In recent projects, BCG collaborated with dealers to develop AI tools that, for example, helped to configure vehicles that sell up to 30% faster and to optimize the pricing of used and new vehicles, improving margins by more than 5%.
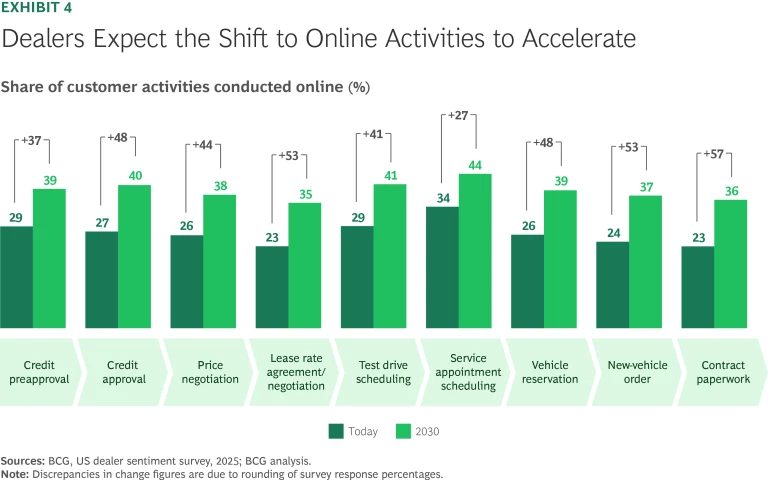
The shift to digital retail continues to reshape the industry, with dealers expecting significant growth in online activities through 2030 across the customer journey. (See Exhibit 4.) Our survey also found that approximately 80% of dealer leads are now generated online, underscoring the need for integration between digital and physical touchpoints. While activities like scheduling test drives and credit pre-approvals are increasingly completed online, finalizing contracts and customizing vehicle specifications are still conducted mainly at the dealership.
A BCG study of customer reviews found that “ease and convenience” is a higher priority for many buyers than financing, sales support, or service. This underscores the need for dealers to deliver a seamless experience across channels to meet customer expectations.
Recognizing the profitability of digital, tech giants are entering the space. For example, Amazon’s e-dealership enables one-click car purchases. Dealers gain a new digital sales channel, while Amazon captures marketing revenue and the ability to steer high-margin financing revenue without the need for floorplan financing, delivery logistics, and service obligations. As more tech companies develop digital platforms for vehicle sales and financing, dealerships risk losing finance revenues unless they enhance their own digital retail capabilities.
To stay competitive, dealers must simplify and digitize the end-to-end purchase experience for both new- and used-vehicle purchases. This means integrating digital credit approvals, streamlining loan processes, and ensuring frictionless transactions across channels. By embracing automation, AI-driven financing models, and user-friendly digital platforms, dealerships can protect and expand their revenue streams in an increasingly digital-first market.
Navigating the Road Ahead
Dealers face growing challenges that are expected to persist in the coming years. To respond effectively, they must adopt bold strategies and be prepared to adjust their traditional operating models and the types and sources of their talent.
Leveraging AI and data-driven tools will be essential for optimizing inventory management, reducing days to sell, enhancing dynamic pricing strategies, and improving customer targeting and conversion. It will also drive operational efficiency across the dealership value stream.
Revamping digital platforms and customer journeys is critical to delivering a seamless experience across digital and physical channels, thereby strengthening customer loyalty through convenience. Additionally, dealerships must build capabilities to support AI adoption, prepare for EV integration, and adapt to emerging technologies. At the same time, they must strategically grow their footprint and expand their service offerings, both organically and through M&A. These actions are essential to navigating current challenges and driving sustainable growth.
The US auto dealership landscape is evolving rapidly, shaped by economic pressures, shifting consumer expectations, and technological disruption. To keep pace, dealers must embrace digital tools and AI, strengthen digital retail capabilities, and expand service offerings. Amid the persistent challenges, dealerships that adapt with data-driven strategies and operational agility will be well positioned for long-term success. In a transforming industry, the ability to innovate and respond to market dynamics will separate the leaders from the laggards.








