The cost of living is rising in many developed markets, but there is one area where consumers are unlikely to scale back their spending: medical aesthetics. A recent BCG survey of 5,000 consumers in ten major global markets, including Brazil, China, and the US, found that 85% plan to spend the same amount or more on procedures over the coming
Overall, the industry has demonstrated remarkable resilience even in the challenging landscape of 2024, and we anticipate continued healthy growth.
Over the years, medical aesthetics has developed through a B2B approach. Our analysis shows the industry can grow even faster by putting the consumer first. We argue that the base of current and potential new consumers can be segmented into six main personas, each with unique preferences and demands. Providers, manufacturers, and investors that have a deep understanding of these segments can shape their go-to-market approach accordingly and offer customized products and services to satisfy specific needs.
Strong Growth Is Projected to Continue
The global market for medical aesthetics (measured by manufacturer sales) is currently valued at approximately $20 billion. As Exhibit 1 shows, the industry has been expanding at 8% a year since 2019, and the future is expected to be nearly as strong at 6%, to reach $27 billion by 2028. This is in line with the trend of the overall beauty retail market. Injectables—neurotoxins and dermal fillers—are forecast to grow 7%, through an increase in the number of procedures, particularly among younger consumers seeking preventative treatments. Injectables are also seeing innovation, with new products of increased effectiveness and other attributes. (See “Continued Innovation Spurs Consumer Demand.”) The medical-grade skin care market is projected to enlarge even faster, at 9%.
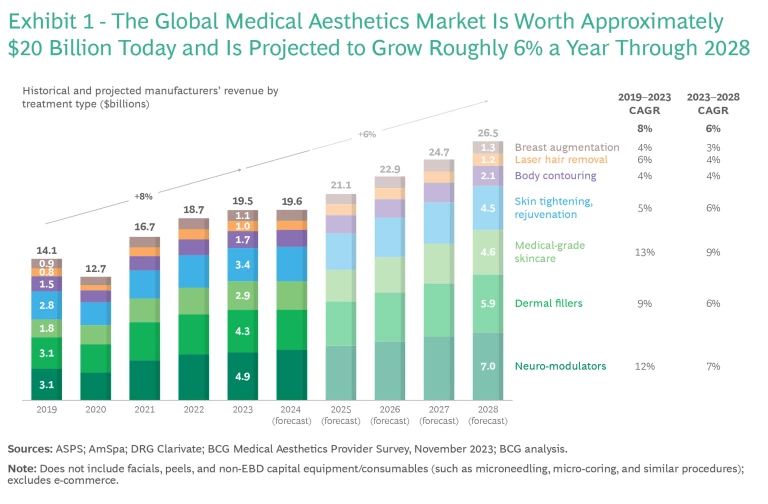
China and the US will remain the biggest markets, together representing about half of the global industry. These two markets will also continue their strong trajectories: up 6% for the US (in line with the global industry) and 9% for China through 2028.
Two other factors underscore the strength of the current market. One is that providers and manufacturers are changing their go-to-market approach to focus more directly on consumers, which will help identify unmet needs and make marketing efforts more effective. (See “Stakeholders Evolve to Address Consumers’ Changing Needs.”)
In addition, the medical aesthetics market continues to draw strong interest from institutional investors. (See “Investment Activity Remains Strong.”)
Continued Innovation Spurs Consumer Demand
Injectables. Longer-acting toxins, pre-mixed liquid toxins, biostimulators, and regenerative fillers are all coming to the market, in response to growing interest among consumers and providers.
Energy-Based Devices (EBDs). Procedures that use EBDs include laser hair removal, skin resurfacing and rejuvenation, and body contouring. Consumers seek noninvasive solutions for skin issues like tissue pigmentation, hyperpigmentation, and age spots. Established manufacturers are launching new devices targeting collagen production and skin regeneration.
Breast Implants. Players are exploring regenerative biomaterials and breast augmentation via fat grafting, showcasing a consumer desire for safer and minimally invasive options with more natural materials.
Skin Care. Innovations involve natural ingredients, collagen products, and solutions for uneven skin tone. In addition, consumers are starting to undergo medical-grade skin care treatments at younger ages. Providers seek technologies to personalize skincare regimens based on individual profiling.
Clinic Services. Providers are increasingly reshaping the experience for consumers, who seek payment- and convenience-oriented innovations such as bundled packages and subscription models. Another common interest is mobile apps that can track consumers’ progress across multiple treatments. Providers also express high demand for AI-assisted treatment planning, personalization, and tailored marketing messages to continually engage consumers and enhance their treatment outcomes.
Stakeholders Evolve to Address Consumers’ Changing Needs
New Technologies. Investors are funding innovation to develop new technologies in line with consumers’ needs.
Incentives. For some consumers, pricing can be a barrier to adoption. To overcome this, manufacturers, especially in the US, are using consumer allowances and more sophisticated loyalty programs and apps to offer financial incentives.
Go-to-Market Approaches. Providers and manufacturers are increasingly offering membership programs and subscriptions, reducing the overall perceived cost burden on the end consumer through bundling discounts and payment amortization.
Investment Activity Remains Strong
PE and VC funds, along with players within the industry, are actively making investments across geographic markets and product segments. In terms of deal volume, the US dominates, accounting for approximately 60% of deals. Asia-Pacific follows with roughly 25%, and Europe makes up the remaining 15%.
Joint Ventures and Alliances. Annually, five to ten joint ventures and alliances take shape as companies strategically expand their geographic footprint through licensing or enhance their product portfolio via co-development and R&D. An illustrative example is Evolus’ announcement of a licensing deal to enter the US dermal filler market with Evolysse, a hyaluronic acid developed by Symatese.
Initial Public Offerings. Although the industry witnessed fewer IPOs in 2021, it typically averages about 10 IPOs each year, including adjacent segments such as regenerative medicine companies. A recent example is Koru Pharma, a South Korea-based manufacturer of injectables, threads, and mesotherapy, which announced plans for an IPO in 2024.
Equity Investments by Private Equity (PE) or Venture Capital (VC) Funds. PE and VC funds are instrumental in the sector, making approximately 50 to 60 equity investments. A noteworthy example is Archimed’s acquisition of WiQo, a producer of skincare and facials with needle-free treatments for skin rejuvenation, aiming to strengthen the company’s global presence.
Equity Investments by Industry Players. Medical aesthetics companies also make strategic equity investments to acquire stakes in other players, to diversify and create synergies in product portfolios. For example, CG Bio, a bio-regenerative medicine company that produces fillers, recently acquired facial thread manufacturer M.Base to diversify its portfolio.
Key Survey Findings
Our survey identified the demographics and preferences influencing the industry and gauged penetration levels for different types of treatments. We considered the population between 25 and 64 years old, with above 50% of median income, and factored in their familiarity with beauty and medical aesthetics products.
The combination of expectation of increased spending and the low penetration of a large potential market is why the industry is projected for such strong growth in the coming five years. Key findings include the following:
Consumers plan to keep spending. Among respondents, 50% of consumers plan to increase their spending on medical aesthetics procedures in the coming year, and 35% plan to keep current spending levels.
Low penetration of the potential market. Use of many procedures is still quite low, with most in the single digit percentage of the population. The overall global average is just 9%, although 23% of consumers in China say they have undergone laser hair removal, the most common medical aesthetics procedure. Neurotoxin treatments show a similar dynamic. The highest penetration is in the South Korea market, but it’s just 8% of the population. US is second, at 7%. (See Exhibit 2.)
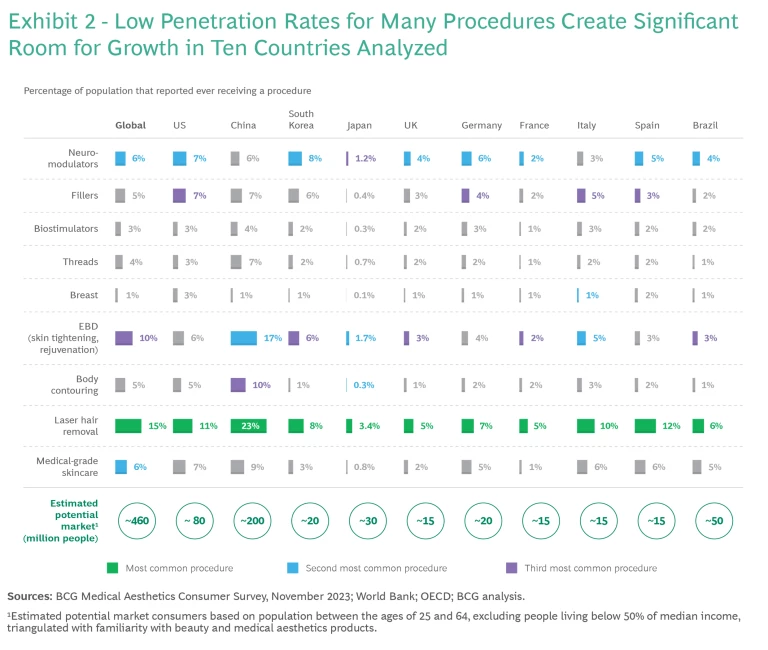
Room for growth. The total market possible for these procedures is far bigger than the current low market size. Potential market in the US is roughly 80 million consumers, 200 million in China, and 50 million in Brazil.
Six Consumer Personas
We found that medical aesthetics consumers can be grouped into six distinct personas based on treatment frequency, preferred treatment combinations, visit patterns, and loyalty to providers. The desire to look better is of course the primary motivation, but there are sizable differences in the underlying functional and emotional needs for each group. (See Exhibit 3.) Providers, manufacturers, and investors should understand these preferences and tailor their marketing accordingly.
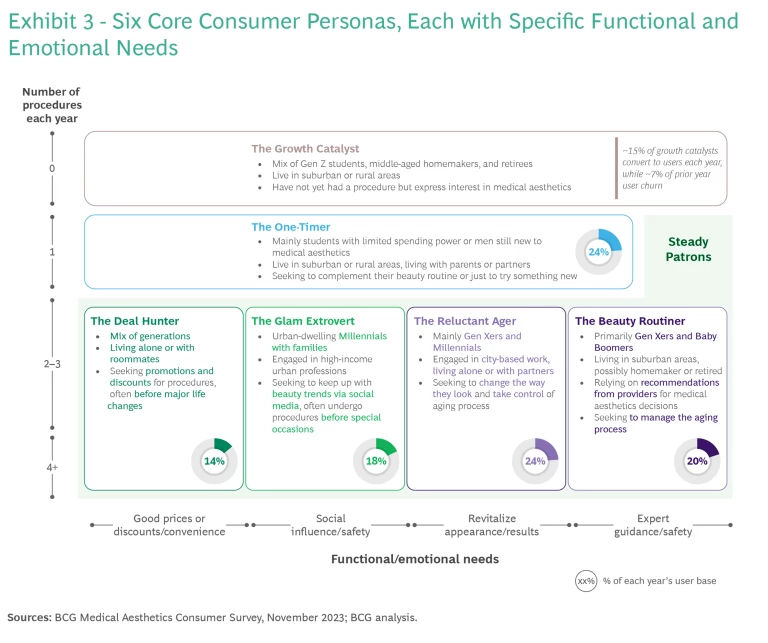
The first four personas are all steady patrons—that is, regular consumers who get two or more medical aesthetics treatments each year.
- The Beauty Routiner. These consumers are older—typically Gen Xers and Baby Boomers—who tend to live in suburbs and get ongoing anti-aging treatments, primarily through professional recommendations from providers. The most common procedures for this group involve neurotoxins and fillers, and their primary functional need is safety.
- The Reluctant Ager. Reluctant agers are slightly younger (Gen Xers and Millennials) who live in cities and seek control over their aging process. They rely on celebrity and social media endorsements to direct their emotional need, and they prioritize results with treatments like neurotoxins, energy-based devices, and fillers.
- The Glam Extrovert. This persona includes high-income, urban-dwelling Millennials who keep up with beauty trends and undergo frequent procedures, often before social events. They are influenced by social media trends and prioritize safe treatments, primarily procedures that use energy-based devices (EBDs)—such as laser hair removal, skin resurfacing and rejuvenation, and body contouring—and injectables.
- The Deal Hunter. The fourth persona among the steady patrons is the deal hunter. This group includes all generations and is the most heavily influenced by price. They seek budget-friendly treatments, promotions, and discounts. Their top functional need is convenience.
For all of these steady patrons, it’s important for companies to foster loyalty and build long-term consumer relationships. Medical staff should be highly focused on customer service, and clinics should diversify their offerings to ensure they have the latest treatments. Providers can create cross-sell opportunities for treatments like biostimulators or facial threads. Bundles and discounts should be offered, especially for price-sensitive consumers.
There are also two personas for new or sporadic consumers:
- The One-Timer. The fifth persona we identified is consumers who limit themselves to a single procedure, primarily due to skepticism or lack of knowledge. This group often favors laser hair removal (with a higher concentration of men) and neurotoxins. Key barriers that prevent one-timers from trying new procedures include a lack of conviction on the necessity of treatment—especially for injectables—and concerns around looking unnatural.
- The Growth Catalyst. The sixth persona intends to explore medical aesthetics in the future. This group comprises a diverse mix of generations, but especially young people and students. The most common entry procedure is laser hair removal, with neurotoxins being popular among older generations. The main barriers for this group include price, lack of knowledge, and safety concerns.
To persuade the one-timers to try additional procedures, providers should emphasize the necessity of treatments and address concerns about outcomes. They should also increase touchpoints for cross-selling desirable procedures like body contouring, skin tightening, and laser hair removal. And it’s crucial to use marketing outreach and loyalty programs to build strong relationships despite less frequent office visits.
To convert the growth catalyst segment to active medical aesthetics consumers should offer discounts for entry procedures and focus on education and marketing through influencers. Laser hair removal can be leveraged as an entry-level procedure and a means of introducing other treatments, including skin tightening, rejuvenation, and body contouring.
The Geographic Breakdown
How the six consumer profiles are spread among the ten countries we studied.
Heavy User Dynamics. Brazil, Germany, Italy, and Spain have a higher percentage of heavy users, aligning with profiles like the glam extrovert, the beauty routiner, and the reluctant ager.
One-Timers. Consumers in France and Japan are more likely to be one-timers, creating opportunities in those markets to overcome hesitancy and encourage broader adoption.
Growth Catalysts. In the US, UK, South Korea, and China, a large portion of consumers expresses an intention to adopt medical aesthetics in the next 12 months.
The medical aesthetics industry is well positioned for sustained growth over the coming five years, thanks to strong consumer spending, technological innovation, and ongoing investment activity. However, it is necessary to understand the needs, preferences, and aspirations of potential consumers. Providers who adjust their market approach to the six consumer profiles we identified can most effectively use the coming period as a springboard to outpace the competition.