In an increasingly volatile world, where navigating risk is a core leadership responsibility, advanced AI models are poised to become indispensable tools for CEOs. Within the next five years, these models could support more than a quarter of a CEO’s responsibilities and transform how companies manage risk. However, the immense potential comes with unprecedented risks. To safely unlock the value of AI , CEOs must combine visionary leadership with strong risk management.
CEOs should look to their
risk and compliance
(R&C) functions to accelerate AI-driven transformations. Across industries, R&C plays a critical role in setting the guardrails to define an AI strategy that balances outcomes and risks. Positioned at the forefront of AI adoption—particularly in health care, banking, and insurance—R&C can guide the organization across three key dimensions: managing AI-generated risks, transforming overall risk processes, and enabling risk-based decision making.
The Big Picture
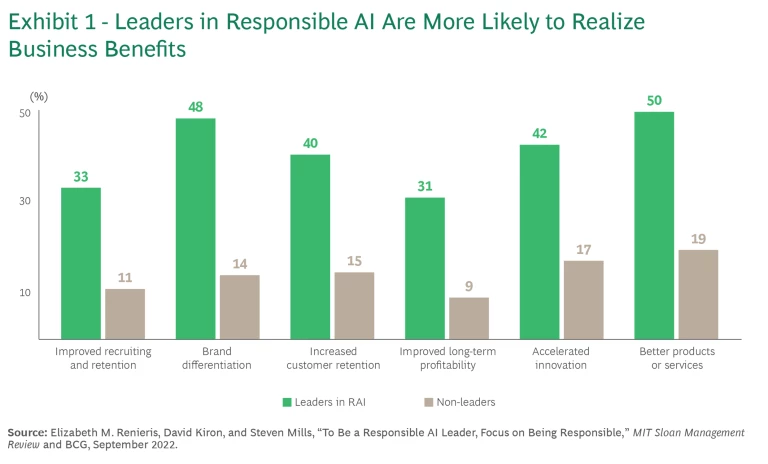
A strong initial focus on mitigating risk is essential, beginning with a comprehensive responsible AI (RAI) framework . By embedding ethical practices, safeguarding data privacy, and upholding regulatory compliance and reputation, R&C can support secure scaling across the enterprise without stifling innovation. A well-executed approach can triple an organization’s chances of fully realizing AI’s advantages .
AI and GenAI applications are already delivering substantial gains in risk processes, automating routine tasks and reducing time spent on routine tasks such as risk report generation by up to 50%. Beyond boosting efficiency, integrating AI into risk processes enhances effectiveness and quality, allowing R&C functions to respond to threats and opportunities faster and with greater accuracy.
AI can also transform strategic decision making, enabling a shift to risk-based, dynamic decision models. With AI-driven insights, R&C functions can adapt to evolving risk landscapes in real time, aligning operations with resilience-focused strategies that maximize economic value. AI supports risk-based scenario planning and identifies key risk indicators, empowering organizations to anticipate challenges and capitalize on opportunities.
With AI-driven insights, R&C functions can adapt to evolving risk landscapes in real time, aligning operations with resilience-focused strategies that maximize economic value.
To prepare for transformative change, R&C functions must shift their focus from low-value to high-value activities and emphasize human-AI collaboration. This mindset enables R&C to redefine risk management while evolving its governance and operating model. Building capabilities in analytics, data validation, and AI ethics and adopting scalable platforms will allow R&C to fully harness GenAI’s potential and deliver substantial value.
Managing AI-Generated Risks
R&C functions have a unique opportunity to unlock the transformative potential of GenAI. With the ability to evaluate both the quality and risks of AI solutions, R&C can strengthen the business case for these technologies by distinguishing real value from hype.
Three AI-related risk categories are particularly significant to address: quality, safety, and security. Safeguarding quality ensures that AI consistently delivers the intended value, addressing challenges such as misinformation, low-quality content, and misaligned responses. Managing safety risks involves promoting fairness by guarding against unintended biases, harmful stereotypes, and offensive content. Mitigating security risks focuses on data protection and intellectual property—countering threats such as data leakage, system manipulation, and operational disruption. Security concerns are heightened as malicious actors exploit AI capabilities, including the use of deepfakes, significantly escalating cyber risks and fraud.
In response to these multiple risks, regulators worldwide are introducing comprehensive guidelines and AI-specific legislation to ensure responsible use, making regulatory and policy compliance more demanding. Chief among these is the EU’s AI Act, which introduces a four-tiered risk classification—unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal—for AI systems. High-risk applications are subject to stringent requirements, including third-party audits and registration. The act also mandates transparency for AI systems interacting with individuals and assigns compliance obligations based on value chain roles, such as provider or distributor. To comply with the act, organizations must develop an AI inventory and implement tailored risk mitigation measures, underscoring the importance of proactive regulatory adherence.
Implementing a comprehensive RAI framework is essential for managing risks and promoting the ethical use of AI in a rapidly evolving environment. By prioritizing responsible practices, organizations can ensure regulatory compliance, uphold ethical standards, and thoughtfully evaluate the benefits and risks of each GenAI application. This approach not only mitigates risks but also unlocks business benefits and serves as a market differentiator. (See Exhibit 1.) To realize meaningful value, organizations must embed RAI practices across the AI product lifecycle.
Transforming Risk Processes
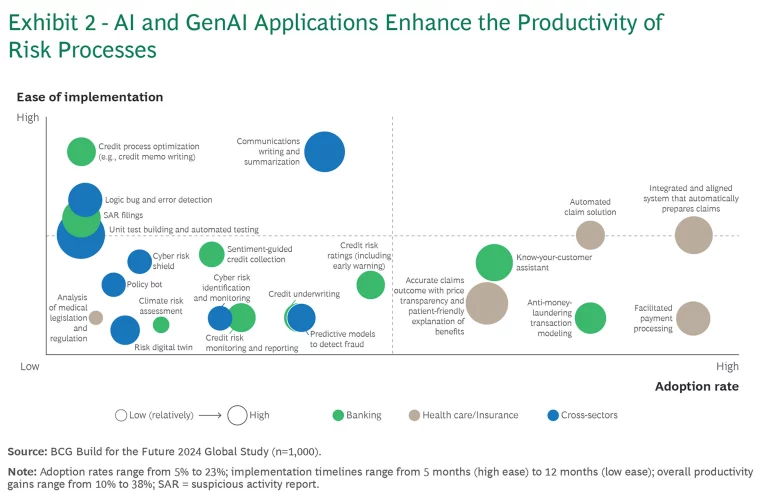
Initial AI pilots are primarily focused on automating labor-intensive, repetitive tasks, with use cases delivering efficiency gains of up to 40% to 50%. Notably, these benefits extend beyond the R&C function to positively impact other business units, especially those involved in operational processes. For example, branches and back-office operations can benefit from R&C’s simplification of control processes in areas such as know-your-customer procedures in financial institutions and customer onboarding across industries—freeing up time for commercial activities and enhancing corporate profitability.
Strategic AI deployment goes beyond operational efficiency gains, enhancing decision quality, driving growth, and increasing shareholder value across industries. However, organizations face the challenge of selecting AI use cases that align with their specific needs. Given the many options available, choosing those with the highest impact on process efficiency and decision making while minimizing risk is essential. R&C functions can play a pivotal role by balancing potential risks and rewards. In lending, for example, AI models can double the rate of automatic approvals by analyzing untapped data sources, such as financial transactions, to more accurately assess repayment capacity without increasing risk.
To navigate this complex landscape, companies need a strategy that maximizes the impact of AI initiatives in supporting R&C. In our experience, a robust strategy begins with identifying and prioritizing high-impact AI value areas that align with strategic goals. These priorities should deliver a competitive edge by targeting critical aspects in the risk value chain. By focusing on these areas, organizations can implement scalable solutions that directly address essential risk requirements.
Exhibit 2 highlights how targeted AI and GenAI can address multiple areas within R&C, enhancing efficiency across industries.
Scalable architectures and strategic partnerships play a crucial role in fully realizing these benefits. They allow organizations to accelerate the integration of third-party data sources and the broader implementation of AI-driven solutions in real-world settings.
Enabling Risk-Based Strategic Decision Making
Combining AI with GenAI enhances risk-based strategic decision making by strengthening predictive capabilities, enabling organizations to transform their approach to managing uncertainty and disruption.
To promote risk-based operational resilience, companies can use AI to simulate a broad variety of disruption scenarios within their acceptable risk tolerance. This allows them to assess impacts, such as the cost of maintaining service continuity during challenging events.
In this capacity, AI overcomes the limitations of traditional medium- to long-term planning by creating and dynamically adjusting multiple scenarios. This helps companies assess potential risks and opportunities in the context of their strategic objectives. Leading risk indicators further enhance this process, enabling simulations that assess the impact on business portfolios of events such as health crises or prolonged geopolitical conflicts. Such capabilities enhance an organization’s ability to adapt swiftly and maintain resilience.
AI overcomes the limitations of traditional medium- to long-term planning by creating and dynamically adjusting multiple scenarios.
Redefining the R&C Function for an AI-Driven Role
Redefining the traditional R&C function is essential as AI reshapes the landscape. R&C must evolve from performing routine, control-focused tasks to taking on a strategic, proactive role that harnesses advanced technologies becoming business enabler. This transformation requires a comprehensive approach encompassing governance, skill development, scalable technology platforms, and a new mindset. Establishing robust AI governance, including dedicated roles and committees, is a critical first step to creating the strong framework needed to fully realize AI’s potential.
Building capabilities within the R&C team is equally vital. Investing in training and upskilling helps the team keep pace with technological advancements, fosters a culture of innovation, and ensures effective oversight.
These changes require a mindset shift that enables R&C teams to transition to high-impact, strategic risk analysis based on data-driven decision making. Team members must “learn with the machine” as AI technology evolves—continuously refining processes based on insights provided by the technology while enhancing their own decision making. This repositions R&C as a strategic partner that unlocks business potential by helping the organization navigate the complex risk landscape.
To support CEOs in the rapid adoption of AI, the R&C function must manage AI-generated risks as well as apply AI to transform risk processes and enable risk-based decision making. To do this successfully, it will have to become a value-creating business partner—an accelerator of innovation rather than a barrier. Moving beyond traditional compliance roles, R&C must adopt a forward-looking perspective, actively anticipating business needs and setting robust standards to ensure the safe and ethical use of AI. By reimagining how its team members work, think, and act, an R&C function can drive meaningful value in this evolving landscape.
The authors thank Tommaso Ingallina, Lisa Guaraglia, and Tauseef Charanya for their contributions to this article.