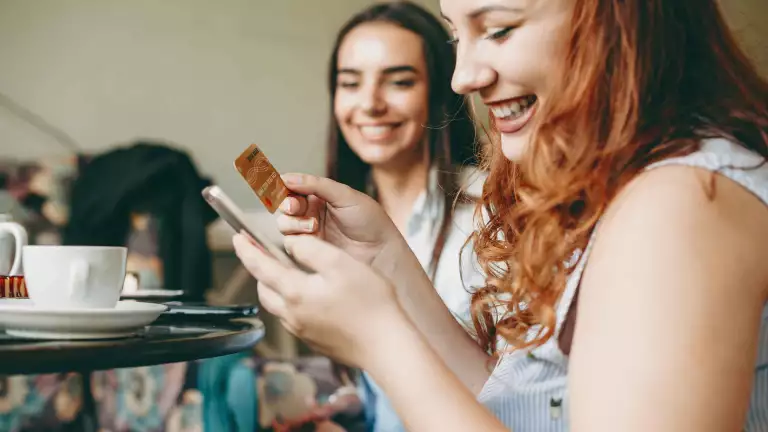
Generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) a set of algorithms capable of generating seemingly new, realistic content such as text, images, or audio from so-called training data in a way that resembles human output represents one the most significant technological advances in recent history. More than just another trendy tech wave, GenAI has the potential to be truly transformational. Already we see evidence of its power in the speed of its adoption, the outsized market expectations surrounding it, and productivity gains it has already achieved in small-scale case examples. Despite its relative youth, GenAI is proving to be a game changer. (See Exhibit 1.)

GenAI is poised to affect many aspects of daily life, including how we purchase goods and, therefore, how we pay, making the payments industry particularly fertile ground for GenAI-based transformation. The technology provides clear opportunities on the consumer-facing side of the business (how people pay online) and even greater opportunities on the operations side (how payments companies construct and execute their business and operating models). But how can different players in the payments ecosystem best harness the capabilities of GenAI to benefit their organizations and their customers?
To explore this and related questions, BCG examined how GenAI is likely impact each link in the payments value chain. Our team followed a structured process that included the following five initiatives:
- Create a list of potential use cases for each link.
- Challenge GenAI applicability to pre-identified use cases.
- Estimate the gross productivity increase by identifying the foreseeable GenAI impact on individual processes.
- Estimate the net productivity savings by applying a discount to use cases where the realizable potential may be lower than expected, owing to low tech maturity or a low share of employee time spent on the task.
- Evaluate ease of implementation, considering such elements as tech requirements, data accessibility, and data-privacy challenges.
Our findings revealed multiple scenarios, with commercial success depending on factors such as the organization’s full understanding of how GenAI actually works, its starting-point tech capabilities, its training quality and efficiency, its dedication to
responsible AI
, and the presence or absence of full C-suite buy-in for transformation. Payments players that do not recognize the potential indeed, the inevitability of GenAI and prepare for its impact may eventually find themselves facing a double-barreled problem: unhappy customers who expect a higher level of service, and advantaged rivals who embraced the technology early and have positioned themselves optimally.
Will GenAI Prompt a Consumer Payments Evolution or Revolution?
On the consumer payments side, over the past 25 years, digital commerce has completely transformed the way people shop, thanks to its convenience and its ubiquity. We expect GenAI to support the next wave of transformation.
More specifically, GenAI is widely anticipated to allow further modernization of the online checkout experience, unlocking a new era of personalized conversational commerce. Here’s how a simplified GenAI-enhanced shopping journey might look:
- A consumer asks a chatbot—either a ChatGPT equivalent or a merchant chatbot—to share product recommendations based on previously observed or expressed preferences.
- The chatbot analyzes and interprets documented product characteristics on the merchant’s website in order to answer detailed questions from the consumer regarding product specifications, and it provides instant customer support to minimize any potential pain points during the shopping journey.
- When the consumer is ready to buy, a payment plug-in linked to the chatbot enables an embedded checkout experience, without requiring the consumer to leave the chat interface.
In addition, behind the scenes, payments companies will play a meaningful role in supporting and further enhancing the shopping experience. Such support may involve a number of actions:
- Providing payment plug-ins to merchants and GenAI providers by furnishing application programming interface (API) access and support for developers
- Giving merchants the power to tailor payment options based on consumer preferences or historical choices
- Enabling dynamic pricing and tailored rewards, such as adaptive pricing to optimize sales conversions on the basis of customer lifetime value
- Permitting recommendations that go beyond payments into areas such as financing
From a product perspective, we foresee a primary need for payments players to enable API access for various intermediaries—such as through conversational commerce and interactions with chatbots through portals—and to support multiple B2C applications in the adjacent, wider financial services space.
Even with GenAI, however, some things will not change. High regulatory and security protocols will remain, and merchants will still have know-your-customer obligations. Overall, we see GenAI on the consumer payments side as being part of a tech evolution rather than a revolution.
There Is Significant Potential for GenAI in Payments Operations
Most of GenAI’s potential in the payments space, in our view, rests on the operations side. This is because the payments industry has many aspects for which the new technology is particularly applicable including high-volume, high-frequency, data-rich operations that involve human-intensive workloads all underpinned by IT setups that combine legacy and next-generation platforms.
Moreover, although the public and the media tend to focus on product advancement—in the form of new features, reengineered experiences, or enhanced security measures we believe productivity gains will play the most pivotal role in shaping the future of the payments industry. Ultimately, the efficiency and seamlessness of payments operations will determine the long-term success of GenAI and its adoption by payments companies.
For our study, we organized our assessments of potential GenAI use cases on the basis of where they occur in the payments value chain: marketing and sales, product development and technology, onboarding and customer support, risk and compliance , and support functions. We also assessed transverse activities, which are relevant along the entire value chain. (See Exhibit 2.)
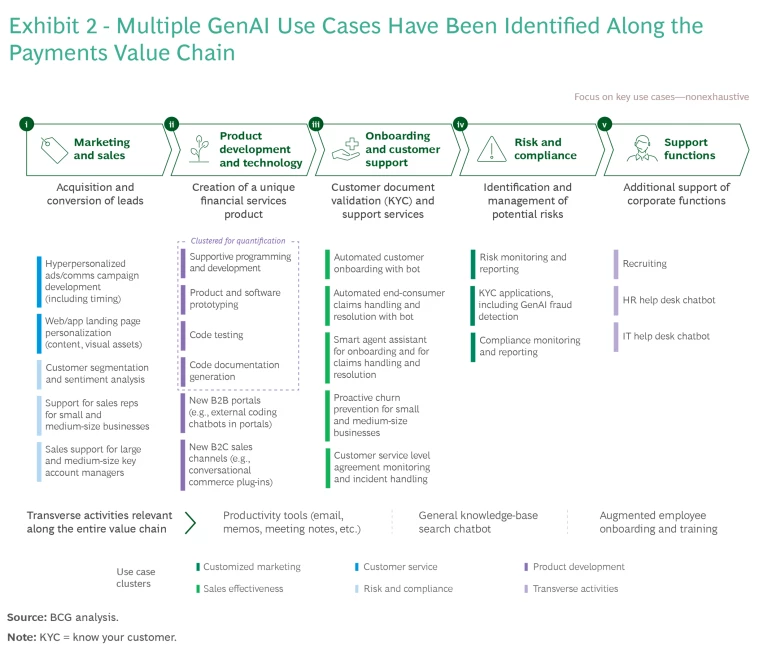
Our analysis indicates that GenAI use cases generally have several types of impact: smoother, more streamlined operations; higher customer satisfaction; lower costs; and more effective risk avoidance. Some use cases have hybrid impacts across categories. We chose to express the potential productivity impact related to GenAI as a percentage of the people cost base associated with clusters of use cases. We found an overall potential improvement in gross productivity of approximately 20% to 30%, and achievable long-term net productivity savings of roughly 10% to 15%. (See Exhibit 3.)
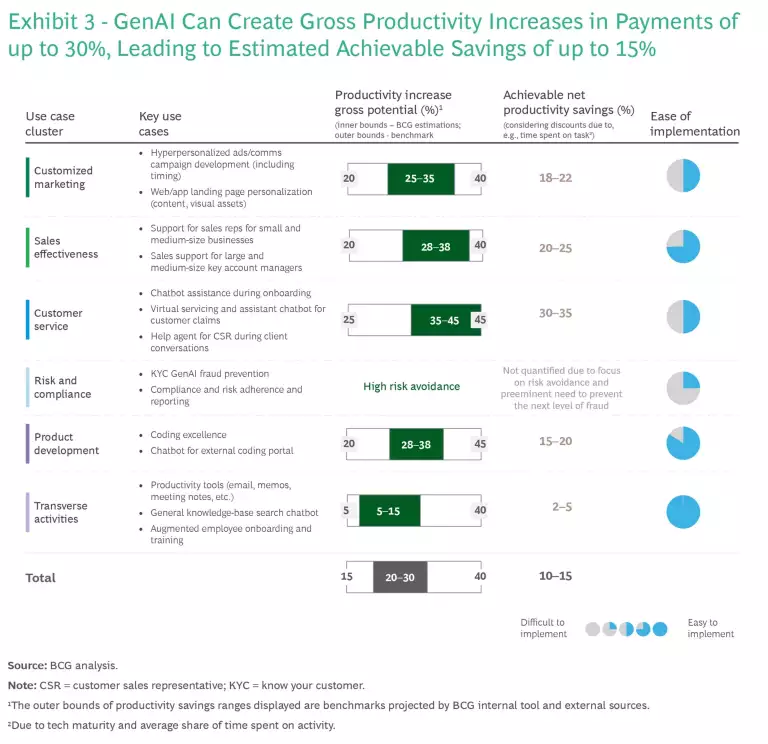
Fully understanding the potential benefits of GenAI entails taking deeper dives into each use case cluster.
Customized Marketing. The marketing campaign funnel contains several areas where GenAI can effectively be applied. These include market research, such as the ingestion of large data sets through GenAI; creation and production, such as automating layout generation, content creation, and multilanguage generation; and monitoring and optimization, such as campaign performance oversight and active advice enhancements. We estimate that Gen AI can deliver an average productivity gain across the value chain of 25% to 35%, although realizing these gains will depend on the intensity of the company’s marketing activities and the extent to which the organization relies on third parties (such as agencies) to execute campaigns.
Sales Effectiveness. Whereas standard practice has long involved sales representatives using client interactions to introduce new products and unlock cross-selling opportunities, GenAI will enable assisted next-best recommendations tied to live conversations, tailored product offerings through deeper personalization, and dynamic pricing. We estimate that sales reps could tap into productivity improvements ranging from 28% to 38% (lower for field sales compared with online sales), along with higher customer satisfaction. The productivity lift could be even greater for key account managers through advanced automation of request for proposal (RfP) processes such as creating documents and answering RfP questions.
Customer Service. GenAI’s transformative impact will extend to customer service, enhancing activities such as claims handling, onboarding support, incident resolution, churn prevention, and service-level-agreement monitoring. We estimate that agents could post a 35% to 45% improvement in productivity by leveraging GenAI-powered tools such as smart agent assistants. In parallel, GenAI could help reduce incoming call volume. We project that an automated claims-handling bot could treat between 40% and 50% of incidents, including resolving 25% to 30% of claims without any human intervention.
Risk and Compliance. The highest stakes in risk and compliance will involve detecting and preventing the next wave of GenAI-driven fraud. More broadly, GenAI is expected to foster efficiencies in monitoring and reporting (through automated report generation), as well as in trend prediction, real-time analysis, context awareness reporting, anomaly detection, and other areas resulting in cost savings, error reduction, and better resource allocation.
Product Development. The coding excellence side of product development—encompassing supportive programming, prototyping, code discovery, code testing, and code documentation—stands out in our analysis as one of the most prominent use cases in terms of business impact, with the potential for productivity improvement of 28% to 38%. GenAI will have a significant effect on coding quality controls and reducing technical debt, as well as on the risk of delayed deployment owing to untested code or deviation from architecture patterns. GenAI will benefit junior developers by facilitating their onboarding and providing code guidance and best practices on the go. It will also help senior developers by relieving them of repetitive tasks such as code review so that they can concentrate on writing complex code, fixing bugs, and mentoring newcomers. Maturity and adoption are already high, with limited friction identified vis-à-vis current IT landscapes and data-privacy issues. The main challenge in this area will be to scale AI-supported coding across the organization.
Transverse Activities. The term transverse activities refers to tasks that all workers perform daily (such as writing emails) or at some point during their employee journey (such as attending onboarding trainings). Multiple use cases exist in this area. With productivity tools, for example, automating time-consuming tasks such as drafting emails and composing meeting summaries is possible. And Gen AI can supply intelligent search tools for in-company knowledge bases. Such tools can significantly reduce the time workers spend on redundant activities and can raise related productivity by up to 15%. In our view, the achievable impact in this area is somewhat lower than for other use cases, owing to the fragmented nature of the tasks impacted; such tasks typically account for a relatively small proportion of each employee’s workday.
The potential benefits stemming from GenAI described above come with various challenges. Implementing the technology requires addressing such issues as developing responsible AI frameworks, ensuring data privacy, and addressing security concerns in the highly regulated payments environment. Integrating GenAI with existing legacy systems and managing unstructured data across the organization are additional hurdles that must be overcome.
How to Implement GenAI and Capture Its Benefits
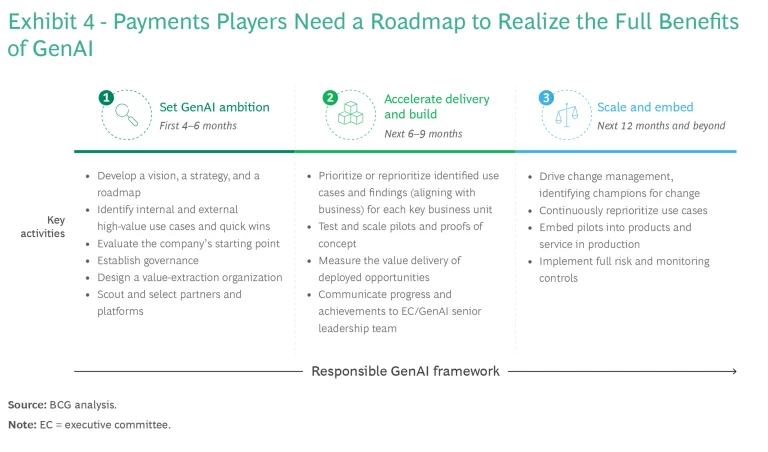
Payments C-suites should approach GenAI not as a collection of individual use cases but as an opportunity for company-wide transformation throughout the value chain, leading to implementation of GenAI at scale. The goal should be to create transformational waves that will change the company’s ways of working, evolve its culture, and raise its performance sustainably. Successfully operationalizing GenAI requires underlying strategic decision making that revolves around three pivotal imperatives: setting ambition, accelerating delivery, and driving scale. BCG has developed a comprehensive roadmap around these initiatives in the context of testing, implementing, and embedding GenAI and ultimately capturing the projected productivity improvements and savings it offers. (See Exhibit 4.)
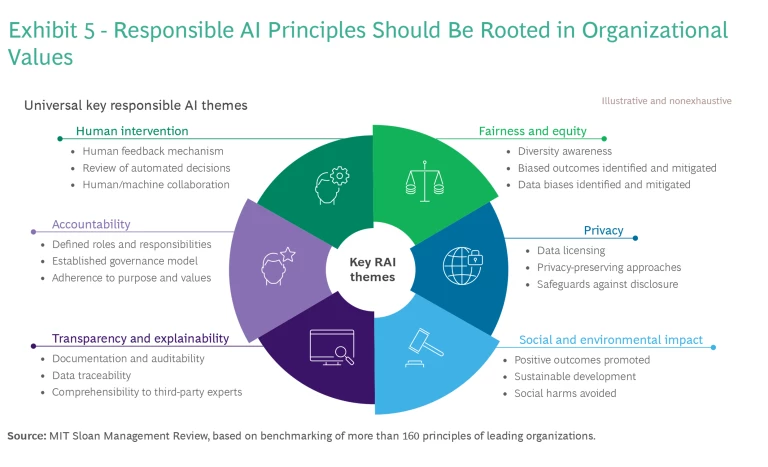
This approach should be rooted in a robust, responsible GenAI framework that spans six essential dimensions. (See Exhibit 5.) It is important for each of these dimensions to be fully aligned with the company’s overall purpose.
The jury is still out on the what the long-term impact of GenAI will be, not only on the payments industry but on the global business climate and on society as a whole. The risks, widely covered in the international press and trade publications, are real and well-known. The overarching issue in the business world is how companies can harness GenAI to enhance human performance, not replace it. In our view, although the payments industry has jumped off to a good start in the GenAI race, much work remains to be done. Companies that seize the moment now will benefit the most in the future.
The authors wish to thank the following colleagues for their valuable contributions to this article: Aristide Barraquand, Cyril Banos, Guillaume Desmartin, Julien Marx, and Davor Zilic.















