Generative Artificial Intelligence (Generative AI), though still in its early stages, is maturing fast and looks set to become one of most important technologies of our time. It has already attracted strong interest, and substantial investment. The launch of ChatGPT last year, with its underlying language-model AI technology, brought to public attention the power of Generative AI technology. New use cases of Generative AI are emerging daily.
Generative AI can leverage very large amounts of propriety data and then support data-led decision-making. The commercial applications of these capabilities are very promising, and are being pursued apace. This report, however, concentrates on the societal implications; it looks at the ways in which Generative AI, together with AI more broadly, can address some of South Africa’s most pressing challenges, and discusses how Generative AI can be responsibly harnessed to transform the lives of South African citizens.
We definitely want the benefits of this technology and we want to mitigate the unintended consequences. — Satya Nadella, Microsoft CEO
This report explores four key areas where Generative AI could play a transformative role:
| Healthcare | Education |
| Financial Inclusion | Agriculture |
The aim is to examine some of the possibilities in each of these areas through various use cases, and also to discuss the risks associated with AI and the ideal environment for realizing AI’s potential benefits. But first, we should define Generative AI—especially in relation to AI in general—and sketch the current state of play.
Defining Generative AI, and Outlining Its Progression and Adoption
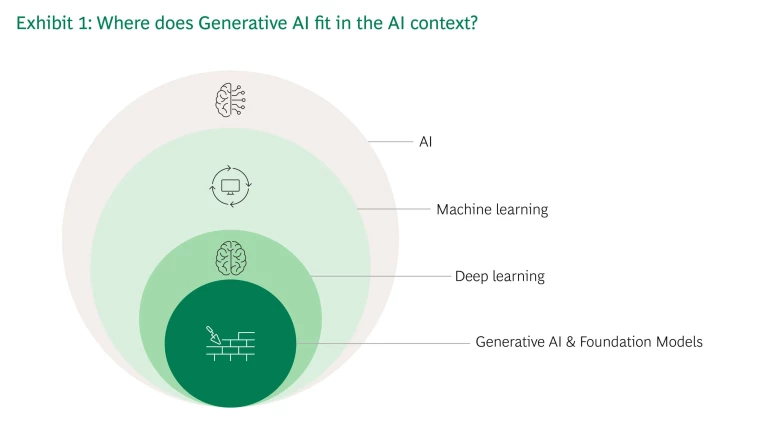
AI is the field of computer science that aims to create machines or systems that are able to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence—tasks involving reasoning, learning, decision-making, or creativity. AI has evolved over the decades from rule-based systems and expert systems to machine learning and deep learning, which can identify patterns and gain insights from data—and can improve over time.
To put it another way, Generative AI is a “set of algorithms, capable of generating seemingly new, realistic content—such as text, images, or audio—from training data.”
As for Generative AI, it is best known through its manifestations such as ChatGPT (text-based AI) and DALL-E (text-to-image AI), but it goes well beyond these applications. Generative AI is a subset of machine-learning techniques and models that can produce original text, images, and audio (see Exhibit 1).
Over the past few years, the barriers to using AI have begun to fall, as the necessary tools and platforms have increasingly become accessible to ordinary citizens. In this fine new world, there is no longer the need for vast datasets or powerful computers, since much of what’s necessary is now available through cloud providers. There is also no need for sophisticated technical knowledge: certainly tech-savvy users can download the code and train and refine the models if they want
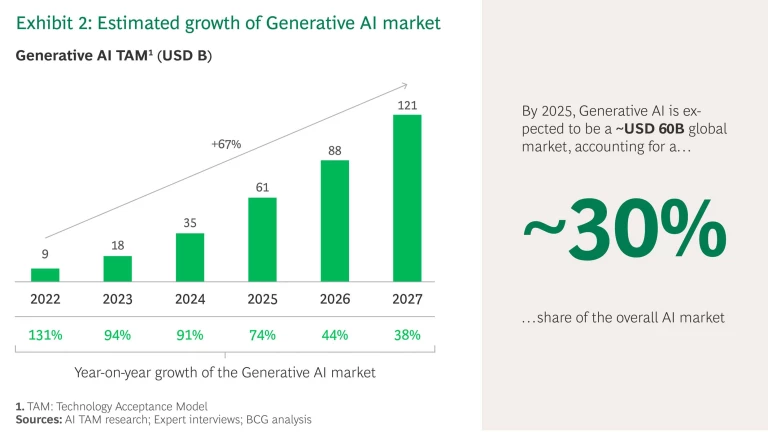
Estimates are that Generative AI will have a market value of $60 billion by 2025 and account for 30% of the total addressable market for AI in general (see Exhibit 2).
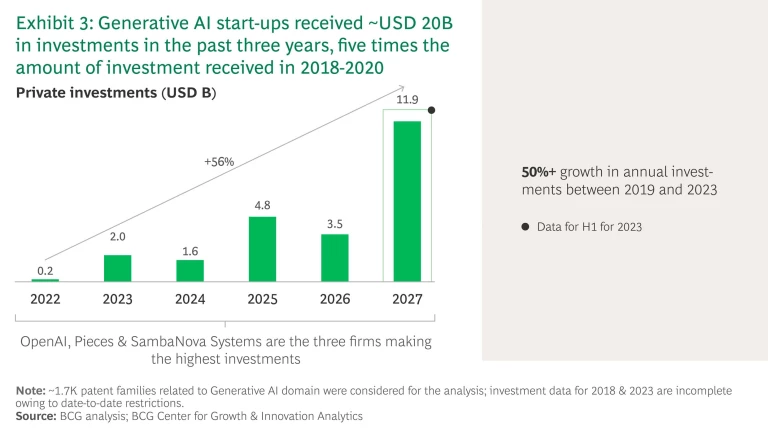
Over the past three years, Generative AI start-ups have attracted soaring levels of investment, receiving $20 billion in funding—five times more than the total investments secured in the previous three years (see Exhibit 3).
The recent launch of various easy-to-use chatbots has led to a rapid and widespread public adoption of Generative AI, with consumers captivated by its ability to create realistic and immersive content (see Exhibit 4 below).
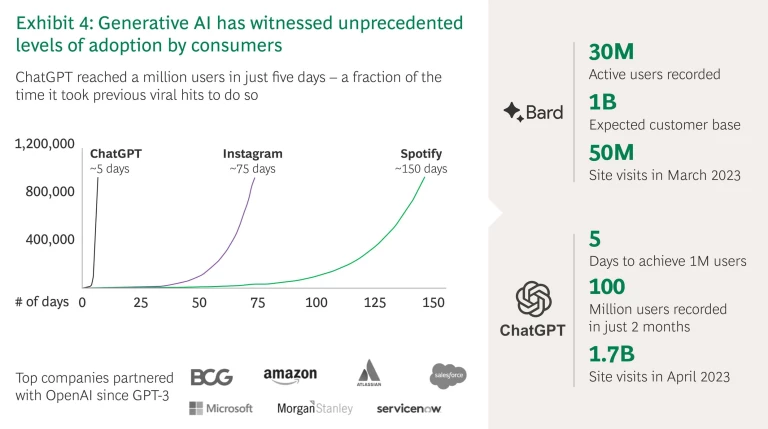
Generative AI can create data-driven, customized, and specific content that is accessible by millions, and as this report shows, it has the potential to address many of South Africa’s societal challenges.
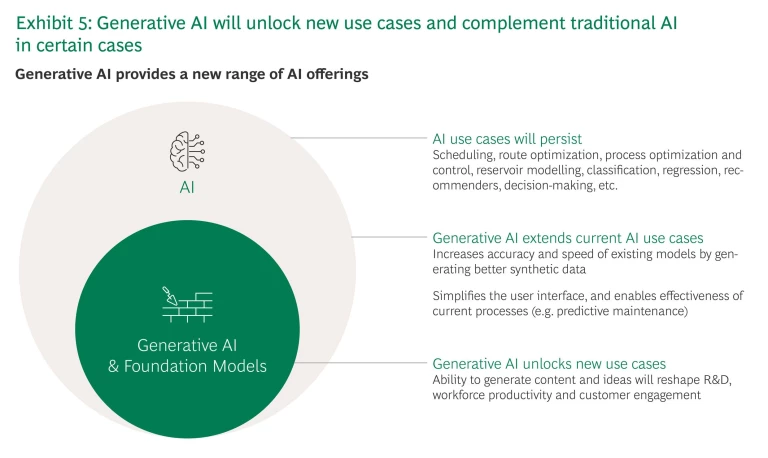
(Note that some of the use cases outlined below are traditional AI use cases that are enhanced when Generative AI is applied to them—see Exhibit 5. Accordingly, the broader term “AI ” is used from now on, rather than “Generative AI.”)
Examining the Possible Uses of AI in South Africa
AI is no silver bullet, but it certainly can make a transformative contribution to easing societal difficulties, notably in four key areas: Healthcare, Education, Financial Inclusion, and Agriculture.
Healthcare
The healthcare system in South Africa faces several challenges. Both public and private sectors are involved in healthcare provision, with ~70% public and ~30%
- AI can function as an assistant, transcribing and summarizing each consultation and automatically keeping patient records regularly updated. That will enable doctors and nurses to spend less time on administrative tasks and more time on patients.
- AI can also support personalized diagnosis and treatment recommendations for patients, by using AI-driven analyses of data and taking account of available inventory in hospital pharmacies. This support in diagnosis and treatment, and the alignment on available drugs, will again free up time for doctors to spend with patients, and will improve patient care and experience. The increase in doctor productivity will improve the efficiency of South Africa’s over-stretched public-health system. Doctors will, however, need to maintain a reasonable mistrust to protect against AI hallucinations and data bias.
- AI can serve as a 24/7 health-education resource, disseminating Health Department alerts and advice regularly, and in various languages. Using analyses of individuals’ data (such as race and age), AI can provide tailored content—in the appropriate language, and in personalized wording, for maximum impact—on healthier lifestyle choices, the managing of chronic conditions, and even prevention guidelines in the event of a pandemic. Again, appropriate disclaimers are needed: for any higher-risk matter, AI advice given to patients should add a warning for them to check with a doctor.
- AI can also generate efficiencies, both for R&D and for the delivery of supplies. AI can assist with conducting virtual compound screening and prediction modelling, and thereby reduce reliance on costly physical experiments. In addition, by generating synthetic data for training models, AI can enhance the efficiency of R&D efforts. AI can also refine supply-chain management and distribution strategies by forecasting demand trends, suggesting ways to reduce waste, and optimizing the timing of medication deliveries to the market. Some of the cost-savings could well be passed on to the patient.
Education
Education in South Africa is characterized by severe disparities between private and public schools. Public schooling in general suffers from teacher shortages and underfunding (especially in rural areas). And among public schools themselves, there are marked differences according to their location, students’ backgrounds, class sizes, and the like. Teachers often lack appropriate resources, including internet access; and many students face hunger and a lack of parental support.
A recent report, based on a survey of 320 schools in South Africa, finds that 81% of grade 4 learners (typically ages 9-11) are still unable to read for
If access to the internet and computers and the digitization of materials were improved appropriately, AI could contribute to several positive shifts in the education sector:
- AI can help with policy, curricula, and content creation. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI can inform policy decisions and syllabus design and create learning materials. The new content can be tailored to various grade levels and to individual students, and can be presented in a student’s preferred language.
- AI can help teachers plan daily classes and can suggest ways of explaining complex ideas. In schools lacking adequate resources and materials, teachers cannot teach their classes as effectively as they might. With the help of AI, however, they will be able to produce stimulating visual aids and easy-to-understand explanations in their daily classes. In that way, they can bring abstract topics to life and sharpen their students’ critical thinking. AI should also eventually fine-tune lesson plans for the teachers, and produce tailored materials.
- AI can both be used to create a “conversational tutor, ” which would enhance student interactions, and also enable better access to resources. Through natural-language processing, AI-powered conversational tutors can make sense of students’ questions and navigate intricate knowledge repositories to retrieve relevant information. It can then generate responses that provide detailed and contextually accurate explanations. This dynamic interaction, in which students engage in seamless and intuitive conversations with a tutor, fosters deeper comprehension.
- AI can develop personalized lesson plans based on students’ strengths and weaknesses. In the medium term, using analyses of data on student performance and learning patterns, AI will be able to generate engaging lesson plans for each individual student. By adapting the curriculum to a student’s individual strengths and weaknesses, AI will ensure better learning outcomes.
Financial Inclusion
Recent efforts to expand financial inclusion in South Africa have met with some success, but far more remains to be done to improve people’s financial literacy, money management, and access to economic opportunities. Currently, ~20% of adults lack even a basic bank account (or ~30% if you exclude social-grant
Many other factors complicate the banking landscape in South Africa, including the following:
- Given the constraints on internet access, only ~5% of people with bank accounts engage in internet banking, and ~18% make basic transactions via their mobile phones.
- Banks struggle to assess creditworthiness for the many customers who cannot provide the traditional metrics.
Although these problems will not be easily or quickly resolved, AI can offer some assistance to foster financial inclusion, including the following:
AI can make financial services more accessible to customers. By deploying AI-powered chatbots to handle routine client queries and provide timely responses, banks will be able to:
- spare customers the inconvenience of going to branches and waiting for a banking consultant to be available
- increase transparency on products and services, and increase trust from clients, given that chatbots consistently provide accurate responses
- communicate in a client’s native language; and
- reduce the costs of serving clients, and thereby reduce prices for clients.
- AI can help provide personalized recommendations and improve financial literacy. AI can assist the underbanked both through education and through financial advice. Via chatbots, AI can engage with users in their natural language, fine-tuning its guidance to cater to individual needs. AI could also produce personalized recommendations, such as budgeting strategies and investment options, to enable the underbanked to make informed financial decisions and gain access to essential financial services that were previously out of reach.
- AI can expedite the drafting of legal documents and assist in explaining, in plain language, pertinent terms to customers. By extracting and analyzing data from client discussions, AI can swiftly produce legal documents in plain language, or even in home languages, reducing the time and costs associated with traditional drafting of contracts. A further benefit might be to increase access to banking facilities such that customers will more easily understand legal agreements and thus will feel more comfortable in signing them.
Agriculture
South Africa has a rich farming history. Agricultural production plays a pivotal role in the country’s economy, contributing ~2.5% to
There are several ways in which AI can engage with these industry challenges, including the following:
AI can analyze data to help farmers optimize the efficiency and sustainability of their farming practices. Farmers can use sensors, drones, and satellites to gather real-time data on their crops, including details on soil health, water usage, crop growth, and the presence of pests. This data can then be analyzed by AI algorithms, with the results guiding farmers on how best to use resources and maximize crop yields. Farmers will be able to:
- determine optimal planting times, and decide how frequently to irrigate or apply pesticides; and
- identify variability within a crop field and apply resources at variable rates where most needed.
- AI can enhance crop-health monitoring through disease detection. AI algorithms, based on images of crops from drones and satellites, can also help identify anomalies and early signs of disease or pest infestations in crops. Farmers can then monitor developments in real time, and intervene as appropriate, thereby minimizing yield losses and achieving food security.
- AI can—via refined credit scoring—expand financial access for smallholder farmers. By integrating field data obtained from satellites, weather stations, and IoT devices (sensors and gadgets placed in fields, on equipment, or on animals), AI can develop algorithms that analyze factors such as crop health, soil quality, and weather patterns in real time. The consequent insights, combined with traditional financial data and predictive analytics, help create a comprehensive credit profile for farmers lacking a conventional credit history. That could enable financial institutions to make more informed lending decisions. It also supports financial inclusion, empowering farmers to invest in their operations, adopt modern agricultural practices, and improve their livelihoods.
Adopting AI within South Africa—Broader Risks and Considerations
While AI opens up a new class of opportunities, it also introduces a new class of risks. Many of the risks implicit in AI have been widely publicized, and some of them will prove difficult to mitigate let alone eradicate. Moreover, given that AI is still maturing, some new and unforeseen risks will emerge. Constant vigilance and evaluation of risks are therefore crucial as the technology progresses. (A comprehensive exploration of the risks is beyond the scope of this report.)
For AI to achieve scalable and affordable adoption in South Africa, and to realize its full potential, several indispensable elements will need to be in place.
Appropriate laws and regulation. AI development should take place within an appropriate legal and regulatory framework, to define standards, priorities, and ethical boundaries, and also to support the growth of AI adoption and mitigate AI risks. A technical working group of experts from relevant industries, including academia, should work with government agencies to develop and continually review all existing and proposed regulations in an effort to enable an optimal and accountable environment for all.
If the use of AI tools is not explicitly regulated, and the personal information of data subjects is processed without their knowledge or consent, could place an organization or business in breach of its obligations under the Protection of Personal Information Act (POPIA). The issues raised, and the possible consequences, would then need to be addressed by appropriate policymakers.
People and workface enablement. South Africa already has an unemployment rate of 33%, as of Q2 2023, and AI will very likely lead to further job displacement. As is the case elsewhere in the world, that downside can be offset by the new work opportunities AI could open up. To mitigate against the risk of job losses, employers could be incentivized to retain workers and/or retrain or upskill employees to transition into roles associated with AI capabilities. They should also champion AI-focused businesses—especially start-ups—as new spaces for employment, and should introduce supportive legislation for them.
Collaboration. Through Public Private Partnerships (PPPs), the public and private sectors can join forces and pool resources to roll out AI. Collaboration through PPPs would facilitate proofs of concept and reduce the cost and increase the speed of a major AI scale-up. It could also ensure that AI solutions are accessible and beneficial to all South Africans, not just an elite few. One option in that regard would be to provide localized AI tech free of charge to everyone as a public service. Of course, it would not really be free, as it would be funded by taxpayers’ contributions, but it might be preferable to the alternatives: becoming reliant on foreign-based private industry to provide crucial AI tech, or having no AI tech at all.
Financial underpinning. Other crucial participants in South Africa’s AI rollout will be Development Finance Institutions (DFIs) and private-sector venture capitalists. They will provide relevant financial support and investment opportunities to local businesses—both new and old—and research institutes. They will also facilitate partnerships between international tech companies and local organizations, promoting knowledge exchange and capacity building. This support will foster an ecosystem in which South African AI innovators can thrive.
Reassuringly, South Africa’s AI start-up landscape is far from empty. The country already boasts a variety of start-ups offering helpful AI-enabled services and solutions. Here are three diverse examples:
- Aerobotics provides AI-enabled pest detection, disease detection, drone imagery services, orchard management, and yield management.
- Envisionit Deep AI utilizes AI to streamline and improve medical imaging diagnosis for radiologists.
- Jumo—an online marketplace—connects banks with traditionally inaccessible customers, to enable loans, savings, and insurance services.
Technological infrastructure. PPPs and DFIs can jointly embed one further foundation-stone of South Africa’s AI development: tech infrastructure. At the top level, data-sharing platforms are needed for building the large and diverse datasets on which AI models are trained. At a local level, stable and high-bandwidth connectivity needs to be available full-time. Only through a major infrastructure upgrade, especially in remote and under-served areas of the country, will AI’s benefits be fairly distributed regionally and socially.
Once all these underpinning components are in place, AI will be positioned—with minimized risk and maximum equitability—to play a transformative, beneficial role across key aspects of South African society.
Call to Action
For AI and Generative AI to fulfil their potential in easing or even resolving South Africa’s most pressing societal issues, the country’s citizens will have to play their part, collectively and individually. Public and private sectors will need to engage in constant open dialogue, concerted action, and cross-functional collaboration.
As shown above in the use-case profiles, many remarkable benefits have already emerged, and countless more opportunities lie in wait. The risks, known and unknown, will have to be navigated and managed. To that end, the correct legislative framework needs to be put in place—and speedily, to match the speedy development of AI itself.
Stakeholders should persevere in exploiting and refining existing technologies, seeking new beneficial applications, and pursuing needs-informed research. Throughout, they should remain mindful of the risks—notably job losses—and push for stronger regulation and mitigating measures as appropriate. If all goes well, AI will live up to its transformative promise, and transform South African society for the better.
This publication synthesizes invaluable insights from discussions with experts. The project team wishes to thank them all for their time, dedication, and guidance.